Xiangming Wang
HSI-VAR: Rethinking Hyperspectral Restoration through Spatial-Spectral Visual Autoregression
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Hyperspectral images (HSIs) capture richer spatial-spectral information beyond RGB, yet real-world HSIs often suffer from a composite mix of degradations, such as noise, blur, and missing bands. Existing generative approaches for HSI restoration like diffusion models require hundreds of iterative steps, making them computationally impractical for high-dimensional HSIs. While regression models tend to produce oversmoothed results, failing to preserve critical structural details. We break this impasse by introducing HSI-VAR, rethinking HSI restoration as an autoregressive generation problem, where spectral and spatial dependencies can be progressively modeled rather than globally reconstructed. HSI-VAR incorporates three key innovations: (1) Latent-condition alignment, which couples semantic consistency between latent priors and conditional embeddings for precise reconstruction; (2) Degradation-aware guidance, which uniquely encodes mixed degradations as linear combinations in the embedding space for automatic control, remarkably achieving a nearly $50\%$ reduction in computational cost at inference; (3) A spatial-spectral adaptation module that refines details across both domains in the decoding phase. Extensive experiments on nine all-in-one HSI restoration benchmarks confirm HSI-VAR's state-of-the-art performance, achieving a 3.77 dB PSNR improvement on \textbf{\textit{ICVL}} and offering superior structure preservation with an inference speed-up of up to $95.5 \times$ compared with diffusion-based methods, making it a highly practical solution for real-world HSI restoration.
Vision-Language Controlled Deep Unfolding for Joint Medical Image Restoration and Segmentation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We propose VL-DUN, a principled framework for joint All-in-One Medical Image Restoration and Segmentation (AiOMIRS) that bridges the gap between low-level signal recovery and high-level semantic understanding. While standard pipelines treat these tasks in isolation, our core insight is that they are fundamentally synergistic: restoration provides clean anatomical structures to improve segmentation, while semantic priors regularize the restoration process. VL-DUN resolves the sub-optimality of sequential processing through two primary innovations. (1) We formulate AiOMIRS as a unified optimization problem, deriving an interpretable joint unfolding mechanism where restoration and segmentation are mathematically coupled for mutual refinement. (2) We introduce a frequency-aware Mamba mechanism to capture long-range dependencies for global segmentation while preserving the high-frequency textures necessary for restoration. This allows for efficient global context modeling with linear complexity, effectively mitigating the spectral bias of standard architectures. As a pioneering work in the AiOMIRS task, VL-DUN establishes a new state-of-the-art across multi-modal benchmarks, improving PSNR by 0.92 dB and the Dice coefficient by 9.76\%. Our results demonstrate that joint collaborative learning offers a superior, more robust solution for complex clinical workflows compared to isolated task processing. The codes are provided in https://github.com/cipi666/VLDUN.
OTLRM: Orthogonal Learning-based Low-Rank Metric for Multi-Dimensional Inverse Problems
Dec 15, 2024

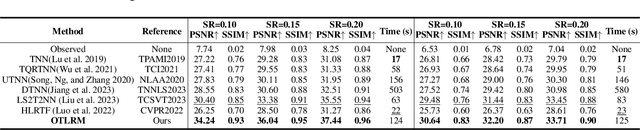

Abstract:In real-world scenarios, complex data such as multispectral images and multi-frame videos inherently exhibit robust low-rank property. This property is vital for multi-dimensional inverse problems, such as tensor completion, spectral imaging reconstruction, and multispectral image denoising. Existing tensor singular value decomposition (t-SVD) definitions rely on hand-designed or pre-given transforms, which lack flexibility for defining tensor nuclear norm (TNN). The TNN-regularized optimization problem is solved by the singular value thresholding (SVT) operator, which leverages the t-SVD framework to obtain the low-rank tensor. However, it is quite complicated to introduce SVT into deep neural networks due to the numerical instability problem in solving the derivatives of the eigenvectors. In this paper, we introduce a novel data-driven generative low-rank t-SVD model based on the learnable orthogonal transform, which can be naturally solved under its representation. Prompted by the linear algebra theorem of the Householder transformation, our learnable orthogonal transform is achieved by constructing an endogenously orthogonal matrix adaptable to neural networks, optimizing it as arbitrary orthogonal matrices. Additionally, we propose a low-rank solver as a generalization of SVT, which utilizes an efficient representation of generative networks to obtain low-rank structures. Extensive experiments highlight its significant restoration enhancements.
WeNet: Production First and Production Ready End-to-End Speech Recognition Toolkit
Feb 02, 2021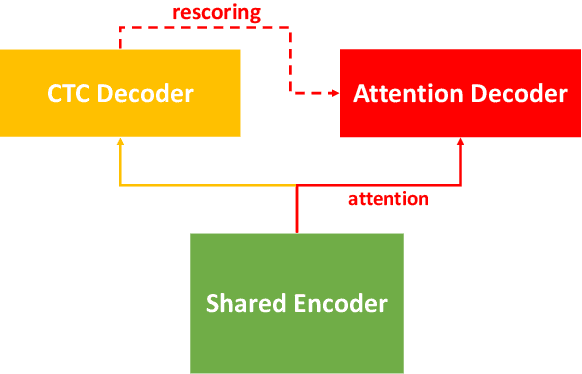
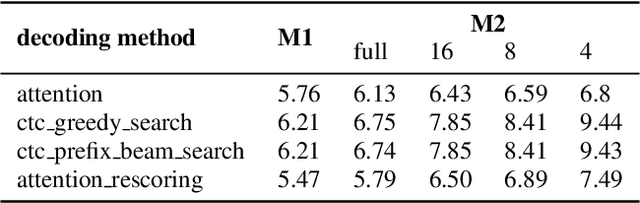
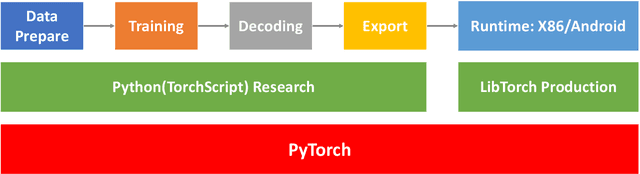
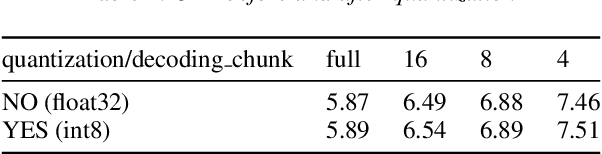
Abstract:In this paper, we present a new open source, production first and production ready end-to-end (E2E) speech recognition toolkit named WeNet. The main motivation of WeNet is to close the gap between the research and the production of E2E speech recognition models. WeNet provides an efficient way to ship ASR applications in several real-world scenarios, which is the main difference and advantage to other open source E2E speech recognition toolkits. This paper introduces WeNet from three aspects, including model architecture, framework design and performance metrics. Our experiments on AISHELL-1 using WeNet, not only give a promising character error rate (CER) on a unified streaming and non-streaming two pass (U2) E2E model but also show reasonable RTF and latency, both of these aspects are favored for production adoption. The toolkit is publicly available at https://github.com/mobvoi/wenet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge