Jiao Wei
Subspace Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for Feature Representation
Apr 18, 2022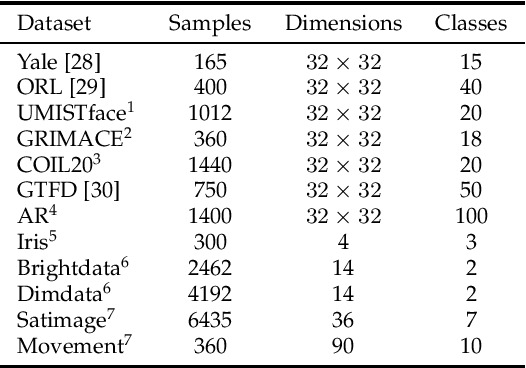
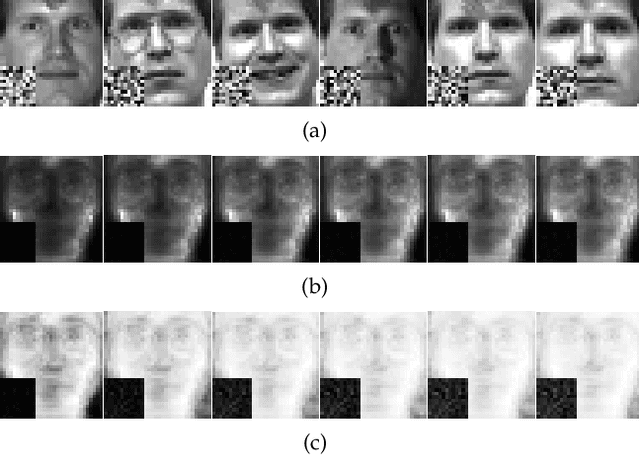

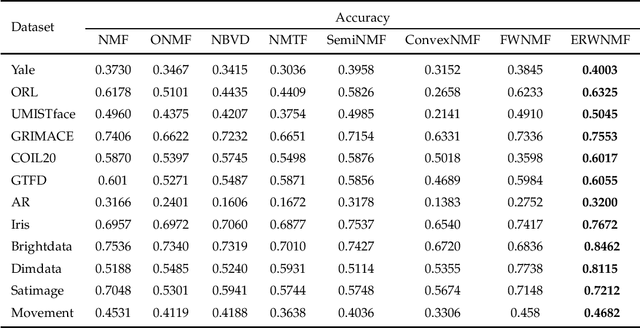
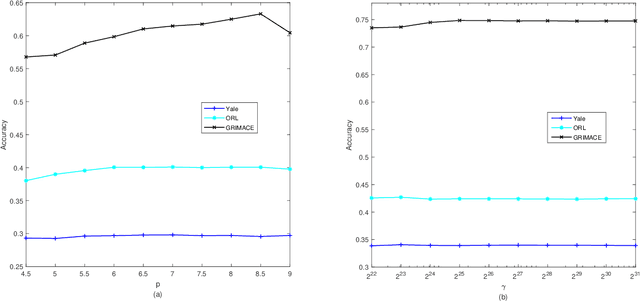
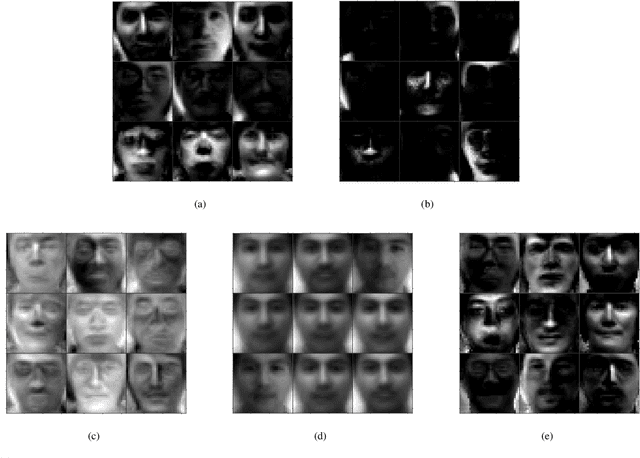
Abstract:Traditional nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) learns a new feature representation on the whole data space, which means treating all features equally. However, a subspace is often sufficient for accurate representation in practical applications, and redundant features can be invalid or even harmful. For example, if a camera has some sensors destroyed, then the corresponding pixels in the photos from this camera are not helpful to identify the content, which means only the subspace consisting of remaining pixels is worthy of attention. This paper proposes a new NMF method by introducing adaptive weights to identify key features in the original space so that only a subspace involves generating the new representation. Two strategies are proposed to achieve this: the fuzzier weighted technique and entropy regularized weighted technique, both of which result in an iterative solution with a simple form. Experimental results on several real-world datasets demonstrated that the proposed methods can generate a more accurate feature representation than existing methods. The code developed in this study is available at https://github.com/WNMF1/FWNMF-ERWNMF.
Entropy Regularized Iterative Weighted Shrinkage-Thresholding Algorithm (ERIWSTA): An Application to CT Image Restoration
Dec 22, 2021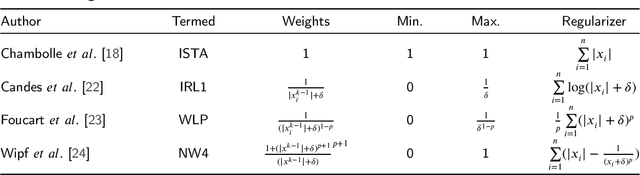
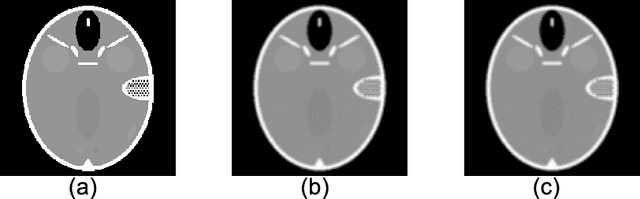


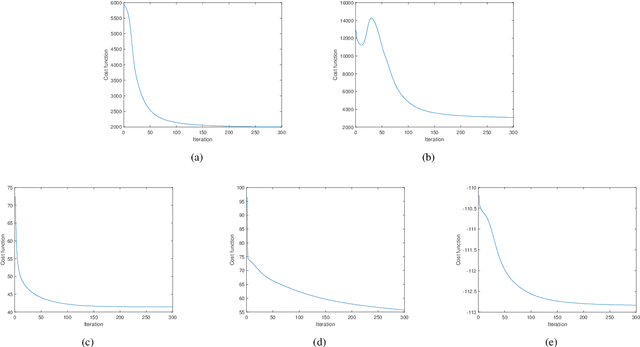
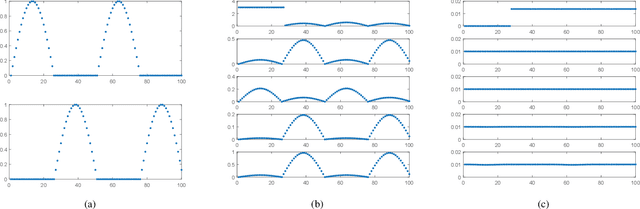
Abstract:The iterative weighted shrinkage-thresholding algorithm (IWSTA) has shown superiority to the classic unweighted iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm (ISTA) for solving linear inverse problems, which address the attributes differently. This paper proposes a new entropy regularized IWSTA (ERIWSTA) that adds an entropy regularizer to the cost function to measure the uncertainty of the weights to stimulate attributes to participate in problem solving. Then, the weights are solved with a Lagrange multiplier method to obtain a simple iterative update. The weights can be explained as the probability of the contribution of an attribute to the problem solution. Experimental results on CT image restoration show that the proposed method has better performance in terms of convergence speed and restoration accuracy than the existing methods.
An Entropy Weighted Nonnegative Matrix Factorization Algorithm for Feature Representation
Nov 27, 2021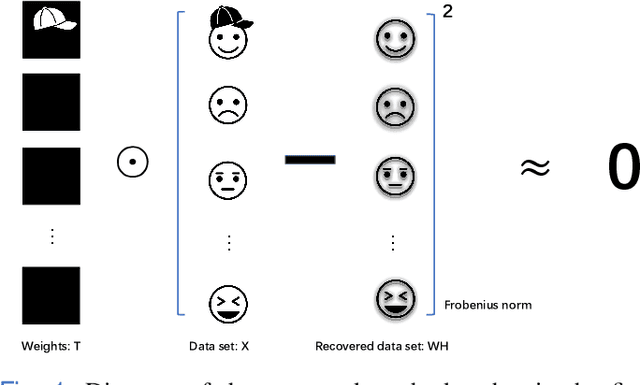

Abstract:Nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) has been widely used to learn low-dimensional representations of data. However, NMF pays the same attention to all attributes of a data point, which inevitably leads to inaccurate representation. For example, in a human-face data set, if an image contains a hat on the head, the hat should be removed or the importance of its corresponding attributes should be decreased during matrix factorizing. This paper proposes a new type of NMF called entropy weighted NMF (EWNMF), which uses an optimizable weight for each attribute of each data point to emphasize their importance. This process is achieved by adding an entropy regularizer to the cost function and then using the Lagrange multiplier method to solve the problem. Experimental results with several data sets demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method. We make our code available at https://github.com/Poisson-EM/Entropy-weighted-NMF.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge