Yungeng Liu
HSI-VAR: Rethinking Hyperspectral Restoration through Spatial-Spectral Visual Autoregression
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Hyperspectral images (HSIs) capture richer spatial-spectral information beyond RGB, yet real-world HSIs often suffer from a composite mix of degradations, such as noise, blur, and missing bands. Existing generative approaches for HSI restoration like diffusion models require hundreds of iterative steps, making them computationally impractical for high-dimensional HSIs. While regression models tend to produce oversmoothed results, failing to preserve critical structural details. We break this impasse by introducing HSI-VAR, rethinking HSI restoration as an autoregressive generation problem, where spectral and spatial dependencies can be progressively modeled rather than globally reconstructed. HSI-VAR incorporates three key innovations: (1) Latent-condition alignment, which couples semantic consistency between latent priors and conditional embeddings for precise reconstruction; (2) Degradation-aware guidance, which uniquely encodes mixed degradations as linear combinations in the embedding space for automatic control, remarkably achieving a nearly $50\%$ reduction in computational cost at inference; (3) A spatial-spectral adaptation module that refines details across both domains in the decoding phase. Extensive experiments on nine all-in-one HSI restoration benchmarks confirm HSI-VAR's state-of-the-art performance, achieving a 3.77 dB PSNR improvement on \textbf{\textit{ICVL}} and offering superior structure preservation with an inference speed-up of up to $95.5 \times$ compared with diffusion-based methods, making it a highly practical solution for real-world HSI restoration.
Vision-Language Controlled Deep Unfolding for Joint Medical Image Restoration and Segmentation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:We propose VL-DUN, a principled framework for joint All-in-One Medical Image Restoration and Segmentation (AiOMIRS) that bridges the gap between low-level signal recovery and high-level semantic understanding. While standard pipelines treat these tasks in isolation, our core insight is that they are fundamentally synergistic: restoration provides clean anatomical structures to improve segmentation, while semantic priors regularize the restoration process. VL-DUN resolves the sub-optimality of sequential processing through two primary innovations. (1) We formulate AiOMIRS as a unified optimization problem, deriving an interpretable joint unfolding mechanism where restoration and segmentation are mathematically coupled for mutual refinement. (2) We introduce a frequency-aware Mamba mechanism to capture long-range dependencies for global segmentation while preserving the high-frequency textures necessary for restoration. This allows for efficient global context modeling with linear complexity, effectively mitigating the spectral bias of standard architectures. As a pioneering work in the AiOMIRS task, VL-DUN establishes a new state-of-the-art across multi-modal benchmarks, improving PSNR by 0.92 dB and the Dice coefficient by 9.76\%. Our results demonstrate that joint collaborative learning offers a superior, more robust solution for complex clinical workflows compared to isolated task processing. The codes are provided in https://github.com/cipi666/VLDUN.
TourSynbio: A Multi-Modal Large Model and Agent Framework to Bridge Text and Protein Sequences for Protein Engineering
Aug 27, 2024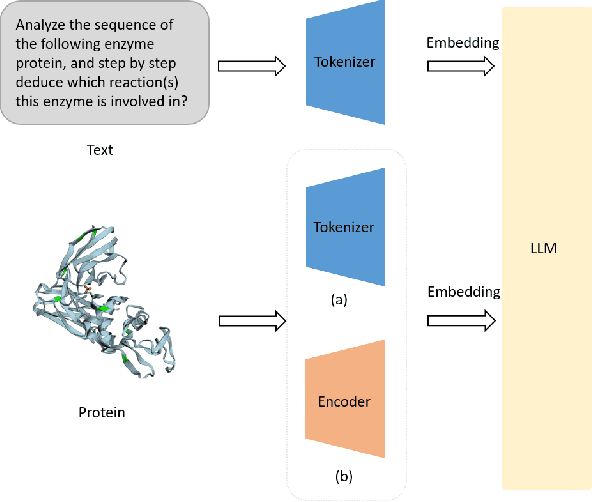
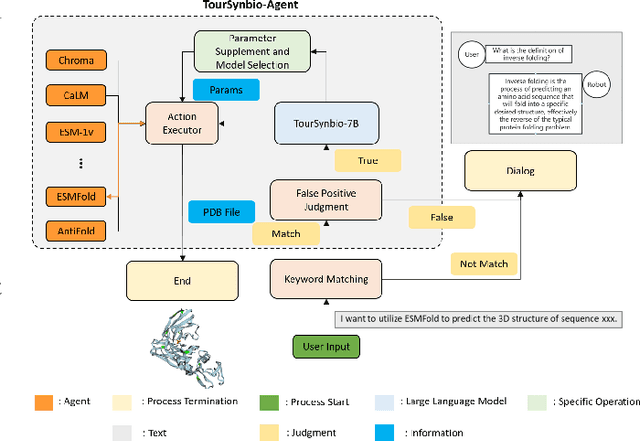
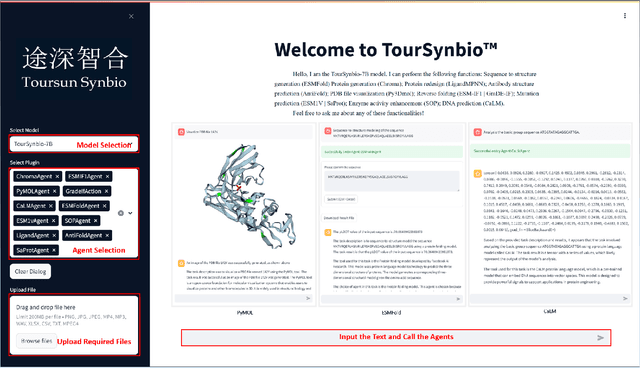
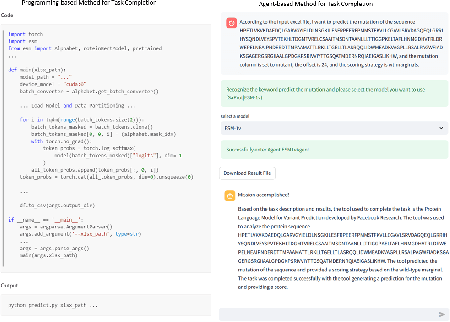
Abstract:The structural similarities between protein sequences and natural languages have led to parallel advancements in deep learning across both domains. While large language models (LLMs) have achieved much progress in the domain of natural language processing, their potential in protein engineering remains largely unexplored. Previous approaches have equipped LLMs with protein understanding capabilities by incorporating external protein encoders, but this fails to fully leverage the inherent similarities between protein sequences and natural languages, resulting in sub-optimal performance and increased model complexity. To address this gap, we present TourSynbio-7B, the first multi-modal large model specifically designed for protein engineering tasks without external protein encoders. TourSynbio-7B demonstrates that LLMs can inherently learn to understand proteins as language. The model is post-trained and instruction fine-tuned on InternLM2-7B using ProteinLMDataset, a dataset comprising 17.46 billion tokens of text and protein sequence for self-supervised pretraining and 893K instructions for supervised fine-tuning. TourSynbio-7B outperforms GPT-4 on the ProteinLMBench, a benchmark of 944 manually verified multiple-choice questions, with 62.18% accuracy. Leveraging TourSynbio-7B's enhanced protein sequence understanding capability, we introduce TourSynbio-Agent, an innovative framework capable of performing various protein engineering tasks, including mutation analysis, inverse folding, protein folding, and visualization. TourSynbio-Agent integrates previously disconnected deep learning models in the protein engineering domain, offering a unified conversational user interface for improved usability. Finally, we demonstrate the efficacy of TourSynbio-7B and TourSynbio-Agent through two wet lab case studies on vanilla key enzyme modification and steroid compound catalysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge