Junyeong Kim
See More, Store Less: Memory-Efficient Resolution for Video Moment Retrieval
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have improved image recognition and reasoning, but video-related tasks remain challenging due to memory constraints from dense frame processing. Existing Video Moment Retrieval (VMR) methodologies rely on sparse frame sampling, risking potential information loss, especially in lengthy videos. We propose SMORE (See MORE, store less), a framework that enhances memory efficiency while maintaining high information resolution. SMORE (1) uses query-guided captions to encode semantics aligned with user intent, (2) applies query-aware importance modulation to highlight relevant segments, and (3) adaptively compresses frames to preserve key content while reducing redundancy. This enables efficient video understanding without exceeding memory budgets. Experimental validation reveals that SMORE achieves state-of-the-art performance on QVHighlights, Charades-STA, and ActivityNet-Captions benchmarks.
Language-Grounded Multi-Domain Image Translation via Semantic Difference Guidance
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Multi-domain image-to-image translation re quires grounding semantic differences ex pressed in natural language prompts into corresponding visual transformations, while preserving unrelated structural and seman tic content. Existing methods struggle to maintain structural integrity and provide fine grained, attribute-specific control, especially when multiple domains are involved. We propose LACE (Language-grounded Attribute Controllable Translation), built on two compo nents: (1) a GLIP-Adapter that fuses global semantics with local structural features to pre serve consistency, and (2) a Multi-Domain Control Guidance mechanism that explicitly grounds the semantic delta between source and target prompts into per-attribute translation vec tors, aligning linguistic semantics with domain level visual changes. Together, these modules enable compositional multi-domain control with independent strength modulation for each attribute. Experiments on CelebA(Dialog) and BDD100K demonstrate that LACE achieves high visual fidelity, structural preservation, and interpretable domain-specific control, surpass ing prior baselines. This positions LACE as a cross-modal content generation framework bridging language semantics and controllable visual translation.
Visual Funnel: Resolving Contextual Blindness in Multimodal Large Language Models
Dec 11, 2025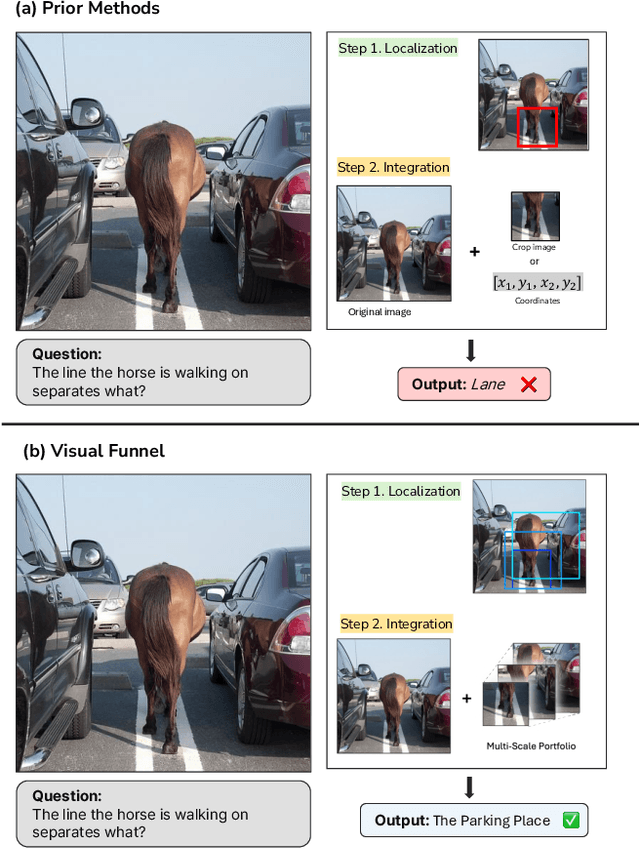
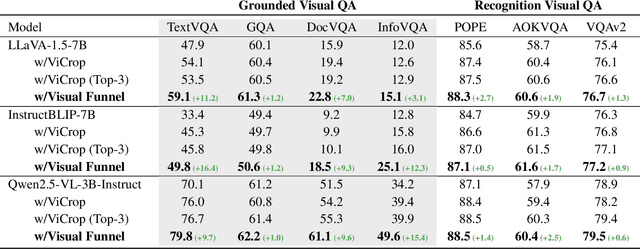
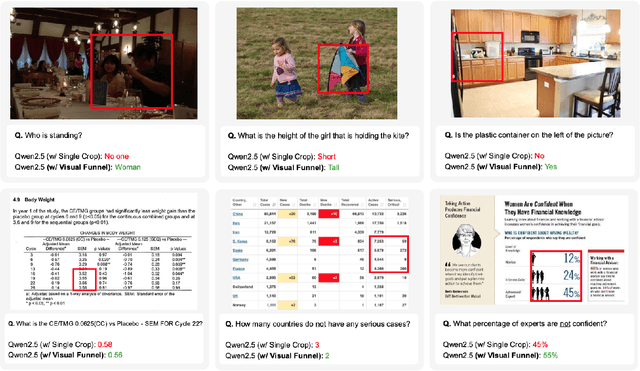
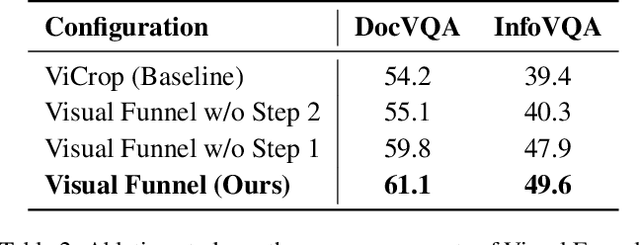
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate impressive reasoning capabilities, but often fail to perceive fine-grained visual details, limiting their applicability in precision-demanding tasks. While methods that crop salient regions of an image offer a partial solution, we identify a critical limitation they introduce: "Contextual Blindness". This failure occurs due to structural disconnect between high-fidelity details (from the crop) and the broader global context (from the original image), even when all necessary visual information is present. We argue that this limitation stems not from a lack of information 'Quantity', but from a lack of 'Structural Diversity' in the model's input. To resolve this, we propose Visual Funnel, a training-free, two-step approach. Visual Funnel first performs Contextual Anchoring to identify the region of interest in a single forward pass. It then constructs an Entropy-Scaled Portfolio that preserves the hierarchical context - ranging from focal detail to broader surroundings - by dynamically determining crop sizes based on attention entropy and refining crop centers. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that Visual Funnel significantly outperforms naive single-crop and unstructured multi-crop baselines. Our results further validate that simply adding more unstructured crops provides limited or even detrimental benefits, confirming that the hierarchical structure of our portfolio is key to resolving Contextual Blindness.
Synergy-CLIP: Extending CLIP with Multi-modal Integration for Robust Representation Learning
Apr 30, 2025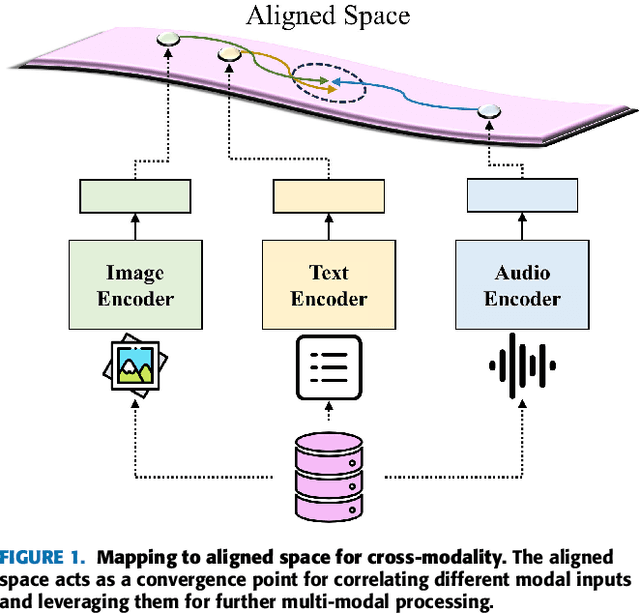
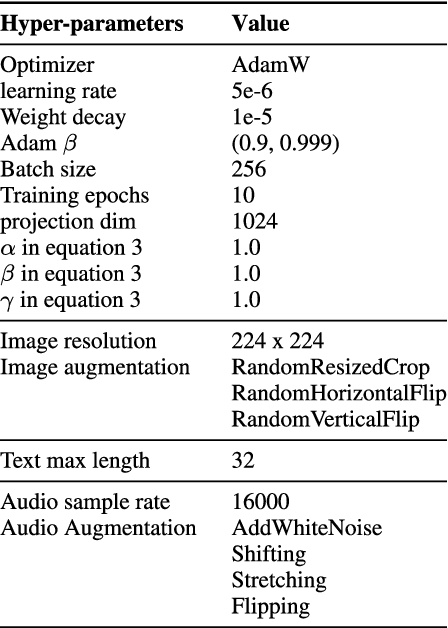

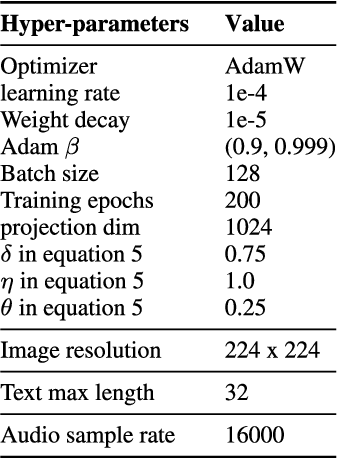
Abstract:Multi-modal representation learning has become a pivotal area in artificial intelligence, enabling the integration of diverse modalities such as vision, text, and audio to solve complex problems. However, existing approaches predominantly focus on bimodal interactions, such as image-text pairs, which limits their ability to fully exploit the richness of multi-modal data. Furthermore, the integration of modalities in equal-scale environments remains underexplored due to the challenges of constructing large-scale, balanced datasets. In this study, we propose Synergy-CLIP, a novel framework that extends the contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) architecture to enhance multi-modal representation learning by integrating visual, textual, and audio modalities. Unlike existing methods that focus on adapting individual modalities to vanilla-CLIP, Synergy-CLIP aligns and captures latent information across three modalities equally. To address the high cost of constructing large-scale multi-modal datasets, we introduce VGG-sound+, a triple-modal dataset designed to provide equal-scale representation of visual, textual, and audio data. Synergy-CLIP is validated on various downstream tasks, including zero-shot classification, where it outperforms existing baselines. Additionally, we introduce a missing modality reconstruction task, demonstrating Synergy-CLIP's ability to extract synergy among modalities in realistic application scenarios. These contributions provide a robust foundation for advancing multi-modal representation learning and exploring new research directions.
BioBridge: Unified Bio-Embedding with Bridging Modality in Code-Switched EMR
Dec 16, 2024
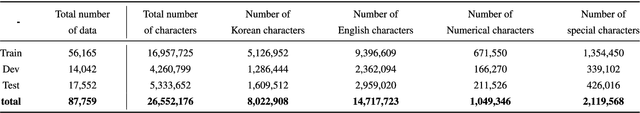
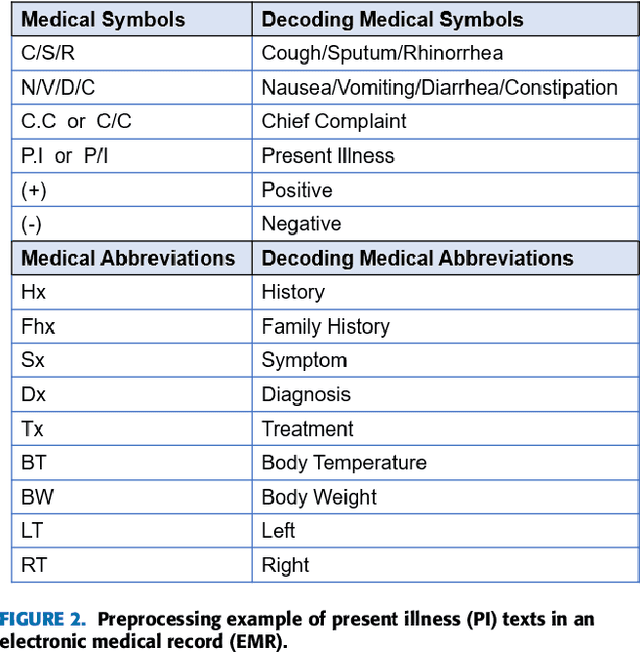
Abstract:Pediatric Emergency Department (PED) overcrowding presents a significant global challenge, prompting the need for efficient solutions. This paper introduces the BioBridge framework, a novel approach that applies Natural Language Processing (NLP) to Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) in written free-text form to enhance decision-making in PED. In non-English speaking countries, such as South Korea, EMR data is often written in a Code-Switching (CS) format that mixes the native language with English, with most code-switched English words having clinical significance. The BioBridge framework consists of two core modules: "bridging modality in context" and "unified bio-embedding." The "bridging modality in context" module improves the contextual understanding of bilingual and code-switched EMRs. In the "unified bio-embedding" module, the knowledge of the model trained in the medical domain is injected into the encoder-based model to bridge the gap between the medical and general domains. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed BioBridge significantly performance traditional machine learning and pre-trained encoder-based models on several metrics, including F1 score, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC), area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC), and Brier score. Specifically, BioBridge-XLM achieved enhancements of 0.85% in F1 score, 0.75% in AUROC, and 0.76% in AUPRC, along with a notable 3.04% decrease in the Brier score, demonstrating marked improvements in accuracy, reliability, and prediction calibration over the baseline XLM model. The source code will be made publicly available.
* Accepted at IEEE Access 2024
Zero-Shot Dual-Path Integration Framework for Open-Vocabulary 3D Instance Segmentation
Aug 16, 2024
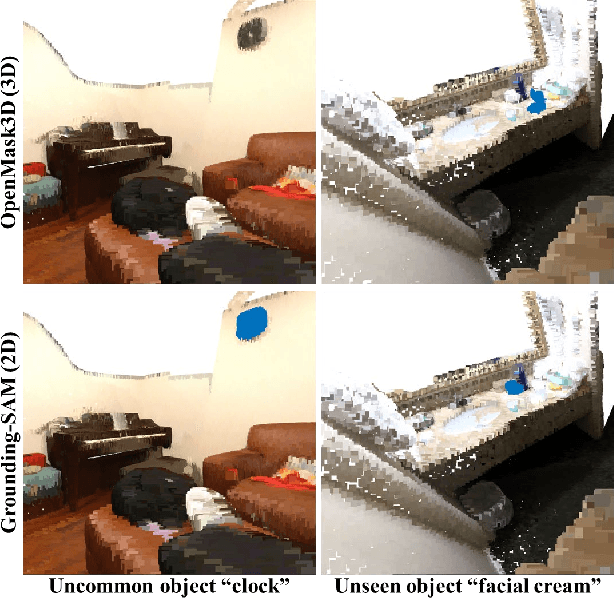

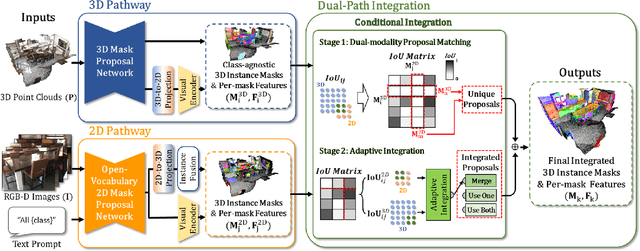
Abstract:Open-vocabulary 3D instance segmentation transcends traditional closed-vocabulary methods by enabling the identification of both previously seen and unseen objects in real-world scenarios. It leverages a dual-modality approach, utilizing both 3D point clouds and 2D multi-view images to generate class-agnostic object mask proposals. Previous efforts predominantly focused on enhancing 3D mask proposal models; consequently, the information that could come from 2D association to 3D was not fully exploited. This bias towards 3D data, while effective for familiar indoor objects, limits the system's adaptability to new and varied object types, where 2D models offer greater utility. Addressing this gap, we introduce Zero-Shot Dual-Path Integration Framework that equally values the contributions of both 3D and 2D modalities. Our framework comprises three components: 3D pathway, 2D pathway, and Dual-Path Integration. 3D pathway generates spatially accurate class-agnostic mask proposals of common indoor objects from 3D point cloud data using a pre-trained 3D model, while 2D pathway utilizes pre-trained open-vocabulary instance segmentation model to identify a diverse array of object proposals from multi-view RGB-D images. In Dual-Path Integration, our Conditional Integration process, which operates in two stages, filters and merges the proposals from both pathways adaptively. This process harmonizes output proposals to enhance segmentation capabilities. Our framework, utilizing pre-trained models in a zero-shot manner, is model-agnostic and demonstrates superior performance on both seen and unseen data, as evidenced by comprehensive evaluations on the ScanNet200 and qualitative results on ARKitScenes datasets.
HEAR: Hearing Enhanced Audio Response for Video-grounded Dialogue
Dec 15, 2023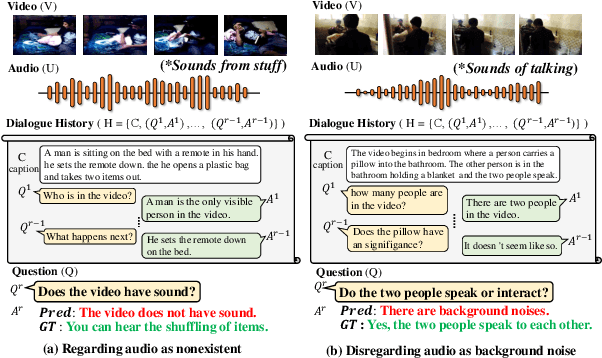
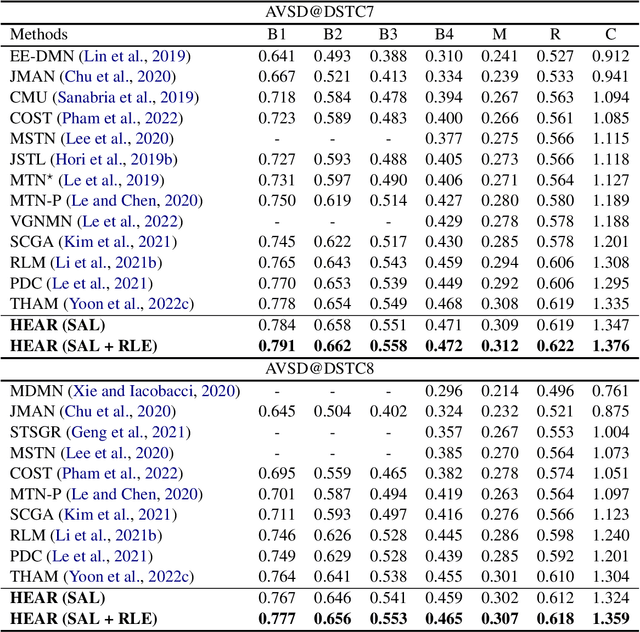
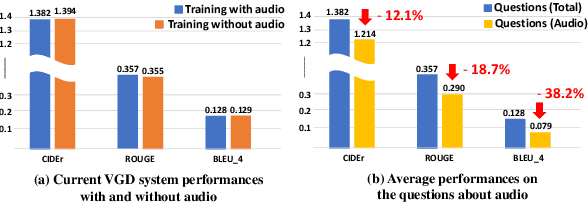

Abstract:Video-grounded Dialogue (VGD) aims to answer questions regarding a given multi-modal input comprising video, audio, and dialogue history. Although there have been numerous efforts in developing VGD systems to improve the quality of their responses, existing systems are competent only to incorporate the information in the video and text and tend to struggle in extracting the necessary information from the audio when generating appropriate responses to the question. The VGD system seems to be deaf, and thus, we coin this symptom of current systems' ignoring audio data as a deaf response. To overcome the deaf response problem, Hearing Enhanced Audio Response (HEAR) framework is proposed to perform sensible listening by selectively attending to audio whenever the question requires it. The HEAR framework enhances the accuracy and audibility of VGD systems in a model-agnostic manner. HEAR is validated on VGD datasets (i.e., AVSD@DSTC7 and AVSD@DSTC8) and shows effectiveness with various VGD systems.
Information-Theoretic Text Hallucination Reduction for Video-grounded Dialogue
Dec 12, 2022
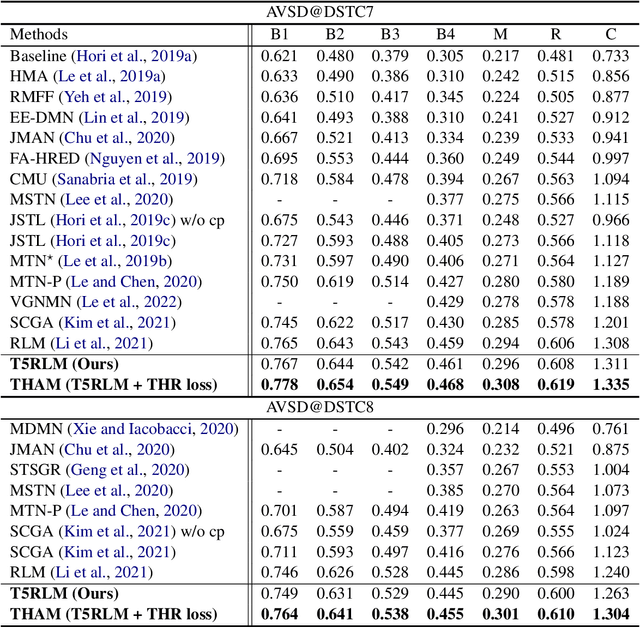


Abstract:Video-grounded Dialogue (VGD) aims to decode an answer sentence to a question regarding a given video and dialogue context. Despite the recent success of multi-modal reasoning to generate answer sentences, existing dialogue systems still suffer from a text hallucination problem, which denotes indiscriminate text-copying from input texts without an understanding of the question. This is due to learning spurious correlations from the fact that answer sentences in the dataset usually include the words of input texts, thus the VGD system excessively relies on copying words from input texts by hoping those words to overlap with ground-truth texts. Hence, we design Text Hallucination Mitigating (THAM) framework, which incorporates Text Hallucination Regularization (THR) loss derived from the proposed information-theoretic text hallucination measurement approach. Applying THAM with current dialogue systems validates the effectiveness on VGD benchmarks (i.e., AVSD@DSTC7 and AVSD@DSTC8) and shows enhanced interpretability.
Selective Query-guided Debiasing Network for Video Corpus Moment Retrieval
Oct 17, 2022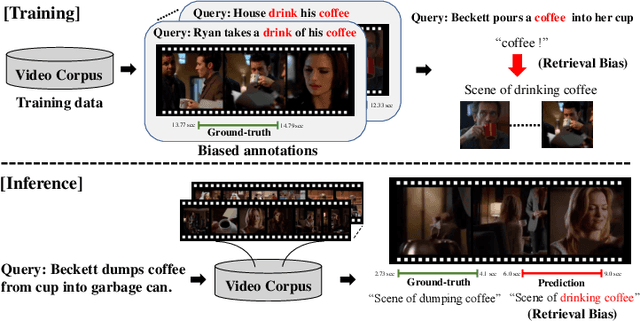
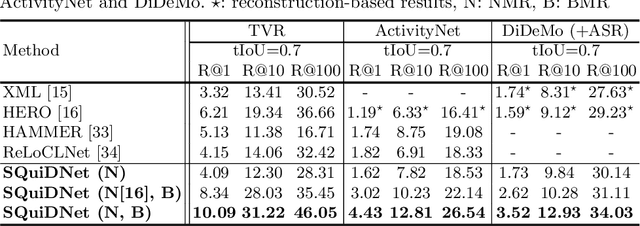
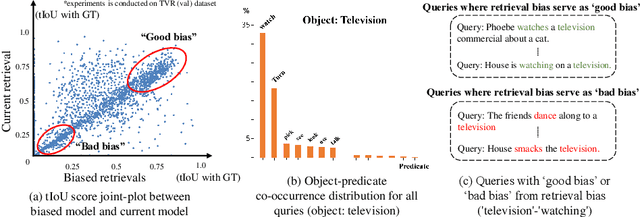
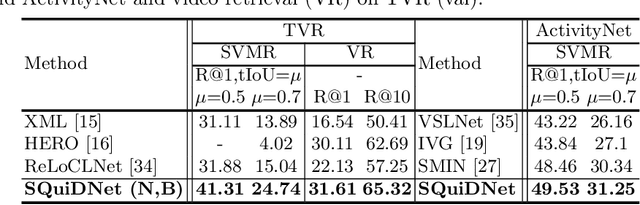
Abstract:Video moment retrieval (VMR) aims to localize target moments in untrimmed videos pertinent to a given textual query. Existing retrieval systems tend to rely on retrieval bias as a shortcut and thus, fail to sufficiently learn multi-modal interactions between query and video. This retrieval bias stems from learning frequent co-occurrence patterns between query and moments, which spuriously correlate objects (e.g., a pencil) referred in the query with moments (e.g., scene of writing with a pencil) where the objects frequently appear in the video, such that they converge into biased moment predictions. Although recent debiasing methods have focused on removing this retrieval bias, we argue that these biased predictions sometimes should be preserved because there are many queries where biased predictions are rather helpful. To conjugate this retrieval bias, we propose a Selective Query-guided Debiasing network (SQuiDNet), which incorporates the following two main properties: (1) Biased Moment Retrieval that intentionally uncovers the biased moments inherent in objects of the query and (2) Selective Query-guided Debiasing that performs selective debiasing guided by the meaning of the query. Our experimental results on three moment retrieval benchmarks (i.e., TVR, ActivityNet, DiDeMo) show the effectiveness of SQuiDNet and qualitative analysis shows improved interpretability.
SoftGroup++: Scalable 3D Instance Segmentation with Octree Pyramid Grouping
Sep 17, 2022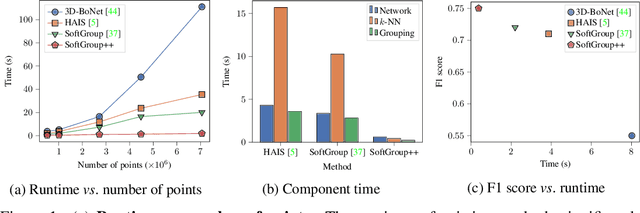
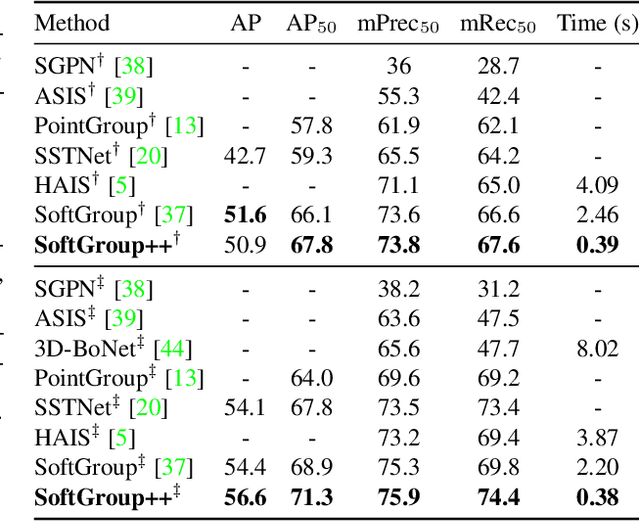
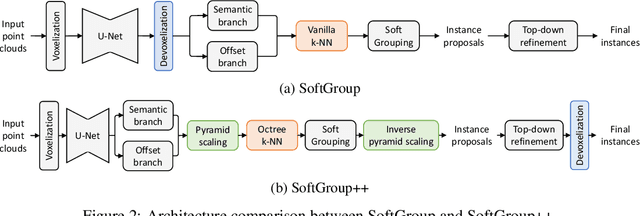
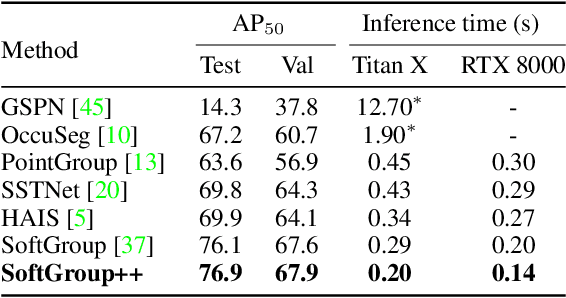
Abstract:Existing state-of-the-art 3D point cloud instance segmentation methods rely on a grouping-based approach that groups points to obtain object instances. Despite improvement in producing accurate segmentation results, these methods lack scalability and commonly require dividing large input into multiple parts. To process a scene with millions of points, the existing fastest method SoftGroup \cite{vu2022softgroup} requires tens of seconds, which is under satisfaction. Our finding is that $k$-Nearest Neighbor ($k$-NN), which serves as the prerequisite of grouping, is a computational bottleneck. This bottleneck severely worsens the inference time in the scene with a large number of points. This paper proposes SoftGroup++ to address this computational bottleneck and further optimize the inference speed of the whole network. SoftGroup++ is built upon SoftGroup, which differs in three important aspects: (1) performs octree $k$-NN instead of vanilla $k$-NN to reduce time complexity from $\mathcal{O}(n^2)$ to $\mathcal{O}(n \log n)$, (2) performs pyramid scaling that adaptively downsamples backbone outputs to reduce search space for $k$-NN and grouping, and (3) performs late devoxelization that delays the conversion from voxels to points towards the end of the model such that intermediate components operate at a low computational cost. Extensive experiments on various indoor and outdoor datasets demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed SoftGroup++. Notably, SoftGroup++ processes large scenes of millions of points by a single forward without dividing the input into multiple parts, thus enriching contextual information. Especially, SoftGroup++ achieves 2.4 points AP$_{50}$ improvement while nearly $6\times$ faster than the existing fastest method on S3DIS dataset. The code and trained models will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge