Trung Pham
Marginalized Generalized IoU (MGIoU): A Unified Objective Function for Optimizing Any Convex Parametric Shapes
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Optimizing the similarity between parametric shapes is crucial for numerous computer vision tasks, where Intersection over Union (IoU) stands as the canonical measure. However, existing optimization methods exhibit significant shortcomings: regression-based losses like L1/L2 lack correlation with IoU, IoU-based losses are unstable and limited to simple shapes, and task-specific methods are computationally intensive and not generalizable accross domains. As a result, the current landscape of parametric shape objective functions has become scattered, with each domain proposing distinct IoU approximations. To address this, we unify the parametric shape optimization objective functions by introducing Marginalized Generalized IoU (MGIoU), a novel loss function that overcomes these challenges by projecting structured convex shapes onto their unique shape Normals to compute one-dimensional normalized GIoU. MGIoU offers a simple, efficient, fully differentiable approximation strongly correlated with IoU. We then extend MGIoU to MGIoU+ that supports optimizing unstructured convex shapes. Together, MGIoU and MGIoU+ unify parametric shape optimization across diverse applications. Experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that MGIoU and MGIoU+ consistently outperform existing losses while reducing loss computation latency by 10-40x. Additionally, MGIoU and MGIoU+ satisfy metric properties and scale-invariance, ensuring robustness as an objective function. We further propose MGIoU- for minimizing overlaps in tasks like collision-free trajectory prediction. Code is available at https://ldtho.github.io/MGIoU
DimCL: Dimensional Contrastive Learning For Improving Self-Supervised Learning
Sep 21, 2023Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has gained remarkable success, for which contrastive learning (CL) plays a key role. However, the recent development of new non-CL frameworks has achieved comparable or better performance with high improvement potential, prompting researchers to enhance these frameworks further. Assimilating CL into non-CL frameworks has been thought to be beneficial, but empirical evidence indicates no visible improvements. In view of that, this paper proposes a strategy of performing CL along the dimensional direction instead of along the batch direction as done in conventional contrastive learning, named Dimensional Contrastive Learning (DimCL). DimCL aims to enhance the feature diversity, and it can serve as a regularizer to prior SSL frameworks. DimCL has been found to be effective, and the hardness-aware property is identified as a critical reason for its success. Extensive experimental results reveal that assimilating DimCL into SSL frameworks leads to performance improvement by a non-trivial margin on various datasets and backbone architectures.
DPPD: Deformable Polar Polygon Object Detection
Apr 05, 2023Abstract:Regular object detection methods output rectangle bounding boxes, which are unable to accurately describe the actual object shapes. Instance segmentation methods output pixel-level labels, which are computationally expensive for real-time applications. Therefore, a polygon representation is needed to achieve precise shape alignment, while retaining low computation cost. We develop a novel Deformable Polar Polygon Object Detection method (DPPD) to detect objects in polygon shapes. In particular, our network predicts, for each object, a sparse set of flexible vertices to construct the polygon, where each vertex is represented by a pair of angle and distance in the Polar coordinate system. To enable training, both ground truth and predicted polygons are densely resampled to have the same number of vertices with equal-spaced raypoints. The resampling operation is fully differentable, allowing gradient back-propagation. Sparse polygon predicton ensures high-speed runtime inference while dense resampling allows the network to learn object shapes with high precision. The polygon detection head is established on top of an anchor-free and NMS-free network architecture. DPPD has been demonstrated successfully in various object detection tasks for autonomous driving such as traffic-sign, crosswalk, vehicle and pedestrian objects.
NVAutoNet: Fast and Accurate 360$^{\circ}$ 3D Visual Perception For Self Driving
Mar 30, 2023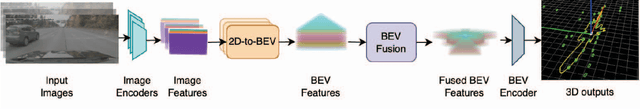
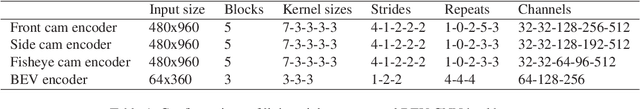
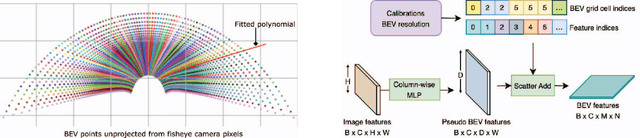
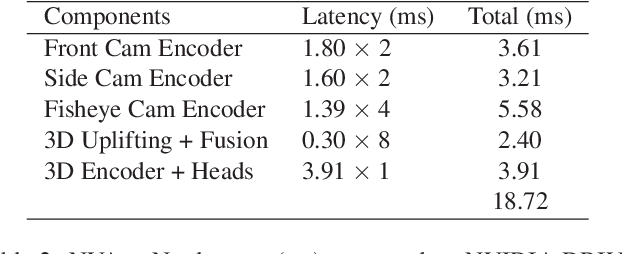
Abstract:Robust real-time perception of 3D world is essential to the autonomous vehicle. We introduce an end-to-end surround camera perception system for self-driving. Our perception system is a novel multi-task, multi-camera network which takes a variable set of time-synced camera images as input and produces a rich collection of 3D signals such as sizes, orientations, locations of obstacles, parking spaces and free-spaces, etc. Our perception network is modular and end-to-end: 1) the outputs can be consumed directly by downstream modules without any post-processing such as clustering and fusion -- improving speed of model deployment and in-car testing 2) the whole network training is done in one single stage -- improving speed of model improvement and iterations. The network is well designed to have high accuracy while running at 53 fps on NVIDIA Orin SoC (system-on-a-chip). The network is robust to sensor mounting variations (within some tolerances) and can be quickly customized for different vehicle types via efficient model fine-tuning thanks of its capability of taking calibration parameters as additional inputs during training and testing. Most importantly, our network has been successfully deployed and being tested on real roads.
On the Pros and Cons of Momentum Encoder in Self-Supervised Visual Representation Learning
Aug 11, 2022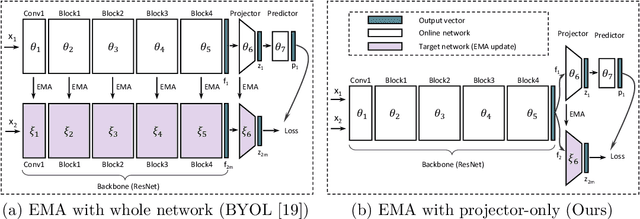
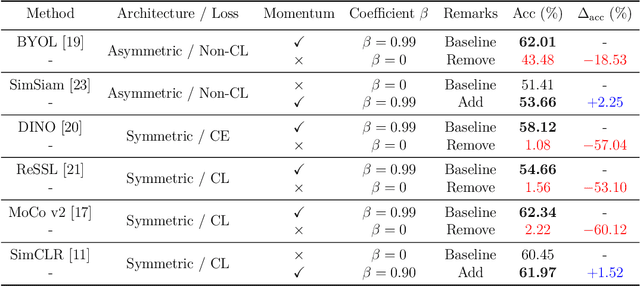
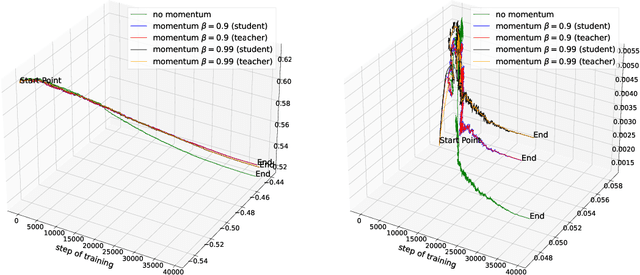
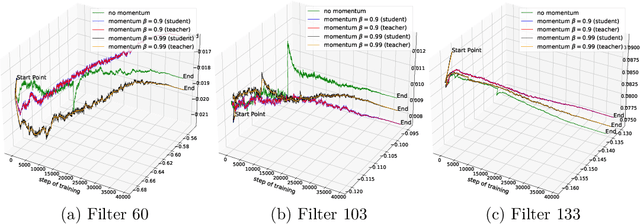
Abstract:Exponential Moving Average (EMA or momentum) is widely used in modern self-supervised learning (SSL) approaches, such as MoCo, for enhancing performance. We demonstrate that such momentum can also be plugged into momentum-free SSL frameworks, such as SimCLR, for a performance boost. Despite its wide use as a fundamental component in modern SSL frameworks, the benefit caused by momentum is not well understood. We find that its success can be at least partly attributed to the stability effect. In the first attempt, we analyze how EMA affects each part of the encoder and reveal that the portion near the encoder's input plays an insignificant role while the latter parts have much more influence. By monitoring the gradient of the overall loss with respect to the output of each block in the encoder, we observe that the final layers tend to fluctuate much more than other layers during backpropagation, i.e. less stability. Interestingly, we show that using EMA to the final part of the SSL encoder, i.e. projector, instead of the whole deep network encoder can give comparable or preferable performance. Our proposed projector-only momentum helps maintain the benefit of EMA but avoids the double forward computation.
Robust MAML: Prioritization task buffer with adaptive learning process for model-agnostic meta-learning
Mar 15, 2021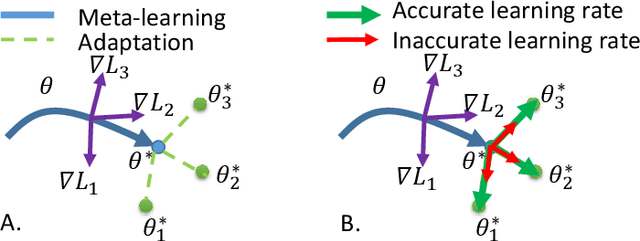
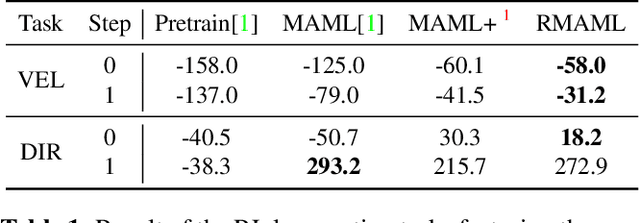
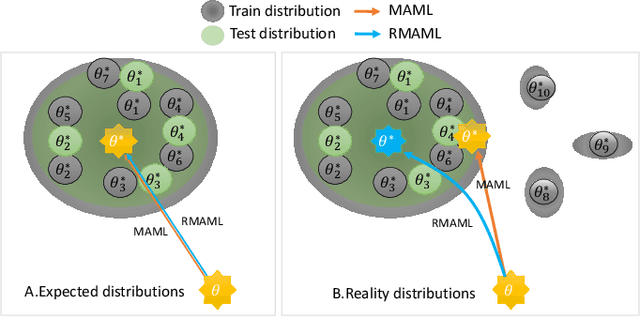
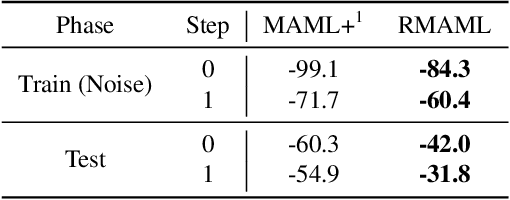
Abstract:Model agnostic meta-learning (MAML) is a popular state-of-the-art meta-learning algorithm that provides good weight initialization of a model given a variety of learning tasks. The model initialized by provided weight can be fine-tuned to an unseen task despite only using a small amount of samples and within a few adaptation steps. MAML is simple and versatile but requires costly learning rate tuning and careful design of the task distribution which affects its scalability and generalization. This paper proposes a more robust MAML based on an adaptive learning scheme and a prioritization task buffer(PTB) referred to as Robust MAML (RMAML) for improving scalability of training process and alleviating the problem of distribution mismatch. RMAML uses gradient-based hyper-parameter optimization to automatically find the optimal learning rate and uses the PTB to gradually adjust train-ing task distribution toward testing task distribution over the course of training. Experimental results on meta reinforcement learning environments demonstrate a substantial performance gain as well as being less sensitive to hyper-parameter choice and robust to distribution mismatch.
Modality Shifting Attention Network for Multi-modal Video Question Answering
Jul 04, 2020
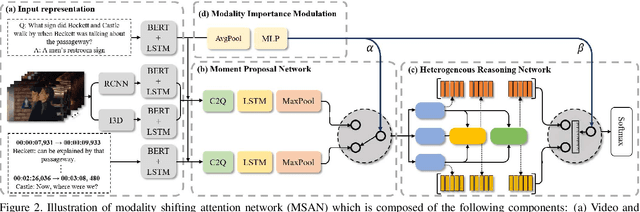
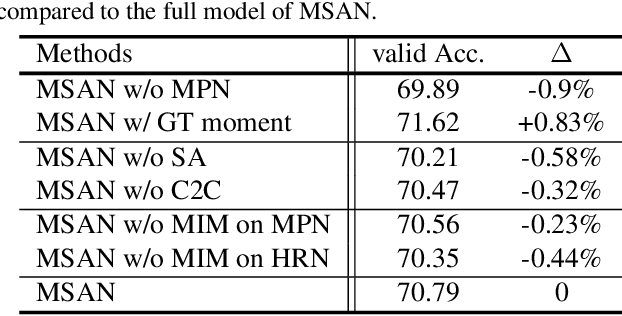
Abstract:This paper considers a network referred to as Modality Shifting Attention Network (MSAN) for Multimodal Video Question Answering (MVQA) task. MSAN decomposes the task into two sub-tasks: (1) localization of temporal moment relevant to the question, and (2) accurate prediction of the answer based on the localized moment. The modality required for temporal localization may be different from that for answer prediction, and this ability to shift modality is essential for performing the task. To this end, MSAN is based on (1) the moment proposal network (MPN) that attempts to locate the most appropriate temporal moment from each of the modalities, and also on (2) the heterogeneous reasoning network (HRN) that predicts the answer using an attention mechanism on both modalities. MSAN is able to place importance weight on the two modalities for each sub-task using a component referred to as Modality Importance Modulation (MIM). Experimental results show that MSAN outperforms previous state-of-the-art by achieving 71.13\% test accuracy on TVQA benchmark dataset. Extensive ablation studies and qualitative analysis are conducted to validate various components of the network.
Structure Aware SLAM using Quadrics and Planes
Nov 02, 2018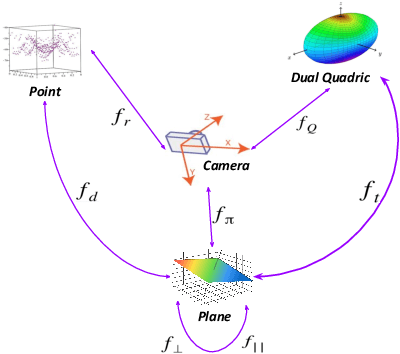
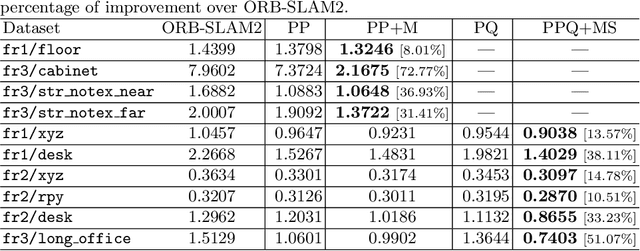
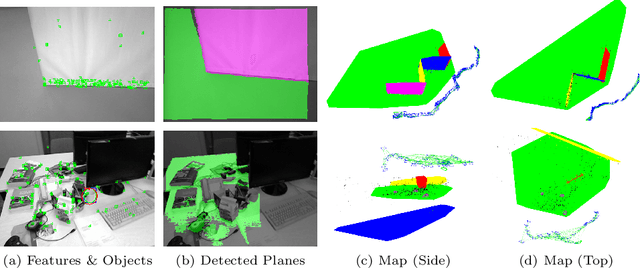
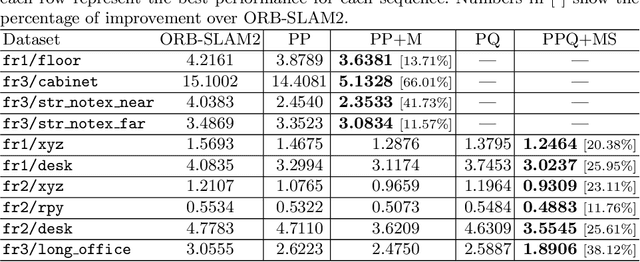
Abstract:Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) is a fundamental problem in mobile robotics. While point-based SLAM methods provide accurate camera localization, the generated maps lack semantic information. On the other hand, state of the art object detection methods provide rich information about entities present in the scene from a single image. This work marries the two and proposes a method for representing generic objects as quadrics which allows object detections to be seamlessly integrated in a SLAM framework. For scene coverage, additional dominant planar structures are modeled as infinite planes. Experiments show that the proposed points-planes-quadrics representation can easily incorporate Manhattan and object affordance constraints, greatly improving camera localization and leading to semantically meaningful maps. The performance of our SLAM system is demonstrated in https://youtu.be/dR-rB9keF8M .
Binary Constrained Deep Hashing Network for Image Retrieval without Manual Annotation
Aug 02, 2018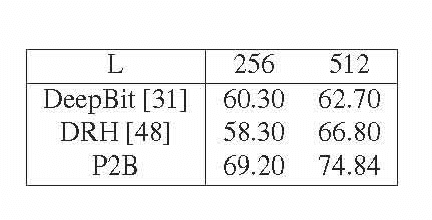
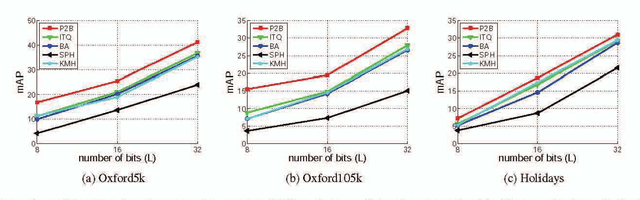
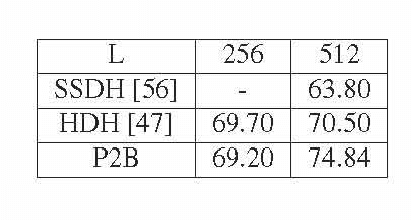
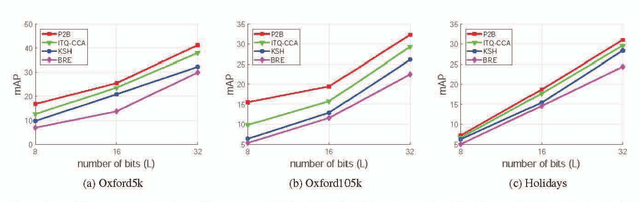
Abstract:Learning compact binary codes for image retrieval problem using deep neural networks has attracted increasing attention recently. However, training deep hashing networks is challenging due to the binary constraints on the hash codes, the similarity preserving property, and the requirement for a vast amount of labelled images. To the best of our knowledge, none of the existing methods has tackled all of these challenges completely in a unified framework. In this work, we propose a novel end-to-end deep hashing approach, which is trained to produce binary codes directly from image pixels without the need of manual annotation. In particular, we propose a novel pairwise binary constrained loss function, which simultaneously encodes the distances between pairs of hash codes, and the binary quantization error. In order to train the network with the proposed loss function, we also propose an efficient parameter learning algorithm. In addition, to provide similar/dissimilar training images to train the network, we exploit 3D models reconstructed from unlabelled images for automatic generation of enormous similar/dissimilar pairs. Extensive experiments on three image retrieval benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method over the state-of-the-art hashing methods on the image retrieval problem.
Bayesian Semantic Instance Segmentation in Open Set World
Jul 30, 2018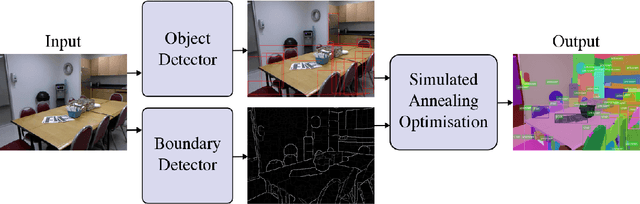
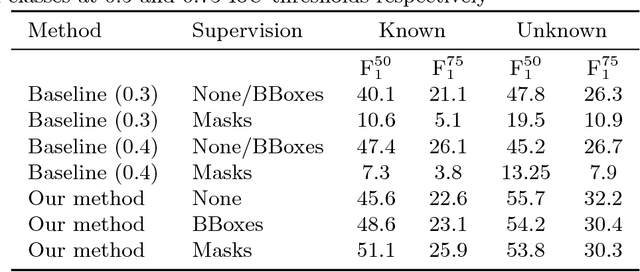
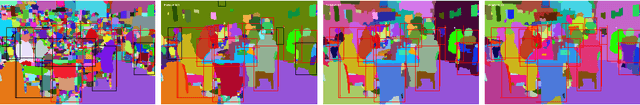

Abstract:This paper addresses the semantic instance segmentation task in the open-set conditions, where input images can contain known and unknown object classes. The training process of existing semantic instance segmentation methods requires annotation masks for all object instances, which is expensive to acquire or even infeasible in some realistic scenarios, where the number of categories may increase boundlessly. In this paper, we present a novel open-set semantic instance segmentation approach capable of segmenting all known and unknown object classes in images, based on the output of an object detector trained on known object classes. We formulate the problem using a Bayesian framework, where the posterior distribution is approximated with a simulated annealing optimization equipped with an efficient image partition sampler. We show empirically that our method is competitive with state-of-the-art supervised methods on known classes, but also performs well on unknown classes when compared with unsupervised methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge