Houquan Zhou
WebWeaver: Structuring Web-Scale Evidence with Dynamic Outlines for Open-Ended Deep Research
Sep 16, 2025



Abstract:This paper tackles open-ended deep research (OEDR), a complex challenge where AI agents must synthesize vast web-scale information into insightful reports. Current approaches are plagued by dual-fold limitations: static research pipelines that decouple planning from evidence acquisition and one-shot generation paradigms that easily suffer from long-context failure issues like "loss in the middle" and hallucinations. To address these challenges, we introduce WebWeaver, a novel dual-agent framework that emulates the human research process. The planner operates in a dynamic cycle, iteratively interleaving evidence acquisition with outline optimization to produce a comprehensive, source-grounded outline linking to a memory bank of evidence. The writer then executes a hierarchical retrieval and writing process, composing the report section by section. By performing targeted retrieval of only the necessary evidence from the memory bank for each part, it effectively mitigates long-context issues. Our framework establishes a new state-of-the-art across major OEDR benchmarks, including DeepResearch Bench, DeepConsult, and DeepResearchGym. These results validate our human-centric, iterative methodology, demonstrating that adaptive planning and focused synthesis are crucial for producing high-quality, reliable, and well-structured reports.
Mixture of Small and Large Models for Chinese Spelling Check
Jun 07, 2025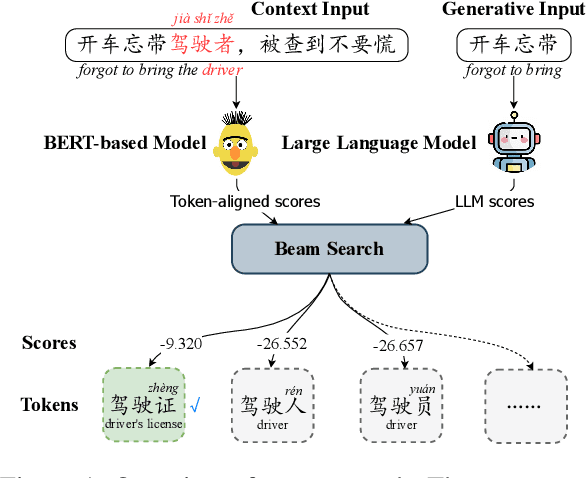
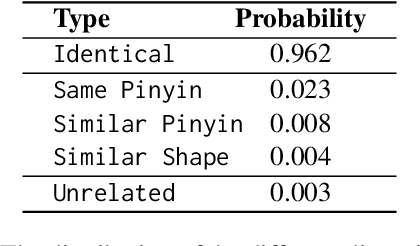
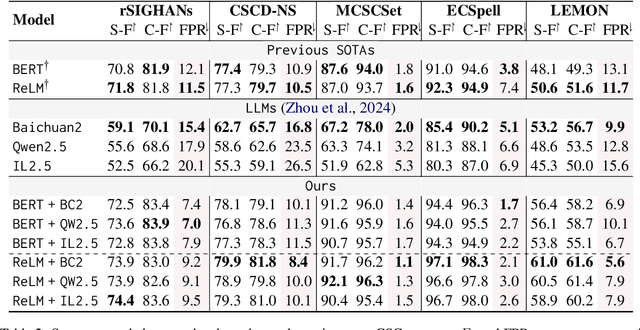
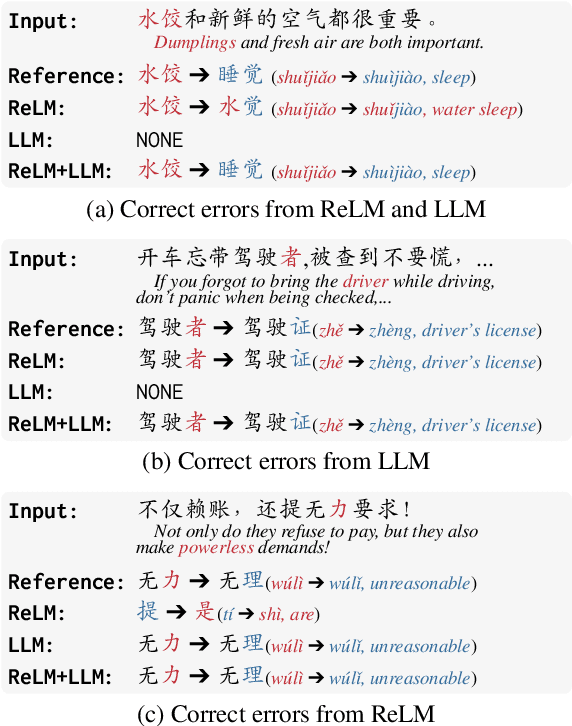
Abstract:In the era of large language models (LLMs), the Chinese Spelling Check (CSC) task has seen various LLM methods developed, yet their performance remains unsatisfactory. In contrast, fine-tuned BERT-based models, relying on high-quality in-domain data, show excellent performance but suffer from edit pattern overfitting. This paper proposes a novel dynamic mixture approach that effectively combines the probability distributions of small models and LLMs during the beam search decoding phase, achieving a balanced enhancement of precise corrections from small models and the fluency of LLMs. This approach also eliminates the need for fine-tuning LLMs, saving significant time and resources, and facilitating domain adaptation. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our mixture approach significantly boosts error correction capabilities, achieving state-of-the-art results across multiple datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/zhqiao-nlp/MSLLM.
A Training-free LLM-based Approach to General Chinese Character Error Correction
Feb 21, 2025



Abstract:Chinese spelling correction (CSC) is a crucial task that aims to correct character errors in Chinese text. While conventional CSC focuses on character substitution errors caused by mistyping, two other common types of character errors, missing and redundant characters, have received less attention. These errors are often excluded from CSC datasets during the annotation process or ignored during evaluation, even when they have been annotated. This issue limits the practicality of the CSC task. To address this issue, we introduce the task of General Chinese Character Error Correction (C2EC), which focuses on all three types of character errors. We construct a high-quality C2EC benchmark by combining and manually verifying data from CCTC and Lemon datasets. We extend the training-free prompt-free CSC method to C2EC by using Levenshtein distance for handling length changes and leveraging an additional prompt-based large language model (LLM) to improve performance. Experiments show that our method enables a 14B-parameter LLM to be on par with models nearly 50 times larger on both conventional CSC and C2EC tasks, without any fine-tuning.
DISC: Plug-and-Play Decoding Intervention with Similarity of Characters for Chinese Spelling Check
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:One key characteristic of the Chinese spelling check (CSC) task is that incorrect characters are usually similar to the correct ones in either phonetics or glyph. To accommodate this, previous works usually leverage confusion sets, which suffer from two problems, i.e., difficulty in determining which character pairs to include and lack of probabilities to distinguish items in the set. In this paper, we propose a light-weight plug-and-play DISC (i.e., decoding intervention with similarity of characters) module for CSC models.DISC measures phonetic and glyph similarities between characters and incorporates this similarity information only during the inference phase. This method can be easily integrated into various existing CSC models, such as ReaLiSe, SCOPE, and ReLM, without additional training costs. Experiments on three CSC benchmarks demonstrate that our proposed method significantly improves model performance, approaching and even surpassing the current state-of-the-art models.
A Simple yet Effective Training-free Prompt-free Approach to Chinese Spelling Correction Based on Large Language Models
Oct 05, 2024



Abstract:This work proposes a simple training-free prompt-free approach to leverage large language models (LLMs) for the Chinese spelling correction (CSC) task, which is totally different from all previous CSC approaches. The key idea is to use an LLM as a pure language model in a conventional manner. The LLM goes through the input sentence from the beginning, and at each inference step, produces a distribution over its vocabulary for deciding the next token, given a partial sentence. To ensure that the output sentence remains faithful to the input sentence, we design a minimal distortion model that utilizes pronunciation or shape similarities between the original and replaced characters. Furthermore, we propose two useful reward strategies to address practical challenges specific to the CSC task. Experiments on five public datasets demonstrate that our approach significantly improves LLM performance, enabling them to compete with state-of-the-art domain-general CSC models.
How Well Do Large Language Models Understand Syntax? An Evaluation by Asking Natural Language Questions
Nov 14, 2023



Abstract:While recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) bring us closer to achieving artificial general intelligence, the question persists: Do LLMs truly understand language, or do they merely mimic comprehension through pattern recognition? This study seeks to explore this question through the lens of syntax, a crucial component of sentence comprehension. Adopting a natural language question-answering (Q&A) scheme, we craft questions targeting nine syntactic knowledge points that are most closely related to sentence comprehension. Experiments conducted on 24 LLMs suggest that most have a limited grasp of syntactic knowledge, exhibiting notable discrepancies across different syntactic knowledge points. In particular, questions involving prepositional phrase attachment pose the greatest challenge, whereas those concerning adjectival modifier and indirect object are relatively easier for LLMs to handle. Furthermore, a case study on the training dynamics of the LLMs reveals that the majority of syntactic knowledge is learned during the initial stages of training, hinting that simply increasing the number of training tokens may not be the `silver bullet' for improving the comprehension ability of LLMs.
Improving Seq2Seq Grammatical Error Correction via Decoding Interventions
Oct 23, 2023Abstract:The sequence-to-sequence (Seq2Seq) approach has recently been widely used in grammatical error correction (GEC) and shows promising performance. However, the Seq2Seq GEC approach still suffers from two issues. First, a Seq2Seq GEC model can only be trained on parallel data, which, in GEC task, is often noisy and limited in quantity. Second, the decoder of a Seq2Seq GEC model lacks an explicit awareness of the correctness of the token being generated. In this paper, we propose a unified decoding intervention framework that employs an external critic to assess the appropriateness of the token to be generated incrementally, and then dynamically influence the choice of the next token. We discover and investigate two types of critics: a pre-trained left-to-right language model critic and an incremental target-side grammatical error detector critic. Through extensive experiments on English and Chinese datasets, our framework consistently outperforms strong baselines and achieves results competitive with state-of-the-art methods.
Learning node embeddings via summary graphs: a brief theoretical analysis
Jul 04, 2022

Abstract:Graph representation learning plays an important role in many graph mining applications, but learning embeddings of large-scale graphs remains a problem. Recent works try to improve scalability via graph summarization -- i.e., they learn embeddings on a smaller summary graph, and then restore the node embeddings of the original graph. However, all existing works depend on heuristic designs and lack theoretical analysis. Different from existing works, we contribute an in-depth theoretical analysis of three specific embedding learning methods based on introduced kernel matrix, and reveal that learning embeddings via graph summarization is actually learning embeddings on a approximate graph constructed by the configuration model. We also give analysis about approximation error. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to give theoretical analysis of this approach. Furthermore, our analysis framework gives interpretation of some existing methods and provides great insights for future work on this problem.
Bridging Pre-trained Language Models and Hand-crafted Features for Unsupervised POS Tagging
Mar 19, 2022



Abstract:In recent years, large-scale pre-trained language models (PLMs) have made extraordinary progress in most NLP tasks. But, in the unsupervised POS tagging task, works utilizing PLMs are few and fail to achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance. The recent SOTA performance is yielded by a Guassian HMM variant proposed by He et al. (2018). However, as a generative model, HMM makes very strong independence assumptions, making it very challenging to incorporate contexualized word representations from PLMs. In this work, we for the first time propose a neural conditional random field autoencoder (CRF-AE) model for unsupervised POS tagging. The discriminative encoder of CRF-AE can straightforwardly incorporate ELMo word representations. Moreover, inspired by feature-rich HMM, we reintroduce hand-crafted features into the decoder of CRF-AE. Finally, experiments clearly show that our model outperforms previous state-of-the-art models by a large margin on Penn Treebank and multilingual Universal Dependencies treebank v2.0.
An In-depth Study on Internal Structure of Chinese Words
Jun 01, 2021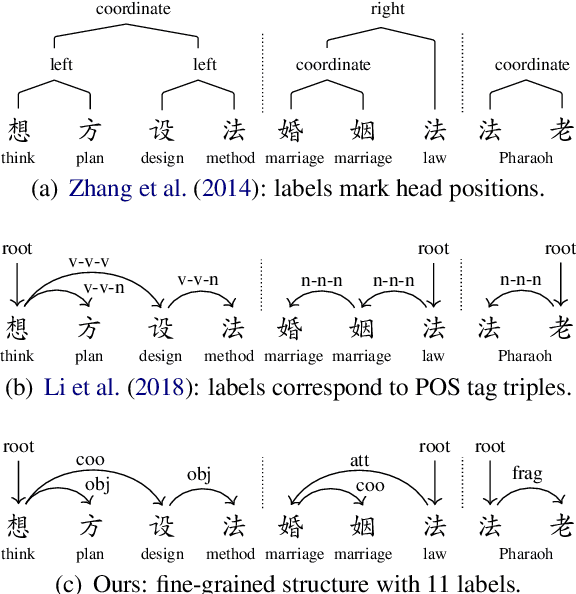
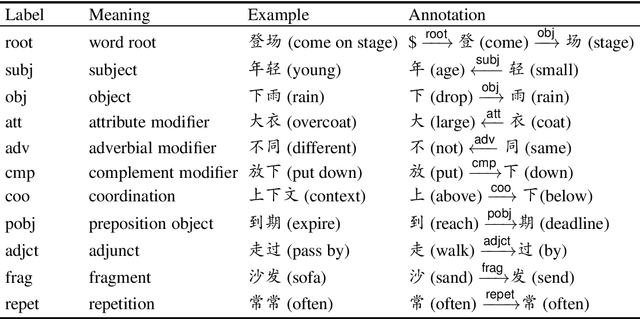
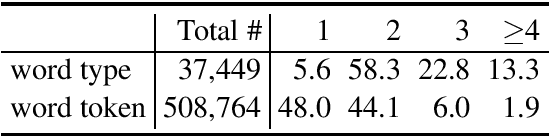
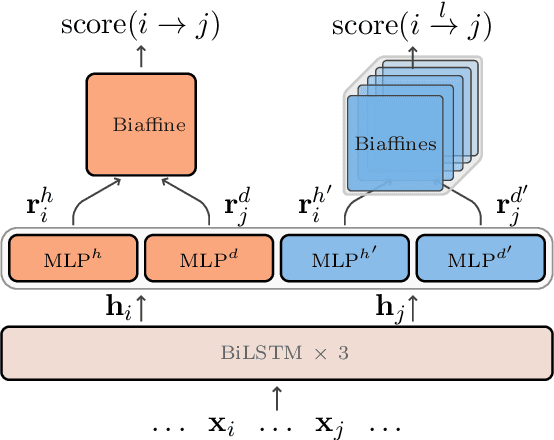
Abstract:Unlike English letters, Chinese characters have rich and specific meanings. Usually, the meaning of a word can be derived from its constituent characters in some way. Several previous works on syntactic parsing propose to annotate shallow word-internal structures for better utilizing character-level information. This work proposes to model the deep internal structures of Chinese words as dependency trees with 11 labels for distinguishing syntactic relationships. First, based on newly compiled annotation guidelines, we manually annotate a word-internal structure treebank (WIST) consisting of over 30K multi-char words from Chinese Penn Treebank. To guarantee quality, each word is independently annotated by two annotators and inconsistencies are handled by a third senior annotator. Second, we present detailed and interesting analysis on WIST to reveal insights on Chinese word formation. Third, we propose word-internal structure parsing as a new task, and conduct benchmark experiments using a competitive dependency parser. Finally, we present two simple ways to encode word-internal structures, leading to promising gains on the sentence-level syntactic parsing task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge