Zhen Fan
EMHI: A Multimodal Egocentric Human Motion Dataset with HMD and Body-Worn IMUs
Aug 30, 2024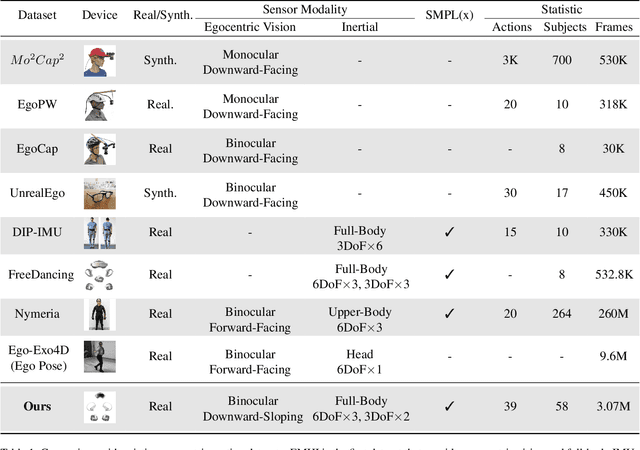
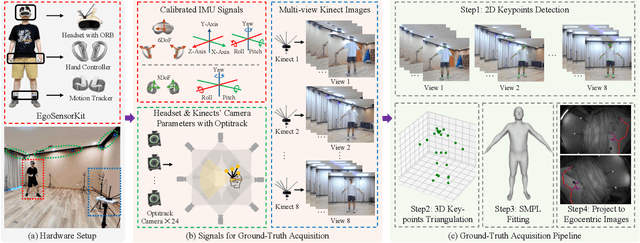
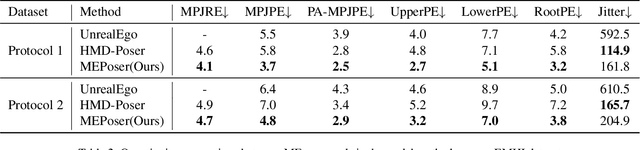
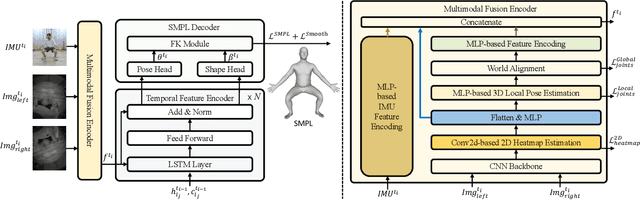
Abstract:Egocentric human pose estimation (HPE) using wearable sensors is essential for VR/AR applications. Most methods rely solely on either egocentric-view images or sparse Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) signals, leading to inaccuracies due to self-occlusion in images or the sparseness and drift of inertial sensors. Most importantly, the lack of real-world datasets containing both modalities is a major obstacle to progress in this field. To overcome the barrier, we propose EMHI, a multimodal \textbf{E}gocentric human \textbf{M}otion dataset with \textbf{H}ead-Mounted Display (HMD) and body-worn \textbf{I}MUs, with all data collected under the real VR product suite. Specifically, EMHI provides synchronized stereo images from downward-sloping cameras on the headset and IMU data from body-worn sensors, along with pose annotations in SMPL format. This dataset consists of 885 sequences captured by 58 subjects performing 39 actions, totaling about 28.5 hours of recording. We evaluate the annotations by comparing them with optical marker-based SMPL fitting results. To substantiate the reliability of our dataset, we introduce MEPoser, a new baseline method for multimodal egocentric HPE, which employs a multimodal fusion encoder, temporal feature encoder, and MLP-based regression heads. The experiments on EMHI show that MEPoser outperforms existing single-modal methods and demonstrates the value of our dataset in solving the problem of egocentric HPE. We believe the release of EMHI and the method could advance the research of egocentric HPE and expedite the practical implementation of this technology in VR/AR products.
HumanSplat: Generalizable Single-Image Human Gaussian Splatting with Structure Priors
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Despite recent advancements in high-fidelity human reconstruction techniques, the requirements for densely captured images or time-consuming per-instance optimization significantly hinder their applications in broader scenarios. To tackle these issues, we present HumanSplat which predicts the 3D Gaussian Splatting properties of any human from a single input image in a generalizable manner. In particular, HumanSplat comprises a 2D multi-view diffusion model and a latent reconstruction transformer with human structure priors that adeptly integrate geometric priors and semantic features within a unified framework. A hierarchical loss that incorporates human semantic information is further designed to achieve high-fidelity texture modeling and better constrain the estimated multiple views. Comprehensive experiments on standard benchmarks and in-the-wild images demonstrate that HumanSplat surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in achieving photorealistic novel-view synthesis.
NAFRSSR: a Lightweight Recursive Network for Efficient Stereo Image Super-Resolution
May 14, 2024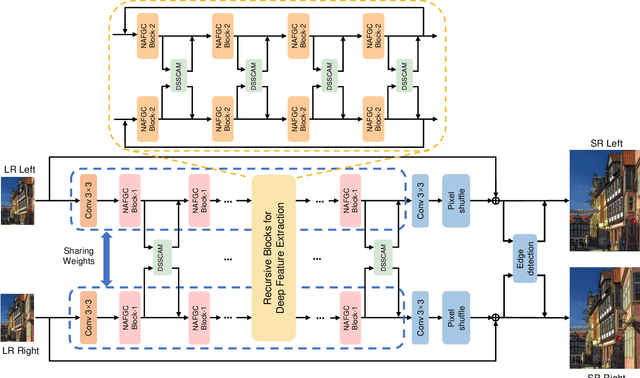
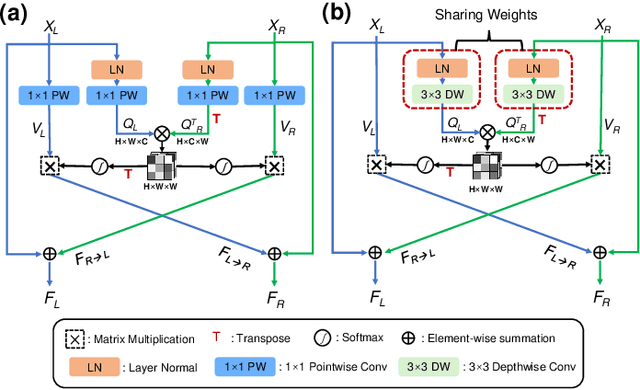
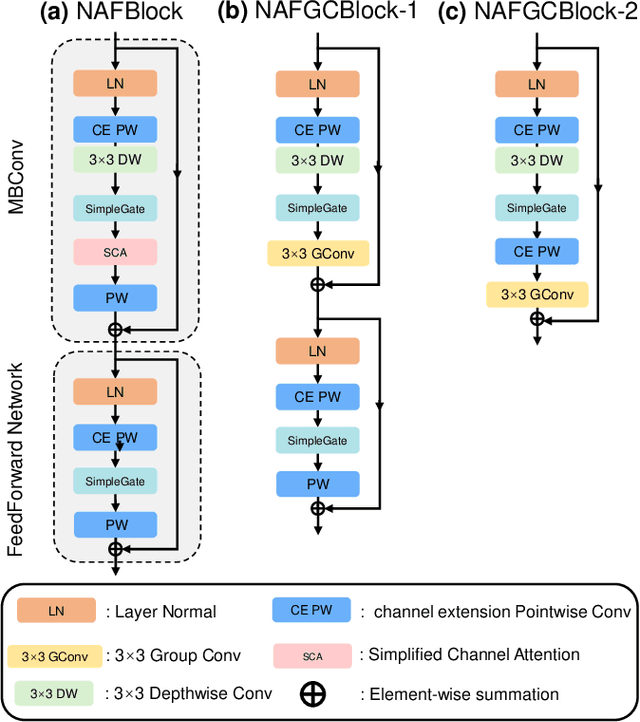
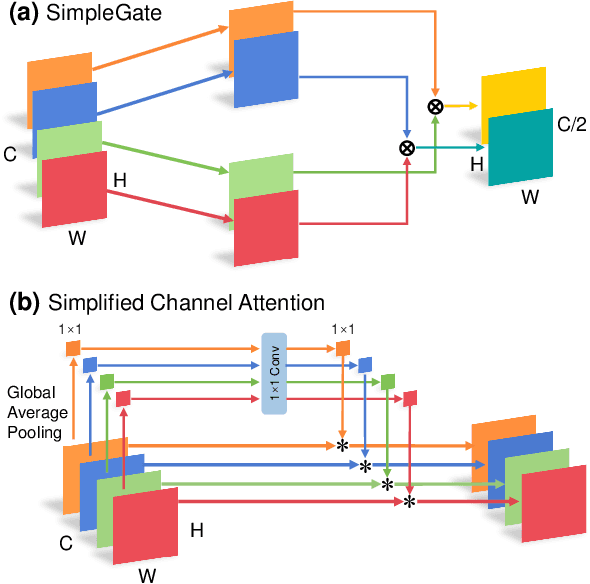
Abstract:Stereo image super-resolution (SR) refers to the reconstruction of a high-resolution (HR) image from a pair of low-resolution (LR) images as typically captured by a dual-camera device. To enhance the quality of SR images, most previous studies focused on increasing the number and size of feature maps and introducing complex and computationally intensive structures, resulting in models with high computational complexity. Here, we propose a simple yet efficient stereo image SR model called NAFRSSR, which is modified from the previous state-of-the-art model NAFSSR by introducing recursive connections and lightweighting the constituent modules. Our NAFRSSR model is composed of nonlinear activation free and group convolution-based blocks (NAFGCBlocks) and depth-separated stereo cross attention modules (DSSCAMs). The NAFGCBlock improves feature extraction and reduces number of parameters by removing the simple channel attention mechanism from NAFBlock and using group convolution. The DSSCAM enhances feature fusion and reduces number of parameters by replacing 1x1 pointwise convolution in SCAM with weight-shared 3x3 depthwise convolution. Besides, we propose to incorporate trainable edge detection operator into NAFRSSR to further improve the model performance. Four variants of NAFRSSR with different sizes, namely, NAFRSSR-Mobile (NAFRSSR-M), NAFRSSR-Tiny (NAFRSSR-T), NAFRSSR-Super (NAFRSSR-S) and NAFRSSR-Base (NAFRSSR-B) are designed, and they all exhibit fewer parameters, higher PSNR/SSIM, and faster speed than the previous state-of-the-art models. In particular, to the best of our knowledge, NAFRSSR-M is the lightest (0.28M parameters) and fastest (50 ms inference time) model achieving an average PSNR/SSIM as high as 24.657 dB/0.7622 on the benchmark datasets. Codes and models will be released at https://github.com/JNUChenYiHong/NAFRSSR.
HMD-Poser: On-Device Real-time Human Motion Tracking from Scalable Sparse Observations
Mar 06, 2024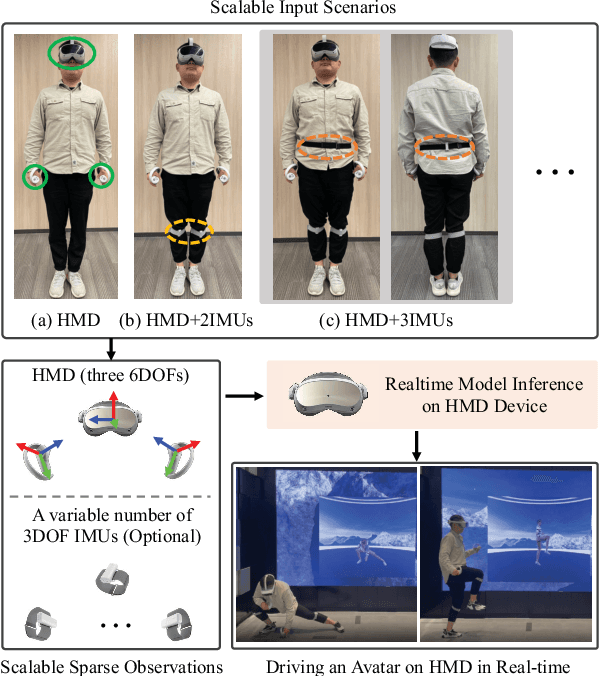
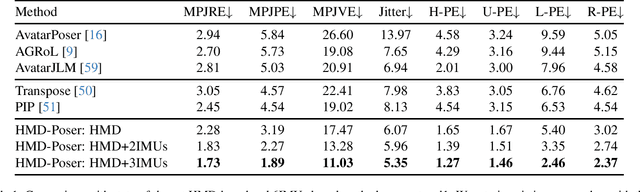
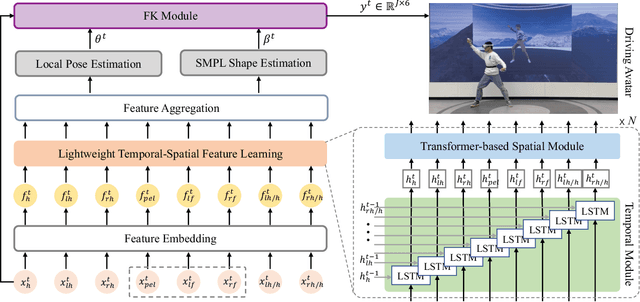
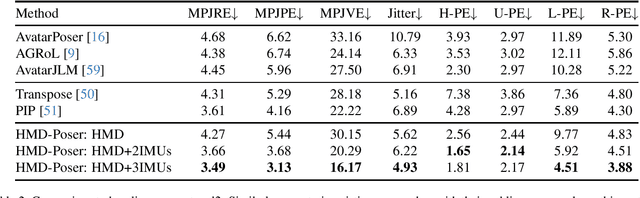
Abstract:It is especially challenging to achieve real-time human motion tracking on a standalone VR Head-Mounted Display (HMD) such as Meta Quest and PICO. In this paper, we propose HMD-Poser, the first unified approach to recover full-body motions using scalable sparse observations from HMD and body-worn IMUs. In particular, it can support a variety of input scenarios, such as HMD, HMD+2IMUs, HMD+3IMUs, etc. The scalability of inputs may accommodate users' choices for both high tracking accuracy and easy-to-wear. A lightweight temporal-spatial feature learning network is proposed in HMD-Poser to guarantee that the model runs in real-time on HMDs. Furthermore, HMD-Poser presents online body shape estimation to improve the position accuracy of body joints. Extensive experimental results on the challenging AMASS dataset show that HMD-Poser achieves new state-of-the-art results in both accuracy and real-time performance. We also build a new free-dancing motion dataset to evaluate HMD-Poser's on-device performance and investigate the performance gap between synthetic data and real-captured sensor data. Finally, we demonstrate our HMD-Poser with a real-time Avatar-driving application on a commercial HMD. Our code and free-dancing motion dataset are available https://pico-ai-team.github.io/hmd-poser
Building Retrieval Systems for the ClueWeb22-B Corpus
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:The ClueWeb22 dataset containing nearly 10 billion documents was released in 2022 to support academic and industry research. The goal of this project was to build retrieval baselines for the English section of the "super head" part (category B) of this dataset. These baselines can then be used by the research community to compare their systems and also to generate data to train/evaluate new retrieval and ranking algorithms. The report covers sparse and dense first stage retrievals as well as neural rerankers that were implemented for this dataset. These systems are available as a service on a Carnegie Mellon University cluster.
Combating Adversarial Attacks with Multi-Agent Debate
Jan 11, 2024Abstract:While state-of-the-art language models have achieved impressive results, they remain susceptible to inference-time adversarial attacks, such as adversarial prompts generated by red teams arXiv:2209.07858. One approach proposed to improve the general quality of language model generations is multi-agent debate, where language models self-evaluate through discussion and feedback arXiv:2305.14325. We implement multi-agent debate between current state-of-the-art language models and evaluate models' susceptibility to red team attacks in both single- and multi-agent settings. We find that multi-agent debate can reduce model toxicity when jailbroken or less capable models are forced to debate with non-jailbroken or more capable models. We also find marginal improvements through the general usage of multi-agent interactions. We further perform adversarial prompt content classification via embedding clustering, and analyze the susceptibility of different models to different types of attack topics.
A Self-enhancement Approach for Domain-specific Chatbot Training via Knowledge Mining and Digest
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs), despite their great power in language generation, often encounter challenges when dealing with intricate and knowledge-demanding queries in specific domains. This paper introduces a novel approach to enhance LLMs by effectively extracting the relevant knowledge from domain-specific textual sources, and the adaptive training of a chatbot with domain-specific inquiries. Our two-step approach starts from training a knowledge miner, namely LLMiner, which autonomously extracts Question-Answer pairs from relevant documents through a chain-of-thought reasoning process. Subsequently, we blend the mined QA pairs with a conversational dataset to fine-tune the LLM as a chatbot, thereby enriching its domain-specific expertise and conversational capabilities. We also developed a new evaluation benchmark which comprises four domain-specific text corpora and associated human-crafted QA pairs for testing. Our model shows remarkable performance improvement over generally aligned LLM and surpasses domain-adapted models directly fine-tuned on domain corpus. In particular, LLMiner achieves this with minimal human intervention, requiring only 600 seed instances, thereby providing a pathway towards self-improvement of LLMs through model-synthesized training data.
Localize, Group, and Select: Boosting Text-VQA by Scene Text Modeling
Aug 20, 2021
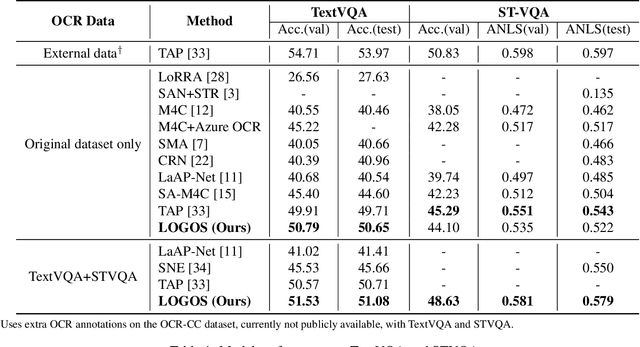
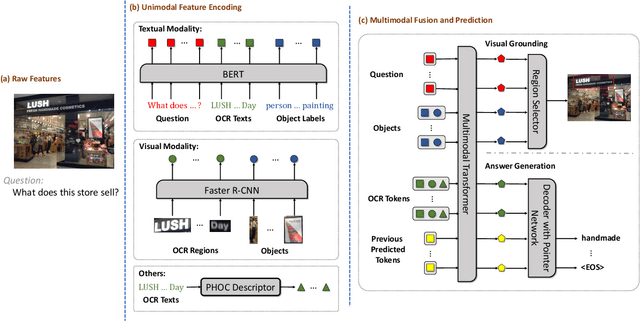
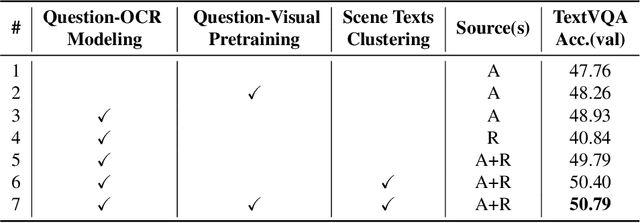
Abstract:As an important task in multimodal context understanding, Text-VQA (Visual Question Answering) aims at question answering through reading text information in images. It differentiates from the original VQA task as Text-VQA requires large amounts of scene-text relationship understanding, in addition to the cross-modal grounding capability. In this paper, we propose Localize, Group, and Select (LOGOS), a novel model which attempts to tackle this problem from multiple aspects. LOGOS leverages two grounding tasks to better localize the key information of the image, utilizes scene text clustering to group individual OCR tokens, and learns to select the best answer from different sources of OCR (Optical Character Recognition) texts. Experiments show that LOGOS outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods on two Text-VQA benchmarks without using additional OCR annotation data. Ablation studies and analysis demonstrate the capability of LOGOS to bridge different modalities and better understand scene text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge