Xin Lei
T-Mimi: A Transformer-based Mimi Decoder for Real-Time On-Phone TTS
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Neural audio codecs provide promising acoustic features for speech synthesis, with representative streaming codecs like Mimi providing high-quality acoustic features for real-time Text-to-Speech (TTS) applications. However, Mimi's decoder, which employs a hybrid transformer and convolution architecture, introduces significant latency bottlenecks on edge devices due to the the compute intensive nature of deconvolution layers which are not friendly for mobile-CPUs, such as the most representative framework XNNPACK. This paper introduces T-Mimi, a novel modification of the Mimi codec decoder that replaces its convolutional components with a purely transformer-based decoder, inspired by the TS3-Codec architecture. This change dramatically reduces on-device TTS latency from 42.1ms to just 4.4ms. Furthermore, we conduct quantization aware training and derive a crucial finding: the final two transformer layers and the concluding linear layers of the decoder, which are close to the waveform, are highly sensitive to quantization and must be preserved at full precision to maintain audio quality.
Query-by-Example Keyword Spotting Using Spectral-Temporal Graph Attentive Pooling and Multi-Task Learning
Aug 27, 2024



Abstract:Existing keyword spotting (KWS) systems primarily rely on predefined keyword phrases. However, the ability to recognize customized keywords is crucial for tailoring interactions with intelligent devices. In this paper, we present a novel Query-by-Example (QbyE) KWS system that employs spectral-temporal graph attentive pooling and multi-task learning. This framework aims to effectively learn speaker-invariant and linguistic-informative embeddings for QbyE KWS tasks. Within this framework, we investigate three distinct network architectures for encoder modeling: LiCoNet, Conformer and ECAPA_TDNN. The experimental results on a substantial internal dataset of $629$ speakers have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed QbyE framework in maximizing the potential of simpler models such as LiCoNet. Particularly, LiCoNet, which is 13x more efficient, achieves comparable performance to the computationally intensive Conformer model (1.98% vs. 1.63\% FRR at 0.3 FAs/Hr).
Disentangled Training with Adversarial Examples For Robust Small-footprint Keyword Spotting
Aug 23, 2024



Abstract:A keyword spotting (KWS) engine that is continuously running on device is exposed to various speech signals that are usually unseen before. It is a challenging problem to build a small-footprint and high-performing KWS model with robustness under different acoustic environments. In this paper, we explore how to effectively apply adversarial examples to improve KWS robustness. We propose datasource-aware disentangled learning with adversarial examples to reduce the mismatch between the original and adversarial data as well as the mismatch across original training datasources. The KWS model architecture is based on depth-wise separable convolution and a simple attention module. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed learning strategy improves false reject rate by $40.31%$ at $1%$ false accept rate on the internal dataset, compared to the strongest baseline without using adversarial examples. Our best-performing system achieves $98.06%$ accuracy on the Google Speech Commands V1 dataset.
LLaMA based Punctuation Restoration With Forward Pass Only Decoding
Aug 09, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces two advancements in the field of Large Language Model Annotation with a focus on punctuation restoration tasks. Our first contribution is the application of LLaMA for punctuation restoration, which demonstrates superior performance compared to the established benchmark. Despite its impressive quality, LLaMA faces challenges regarding inference speed and hallucinations. To address this, our second contribution presents Forward Pass Only Decoding (FPOD), a novel decoding approach for annotation tasks. This innovative method results in a substantial 19.8x improvement in inference speed, effectively addressing a critical bottleneck and enhancing the practical utility of LLaMA for large-scale data annotation tasks without hallucinations. The combination of these contributions not only solidifies LLaMA as a powerful tool for punctuation restoration but also highlights FPOD as a crucial strategy for overcoming speed constraints.
FADI-AEC: Fast Score Based Diffusion Model Guided by Far-end Signal for Acoustic Echo Cancellation
Jan 08, 2024Abstract:Despite the potential of diffusion models in speech enhancement, their deployment in Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) has been restricted. In this paper, we propose DI-AEC, pioneering a diffusion-based stochastic regeneration approach dedicated to AEC. Further, we propose FADI-AEC, fast score-based diffusion AEC framework to save computational demands, making it favorable for edge devices. It stands out by running the score model once per frame, achieving a significant surge in processing efficiency. Apart from that, we introduce a novel noise generation technique where far-end signals are utilized, incorporating both far-end and near-end signals to refine the score model's accuracy. We test our proposed method on the ICASSP2023 Microsoft deep echo cancellation challenge evaluation dataset, where our method outperforms some of the end-to-end methods and other diffusion based echo cancellation methods.
Directional Source Separation for Robust Speech Recognition on Smart Glasses
Sep 20, 2023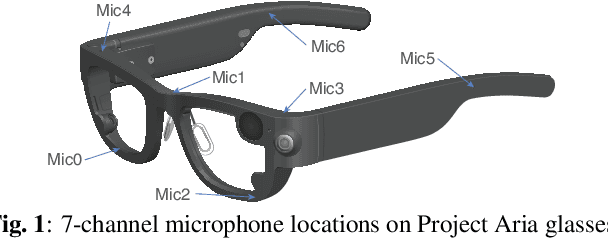
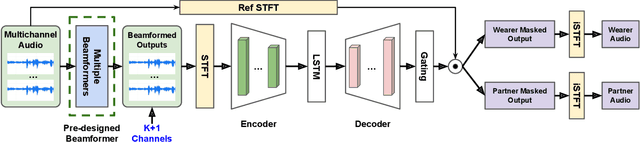
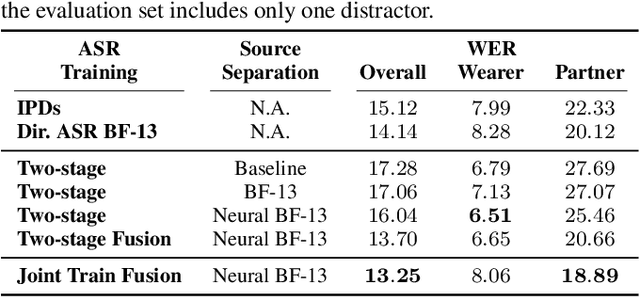
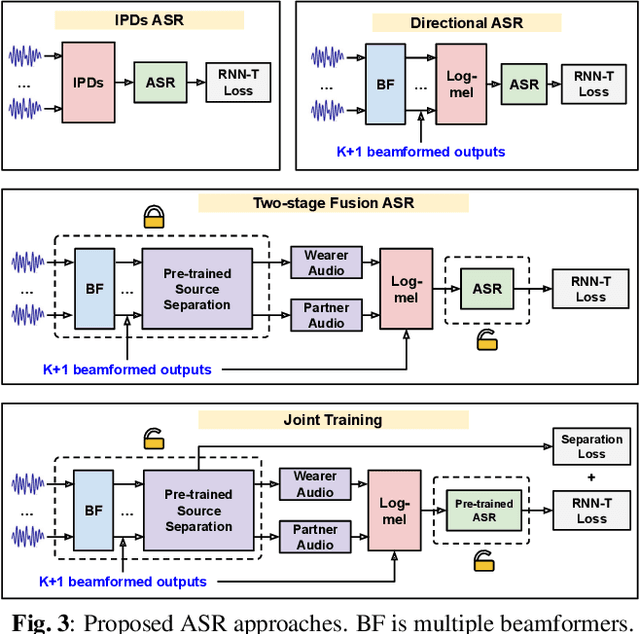
Abstract:Modern smart glasses leverage advanced audio sensing and machine learning technologies to offer real-time transcribing and captioning services, considerably enriching human experiences in daily communications. However, such systems frequently encounter challenges related to environmental noises, resulting in degradation to speech recognition and speaker change detection. To improve voice quality, this work investigates directional source separation using the multi-microphone array. We first explore multiple beamformers to assist source separation modeling by strengthening the directional properties of speech signals. In addition to relying on predetermined beamformers, we investigate neural beamforming in multi-channel source separation, demonstrating that automatic learning directional characteristics effectively improves separation quality. We further compare the ASR performance leveraging separated outputs to noisy inputs. Our results show that directional source separation benefits ASR for the wearer but not for the conversation partner. Lastly, we perform the joint training of the directional source separation and ASR model, achieving the best overall ASR performance.
TODM: Train Once Deploy Many Efficient Supernet-Based RNN-T Compression For On-device ASR Models
Sep 05, 2023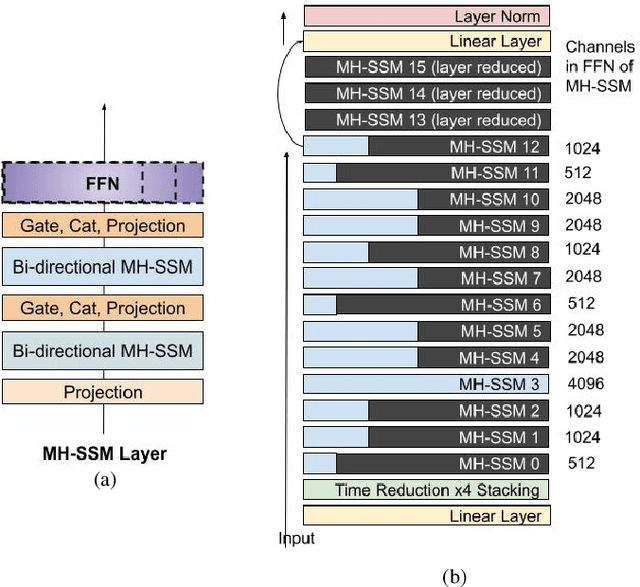
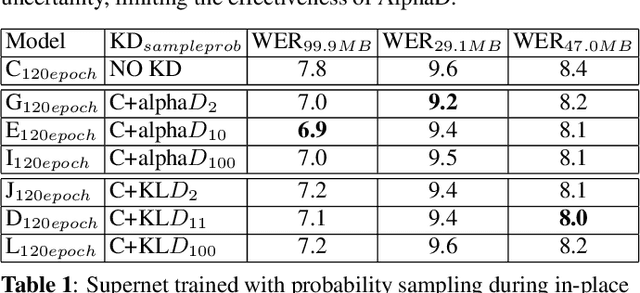
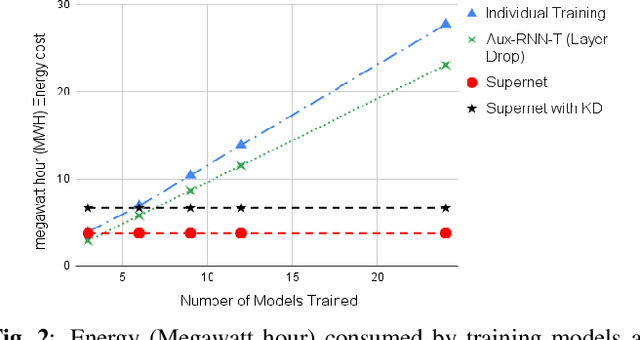
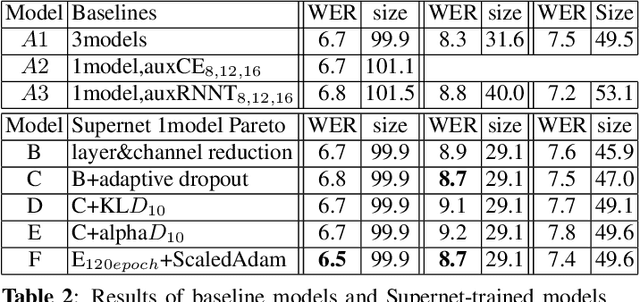
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models need to be optimized for specific hardware before they can be deployed on devices. This can be done by tuning the model's hyperparameters or exploring variations in its architecture. Re-training and re-validating models after making these changes can be a resource-intensive task. This paper presents TODM (Train Once Deploy Many), a new approach to efficiently train many sizes of hardware-friendly on-device ASR models with comparable GPU-hours to that of a single training job. TODM leverages insights from prior work on Supernet, where Recurrent Neural Network Transducer (RNN-T) models share weights within a Supernet. It reduces layer sizes and widths of the Supernet to obtain subnetworks, making them smaller models suitable for all hardware types. We introduce a novel combination of three techniques to improve the outcomes of the TODM Supernet: adaptive dropouts, an in-place Alpha-divergence knowledge distillation, and the use of ScaledAdam optimizer. We validate our approach by comparing Supernet-trained versus individually tuned Multi-Head State Space Model (MH-SSM) RNN-T using LibriSpeech. Results demonstrate that our TODM Supernet either matches or surpasses the performance of manually tuned models by up to a relative of 3% better in word error rate (WER), while efficiently keeping the cost of training many models at a small constant.
LiCo-Net: Linearized Convolution Network for Hardware-efficient Keyword Spotting
Nov 09, 2022



Abstract:This paper proposes a hardware-efficient architecture, Linearized Convolution Network (LiCo-Net) for keyword spotting. It is optimized specifically for low-power processor units like microcontrollers. ML operators exhibit heterogeneous efficiency profiles on power-efficient hardware. Given the exact theoretical computation cost, int8 operators are more computation-effective than float operators, and linear layers are often more efficient than other layers. The proposed LiCo-Net is a dual-phase system that uses the efficient int8 linear operators at the inference phase and applies streaming convolutions at the training phase to maintain a high model capacity. The experimental results show that LiCo-Net outperforms single-value decomposition filter (SVDF) on hardware efficiency with on-par detection performance. Compared to SVDF, LiCo-Net reduces cycles by 40% on HiFi4 DSP.
SCA: Streaming Cross-attention Alignment for Echo Cancellation
Nov 01, 2022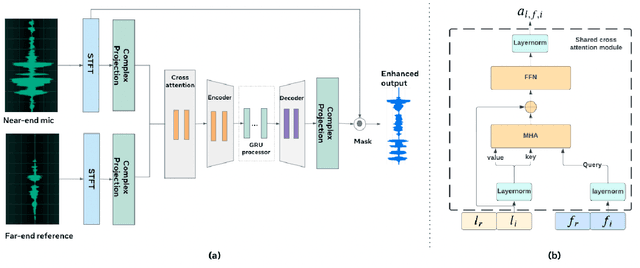
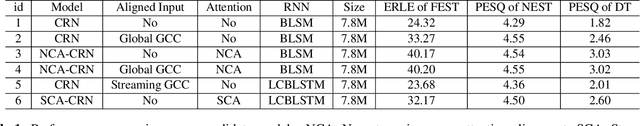
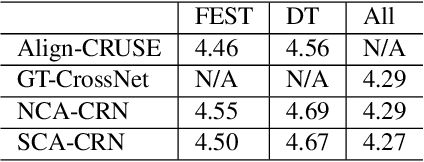
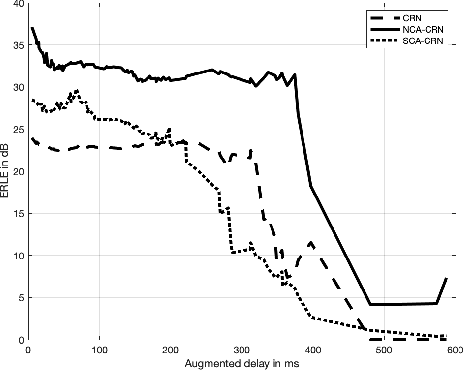
Abstract:End-to-End deep learning has shown promising results for speech enhancement tasks, such as noise suppression, dereverberation, and speech separation. However, most state-of-the-art methods for echo cancellation are either classical DSP-based or hybrid DSP-ML algorithms. Components such as the delay estimator and adaptive linear filter are based on traditional signal processing concepts, and deep learning algorithms typically only serve to replace the non-linear residual echo suppressor. This paper introduces an end-to-end echo cancellation network with a streaming cross-attention alignment (SCA). Our proposed method can handle unaligned inputs without requiring external alignment and generate high-quality speech without echoes. At the same time, the end-to-end algorithm simplifies the current echo cancellation pipeline for time-variant echo path cases. We test our proposed method on the ICASSP2022 and Interspeech2021 Microsoft deep echo cancellation challenge evaluation dataset, where our method outperforms some of the other hybrid and end-to-end methods.
U2++: Unified Two-pass Bidirectional End-to-end Model for Speech Recognition
Jul 07, 2021



Abstract:The unified streaming and non-streaming two-pass (U2) end-to-end model for speech recognition has shown great performance in terms of streaming capability, accuracy, real-time factor (RTF), and latency. In this paper, we present U2++, an enhanced version of U2 to further improve the accuracy. The core idea of U2++ is to use the forward and the backward information of the labeling sequences at the same time at training to learn richer information, and combine the forward and backward prediction at decoding to give more accurate recognition results. We also proposed a new data augmentation method called SpecSub to help the U2++ model to be more accurate and robust. Our experiments show that, compared with U2, U2++ shows faster convergence at training, better robustness to the decoding method, as well as consistent 5\% - 8\% word error rate reduction gain over U2. On the experiment of AISHELL-1, we achieve a 4.63\% character error rate (CER) with a non-streaming setup and 5.05\% with a streaming setup with 320ms latency by U2++. To the best of our knowledge, 5.05\% is the best-published streaming result on the AISHELL-1 test set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge