Yumeng Liu
Unitho: A Unified Multi-Task Framework for Computational Lithography
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Reliable, generalizable data foundations are critical for enabling large-scale models in computational lithography. However, essential tasks-mask generation, rule violation detection, and layout optimization-are often handled in isolation, hindered by scarce datasets and limited modeling approaches. To address these challenges, we introduce Unitho, a unified multi-task large vision model built upon the Transformer architecture. Trained on a large-scale industrial lithography simulation dataset with hundreds of thousands of cases, Unitho supports end-to-end mask generation, lithography simulation, and rule violation detection. By enabling agile and high-fidelity lithography simulation, Unitho further facilitates the construction of robust data foundations for intelligent EDA. Experimental results validate its effectiveness and generalizability, with performance substantially surpassing academic baselines.
Enhancing Multimodal Protein Function Prediction Through Dual-Branch Dynamic Selection with Reconstructive Pre-Training
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Multimodal protein features play a crucial role in protein function prediction. However, these features encompass a wide range of information, ranging from structural data and sequence features to protein attributes and interaction networks, making it challenging to decipher their complex interconnections. In this work, we propose a multimodal protein function prediction method (DSRPGO) by utilizing dynamic selection and reconstructive pre-training mechanisms. To acquire complex protein information, we introduce reconstructive pre-training to mine more fine-grained information with low semantic levels. Moreover, we put forward the Bidirectional Interaction Module (BInM) to facilitate interactive learning among multimodal features. Additionally, to address the difficulty of hierarchical multi-label classification in this task, a Dynamic Selection Module (DSM) is designed to select the feature representation that is most conducive to current protein function prediction. Our proposed DSRPGO model improves significantly in BPO, MFO, and CCO on human datasets, thereby outperforming other benchmark models.
ChiMDQA: Towards Comprehensive Chinese Document QA with Fine-grained Evaluation
Nov 05, 2025Abstract:With the rapid advancement of natural language processing (NLP) technologies, the demand for high-quality Chinese document question-answering datasets is steadily growing. To address this issue, we present the Chinese Multi-Document Question Answering Dataset(ChiMDQA), specifically designed for downstream business scenarios across prevalent domains including academic, education, finance, law, medical treatment, and news. ChiMDQA encompasses long-form documents from six distinct fields, consisting of 6,068 rigorously curated, high-quality question-answer (QA) pairs further classified into ten fine-grained categories. Through meticulous document screening and a systematic question-design methodology, the dataset guarantees both diversity and high quality, rendering it applicable to various NLP tasks such as document comprehension, knowledge extraction, and intelligent QA systems. Additionally, this paper offers a comprehensive overview of the dataset's design objectives, construction methodologies, and fine-grained evaluation system, supplying a substantial foundation for future research and practical applications in Chinese QA. The code and data are available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Foxit-CHiMDQA/.
A Survey: Learning Embodied Intelligence from Physical Simulators and World Models
Jul 01, 2025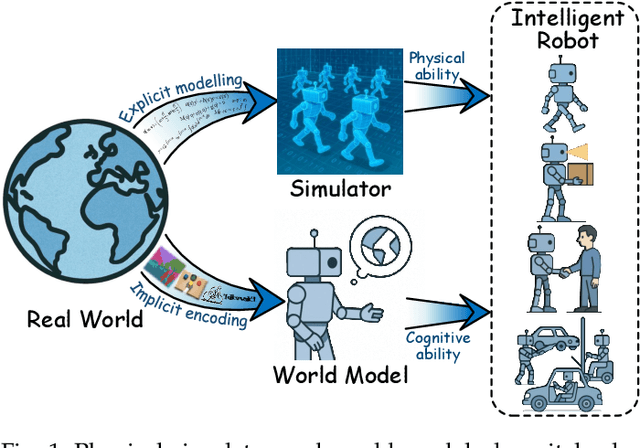
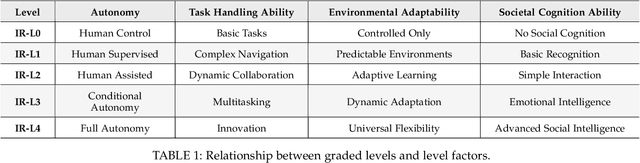
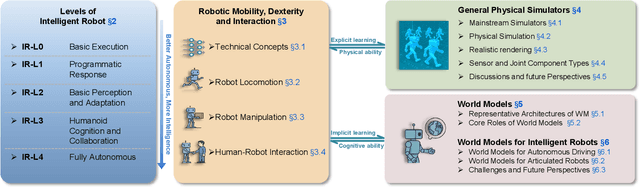

Abstract:The pursuit of artificial general intelligence (AGI) has placed embodied intelligence at the forefront of robotics research. Embodied intelligence focuses on agents capable of perceiving, reasoning, and acting within the physical world. Achieving robust embodied intelligence requires not only advanced perception and control, but also the ability to ground abstract cognition in real-world interactions. Two foundational technologies, physical simulators and world models, have emerged as critical enablers in this quest. Physical simulators provide controlled, high-fidelity environments for training and evaluating robotic agents, allowing safe and efficient development of complex behaviors. In contrast, world models empower robots with internal representations of their surroundings, enabling predictive planning and adaptive decision-making beyond direct sensory input. This survey systematically reviews recent advances in learning embodied AI through the integration of physical simulators and world models. We analyze their complementary roles in enhancing autonomy, adaptability, and generalization in intelligent robots, and discuss the interplay between external simulation and internal modeling in bridging the gap between simulated training and real-world deployment. By synthesizing current progress and identifying open challenges, this survey aims to provide a comprehensive perspective on the path toward more capable and generalizable embodied AI systems. We also maintain an active repository that contains up-to-date literature and open-source projects at https://github.com/NJU3DV-LoongGroup/Embodied-World-Models-Survey.
DISC: Plug-and-Play Decoding Intervention with Similarity of Characters for Chinese Spelling Check
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:One key characteristic of the Chinese spelling check (CSC) task is that incorrect characters are usually similar to the correct ones in either phonetics or glyph. To accommodate this, previous works usually leverage confusion sets, which suffer from two problems, i.e., difficulty in determining which character pairs to include and lack of probabilities to distinguish items in the set. In this paper, we propose a light-weight plug-and-play DISC (i.e., decoding intervention with similarity of characters) module for CSC models.DISC measures phonetic and glyph similarities between characters and incorporates this similarity information only during the inference phase. This method can be easily integrated into various existing CSC models, such as ReaLiSe, SCOPE, and ReLM, without additional training costs. Experiments on three CSC benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed method significantly improves model performance, approaching and even surpassing the current state-of-the-art models.
Creating a Cooperative AI Policymaking Platform through Open Source Collaboration
Dec 09, 2024

Abstract:Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) present significant risks and opportunities, requiring improved governance to mitigate societal harms and promote equitable benefits. Current incentive structures and regulatory delays may hinder responsible AI development and deployment, particularly in light of the transformative potential of large language models (LLMs). To address these challenges, we propose developing the following three contributions: (1) a large multimodal text and economic-timeseries foundation model that integrates economic and natural language policy data for enhanced forecasting and decision-making, (2) algorithmic mechanisms for eliciting diverse and representative perspectives, enabling the creation of data-driven public policy recommendations, and (3) an AI-driven web platform for supporting transparent, inclusive, and data-driven policymaking.
EasyHOI: Unleashing the Power of Large Models for Reconstructing Hand-Object Interactions in the Wild
Nov 21, 2024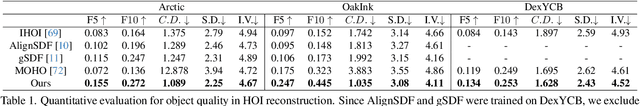
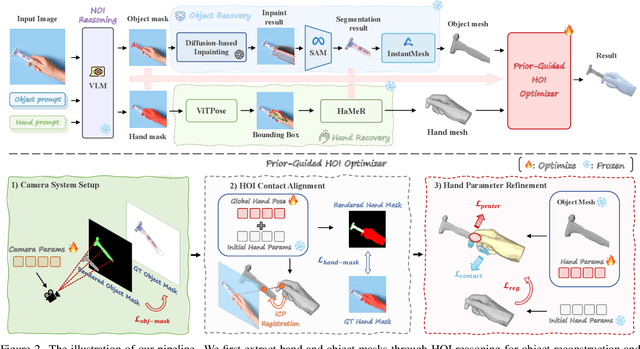
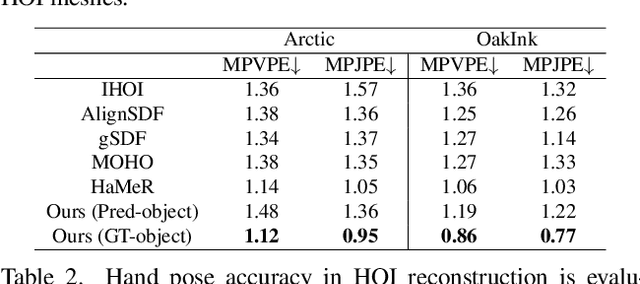
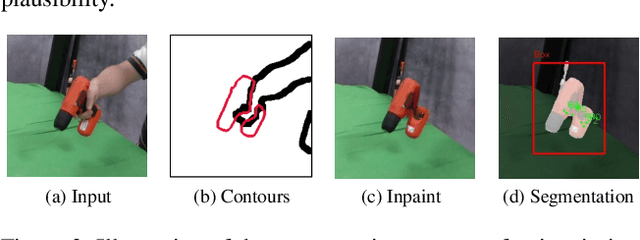
Abstract:Our work aims to reconstruct hand-object interactions from a single-view image, which is a fundamental but ill-posed task. Unlike methods that reconstruct from videos, multi-view images, or predefined 3D templates, single-view reconstruction faces significant challenges due to inherent ambiguities and occlusions. These challenges are further amplified by the diverse nature of hand poses and the vast variety of object shapes and sizes. Our key insight is that current foundational models for segmentation, inpainting, and 3D reconstruction robustly generalize to in-the-wild images, which could provide strong visual and geometric priors for reconstructing hand-object interactions. Specifically, given a single image, we first design a novel pipeline to estimate the underlying hand pose and object shape using off-the-shelf large models. Furthermore, with the initial reconstruction, we employ a prior-guided optimization scheme, which optimizes hand pose to comply with 3D physical constraints and the 2D input image content. We perform experiments across several datasets and show that our method consistently outperforms baselines and faithfully reconstructs a diverse set of hand-object interactions. Here is the link of our project page: https://lym29.github.io/EasyHOI-page/
RealDex: Towards Human-like Grasping for Robotic Dexterous Hand
Feb 21, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce RealDex, a pioneering dataset capturing authentic dexterous hand grasping motions infused with human behavioral patterns, enriched by multi-view and multimodal visual data. Utilizing a teleoperation system, we seamlessly synchronize human-robot hand poses in real time. This collection of human-like motions is crucial for training dexterous hands to mimic human movements more naturally and precisely. RealDex holds immense promise in advancing humanoid robot for automated perception, cognition, and manipulation in real-world scenarios. Moreover, we introduce a cutting-edge dexterous grasping motion generation framework, which aligns with human experience and enhances real-world applicability through effectively utilizing Multimodal Large Language Models. Extensive experiments have demonstrated the superior performance of our method on RealDex and other open datasets. The complete dataset and code will be made available upon the publication of this work.
Improving Seq2Seq Grammatical Error Correction via Decoding Interventions
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:The sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) approach has recently been widely used in grammatical error correction (GEC) and shows promising performance. However, the Seq2Seq GEC approach still suffers from two issues. First, a Seq2Seq GEC model can only be trained on parallel data, which, in GEC task, is often noisy and limited in quantity. Second, the decoder of a Seq2Seq GEC model lacks an explicit awareness of the correctness of the token being generated. In this paper, we propose a unified decoding intervention framework that employs an external critic to assess the appropriateness of the token to be generated incrementally, and then dynamically influence the choice of the next token. We discover and investigate two types of critics: a pre-trained left-to-right language model critic and an incremental target-side grammatical error detector critic. Through extensive experiments on English and Chinese datasets, our framework consistently outperforms strong baselines and achieves results competitive with state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge