Tingting Shen
HumanSplat: Generalizable Single-Image Human Gaussian Splatting with Structure Priors
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Despite recent advancements in high-fidelity human reconstruction techniques, the requirements for densely captured images or time-consuming per-instance optimization significantly hinder their applications in broader scenarios. To tackle these issues, we present HumanSplat which predicts the 3D Gaussian Splatting properties of any human from a single input image in a generalizable manner. In particular, HumanSplat comprises a 2D multi-view diffusion model and a latent reconstruction transformer with human structure priors that adeptly integrate geometric priors and semantic features within a unified framework. A hierarchical loss that incorporates human semantic information is further designed to achieve high-fidelity texture modeling and better constrain the estimated multiple views. Comprehensive experiments on standard benchmarks and in-the-wild images demonstrate that HumanSplat surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in achieving photorealistic novel-view synthesis.
Adaptive Weighted Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for Robust Feature Representation
Jun 07, 2022
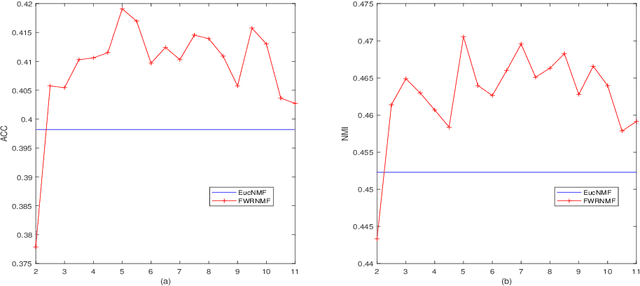
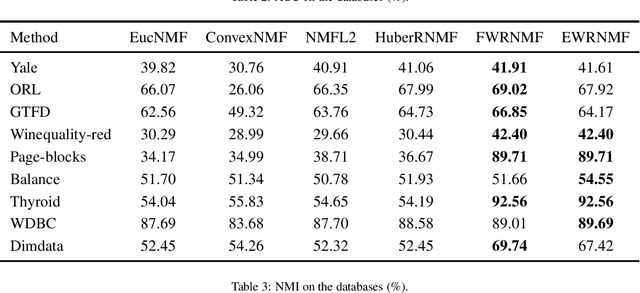
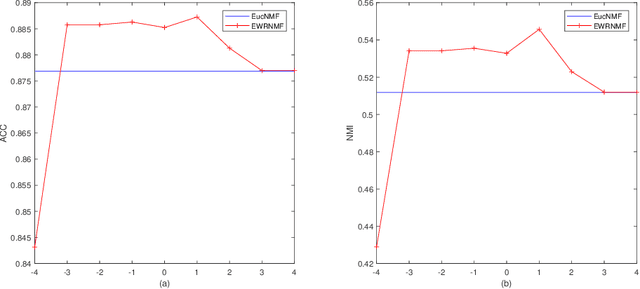
Abstract:Nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) has been widely used to dimensionality reduction in machine learning. However, the traditional NMF does not properly handle outliers, so that it is sensitive to noise. In order to improve the robustness of NMF, this paper proposes an adaptive weighted NMF, which introduces weights to emphasize the different importance of each data point, thus the algorithmic sensitivity to noisy data is decreased. It is very different from the existing robust NMFs that use a slow growth similarity measure. Specifically, two strategies are proposed to achieve this: fuzzier weighted technique and entropy weighted regularized technique, and both of them lead to an iterative solution with a simple form. Experimental results showed that new methods have more robust feature representation on several real datasets with noise than exsiting methods.
Subspace Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for Feature Representation
Apr 18, 2022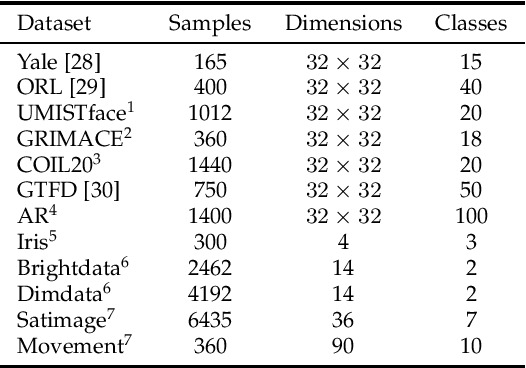
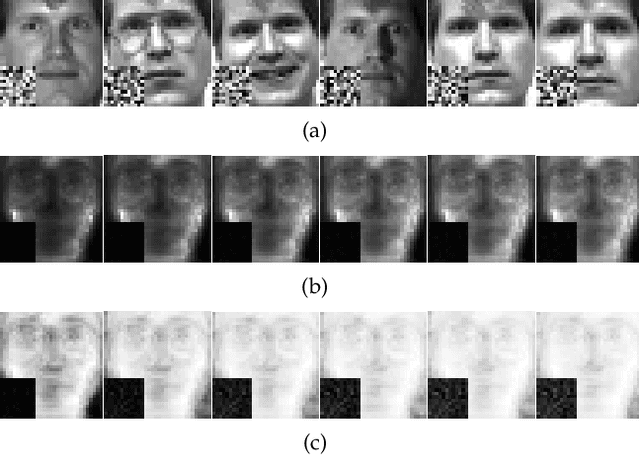

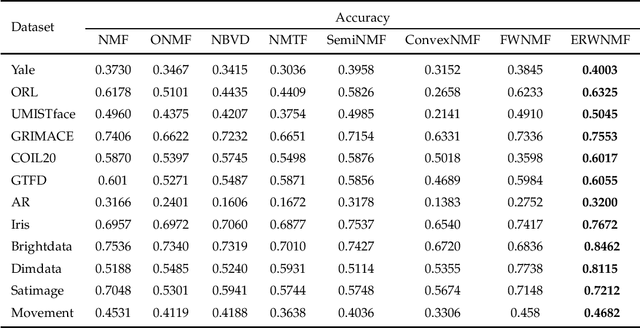
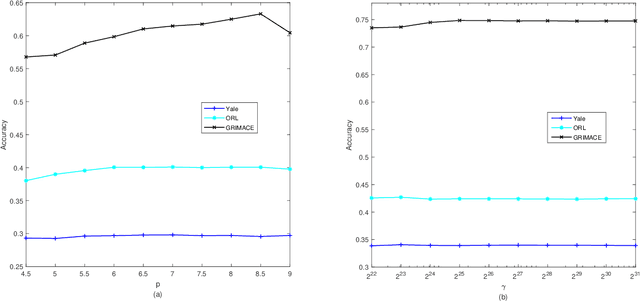
Abstract:Traditional nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) learns a new feature representation on the whole data space, which means treating all features equally. However, a subspace is often sufficient for accurate representation in practical applications, and redundant features can be invalid or even harmful. For example, if a camera has some sensors destroyed, then the corresponding pixels in the photos from this camera are not helpful to identify the content, which means only the subspace consisting of remaining pixels is worthy of attention. This paper proposes a new NMF method by introducing adaptive weights to identify key features in the original space so that only a subspace involves generating the new representation. Two strategies are proposed to achieve this: the fuzzier weighted technique and entropy regularized weighted technique, both of which result in an iterative solution with a simple form. Experimental results on several real-world datasets demonstrated that the proposed methods can generate a more accurate feature representation than existing methods. The code developed in this study is available at https://github.com/WNMF1/FWNMF-ERWNMF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge