Sunjae Yoon
Language-Grounded Multi-Domain Image Translation via Semantic Difference Guidance
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Multi-domain image-to-image translation re quires grounding semantic differences ex pressed in natural language prompts into corresponding visual transformations, while preserving unrelated structural and seman tic content. Existing methods struggle to maintain structural integrity and provide fine grained, attribute-specific control, especially when multiple domains are involved. We propose LACE (Language-grounded Attribute Controllable Translation), built on two compo nents: (1) a GLIP-Adapter that fuses global semantics with local structural features to pre serve consistency, and (2) a Multi-Domain Control Guidance mechanism that explicitly grounds the semantic delta between source and target prompts into per-attribute translation vec tors, aligning linguistic semantics with domain level visual changes. Together, these modules enable compositional multi-domain control with independent strength modulation for each attribute. Experiments on CelebA(Dialog) and BDD100K demonstrate that LACE achieves high visual fidelity, structural preservation, and interpretable domain-specific control, surpass ing prior baselines. This positions LACE as a cross-modal content generation framework bridging language semantics and controllable visual translation.
GranAlign: Granularity-Aware Alignment Framework for Zero-Shot Video Moment Retrieval
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Zero-shot video moment retrieval (ZVMR) is the task of localizing a temporal moment within an untrimmed video using a natural language query without relying on task-specific training data. The primary challenge in this setting lies in the mismatch in semantic granularity between textual queries and visual content. Previous studies in ZVMR have attempted to achieve alignment by leveraging high-quality pre-trained knowledge that represents video and language in a joint space. However, these approaches failed to balance the semantic granularity between the pre-trained knowledge provided by each modality for a given scene. As a result, despite the high quality of each modality's representations, the mismatch in granularity led to inaccurate retrieval. In this paper, we propose a training-free framework, called Granularity-Aware Alignment (GranAlign), that bridges this gap between coarse and fine semantic representations. Our approach introduces two complementary techniques: granularity-based query rewriting to generate varied semantic granularities, and query-aware caption generation to embed query intent into video content. By pairing multi-level queries with both query-agnostic and query-aware captions, we effectively resolve semantic mismatches. As a result, our method sets a new state-of-the-art across all three major benchmarks (QVHighlights, Charades-STA, ActivityNet-Captions), with a notable 3.23% mAP@avg improvement on the challenging QVHighlights dataset.
Point to Span: Zero-Shot Moment Retrieval for Navigating Unseen Hour-Long Videos
Dec 11, 2025



Abstract:Zero-shot Long Video Moment Retrieval (ZLVMR) is the task of identifying temporal segments in hour-long videos using a natural language query without task-specific training. The core technical challenge of LVMR stems from the computational infeasibility of processing entire lengthy videos in a single pass. This limitation has established a 'Search-then-Refine' approach, where candidates are rapidly narrowed down, and only those portions are analyzed, as the dominant paradigm for LVMR. However, existing approaches to this paradigm face severe limitations. Conventional supervised learning suffers from limited scalability and poor generalization, despite substantial resource consumption. Yet, existing zero-shot methods also fail, facing a dual challenge: (1) their heuristic strategies cause a 'search' phase candidate explosion, and (2) the 'refine' phase, which is vulnerable to semantic discrepancy, requires high-cost VLMs for verification, incurring significant computational overhead. We propose \textbf{P}oint-\textbf{to}-\textbf{S}pan (P2S), a novel training-free framework to overcome this challenge of inefficient 'search' and costly 'refine' phases. P2S overcomes these challenges with two key innovations: an 'Adaptive Span Generator' to prevent the search phase candidate explosion, and 'Query Decomposition' to refine candidates without relying on high-cost VLM verification. To our knowledge, P2S is the first zero-shot framework capable of temporal grounding in hour-long videos, outperforming supervised state-of-the-art methods by a significant margin (e.g., +3.7\% on R5@0.1 on MAD).
Visual Funnel: Resolving Contextual Blindness in Multimodal Large Language Models
Dec 11, 2025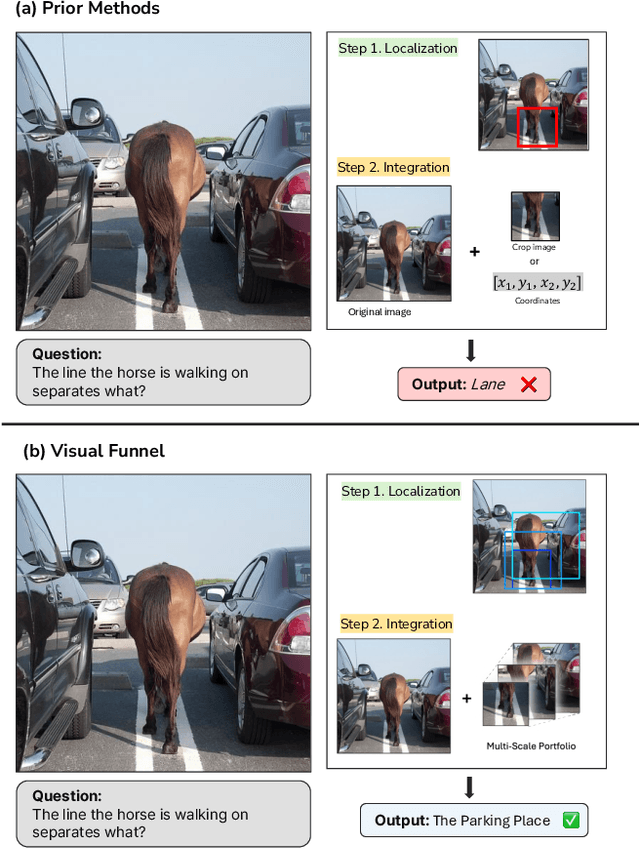
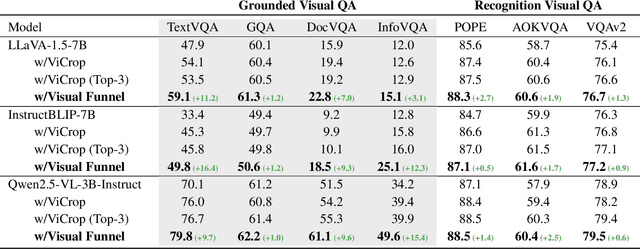
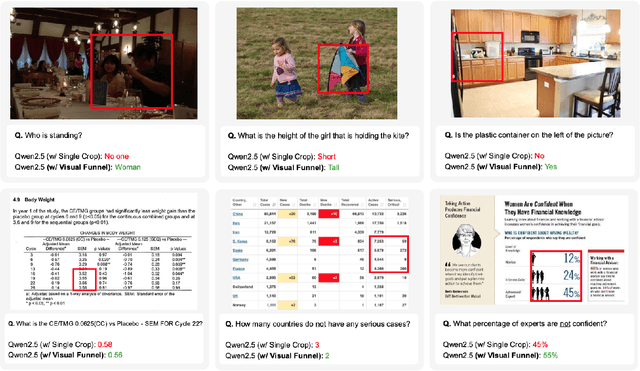
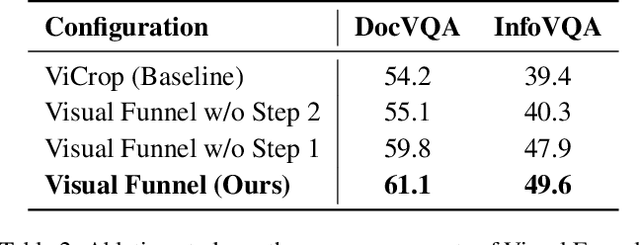
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) demonstrate impressive reasoning capabilities, but often fail to perceive fine-grained visual details, limiting their applicability in precision-demanding tasks. While methods that crop salient regions of an image offer a partial solution, we identify a critical limitation they introduce: "Contextual Blindness". This failure occurs due to structural disconnect between high-fidelity details (from the crop) and the broader global context (from the original image), even when all necessary visual information is present. We argue that this limitation stems not from a lack of information 'Quantity', but from a lack of 'Structural Diversity' in the model's input. To resolve this, we propose Visual Funnel, a training-free, two-step approach. Visual Funnel first performs Contextual Anchoring to identify the region of interest in a single forward pass. It then constructs an Entropy-Scaled Portfolio that preserves the hierarchical context - ranging from focal detail to broader surroundings - by dynamically determining crop sizes based on attention entropy and refining crop centers. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that Visual Funnel significantly outperforms naive single-crop and unstructured multi-crop baselines. Our results further validate that simply adding more unstructured crops provides limited or even detrimental benefits, confirming that the hierarchical structure of our portfolio is key to resolving Contextual Blindness.
ITA-MDT: Image-Timestep-Adaptive Masked Diffusion Transformer Framework for Image-Based Virtual Try-On
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces ITA-MDT, the Image-Timestep-Adaptive Masked Diffusion Transformer Framework for Image-Based Virtual Try-On (IVTON), designed to overcome the limitations of previous approaches by leveraging the Masked Diffusion Transformer (MDT) for improved handling of both global garment context and fine-grained details. The IVTON task involves seamlessly superimposing a garment from one image onto a person in another, creating a realistic depiction of the person wearing the specified garment. Unlike conventional diffusion-based virtual try-on models that depend on large pre-trained U-Net architectures, ITA-MDT leverages a lightweight, scalable transformer-based denoising diffusion model with a mask latent modeling scheme, achieving competitive results while reducing computational overhead. A key component of ITA-MDT is the Image-Timestep Adaptive Feature Aggregator (ITAFA), a dynamic feature aggregator that combines all of the features from the image encoder into a unified feature of the same size, guided by diffusion timestep and garment image complexity. This enables adaptive weighting of features, allowing the model to emphasize either global information or fine-grained details based on the requirements of the denoising stage. Additionally, the Salient Region Extractor (SRE) module is presented to identify complex region of the garment to provide high-resolution local information to the denoising model as an additional condition alongside the global information of the full garment image. This targeted conditioning strategy enhances detail preservation of fine details in highly salient garment regions, optimizing computational resources by avoiding unnecessarily processing entire garment image. Comparative evaluations confirms that ITA-MDT improves efficiency while maintaining strong performance, reaching state-of-the-art results in several metrics.
TPC: Test-time Procrustes Calibration for Diffusion-based Human Image Animation
Oct 31, 2024



Abstract:Human image animation aims to generate a human motion video from the inputs of a reference human image and a target motion video. Current diffusion-based image animation systems exhibit high precision in transferring human identity into targeted motion, yet they still exhibit irregular quality in their outputs. Their optimal precision is achieved only when the physical compositions (i.e., scale and rotation) of the human shapes in the reference image and target pose frame are aligned. In the absence of such alignment, there is a noticeable decline in fidelity and consistency. Especially, in real-world environments, this compositional misalignment commonly occurs, posing significant challenges to the practical usage of current systems. To this end, we propose Test-time Procrustes Calibration (TPC), which enhances the robustness of diffusion-based image animation systems by maintaining optimal performance even when faced with compositional misalignment, effectively addressing real-world scenarios. The TPC provides a calibrated reference image for the diffusion model, enhancing its capability to understand the correspondence between human shapes in the reference and target images. Our method is simple and can be applied to any diffusion-based image animation system in a model-agnostic manner, improving the effectiveness at test time without additional training.
FlexiEdit: Frequency-Aware Latent Refinement for Enhanced Non-Rigid Editing
Jul 25, 2024

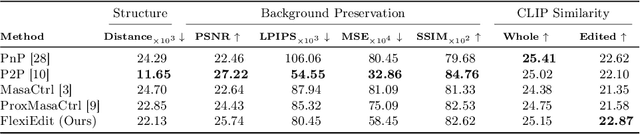

Abstract:Current image editing methods primarily utilize DDIM Inversion, employing a two-branch diffusion approach to preserve the attributes and layout of the original image. However, these methods encounter challenges with non-rigid edits, which involve altering the image's layout or structure. Our comprehensive analysis reveals that the high-frequency components of DDIM latent, crucial for retaining the original image's key features and layout, significantly contribute to these limitations. Addressing this, we introduce FlexiEdit, which enhances fidelity to input text prompts by refining DDIM latent, by reducing high-frequency components in targeted editing areas. FlexiEdit comprises two key components: (1) Latent Refinement, which modifies DDIM latent to better accommodate layout adjustments, and (2) Edit Fidelity Enhancement via Re-inversion, aimed at ensuring the edits more accurately reflect the input text prompts. Our approach represents notable progress in image editing, particularly in performing complex non-rigid edits, showcasing its enhanced capability through comparative experiments.
FRAG: Frequency Adapting Group for Diffusion Video Editing
Jun 10, 2024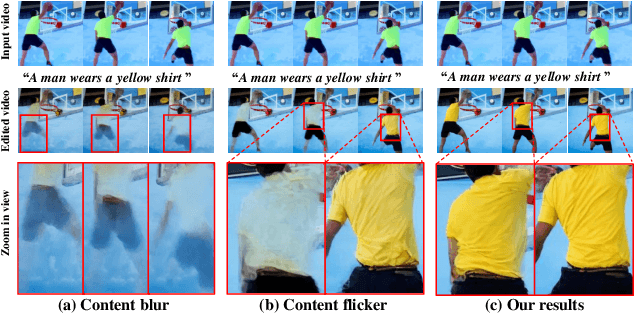
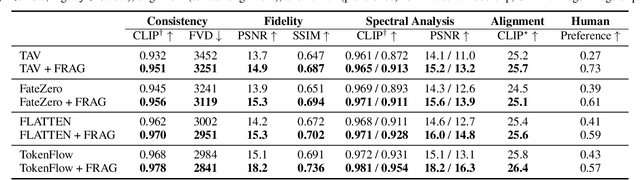
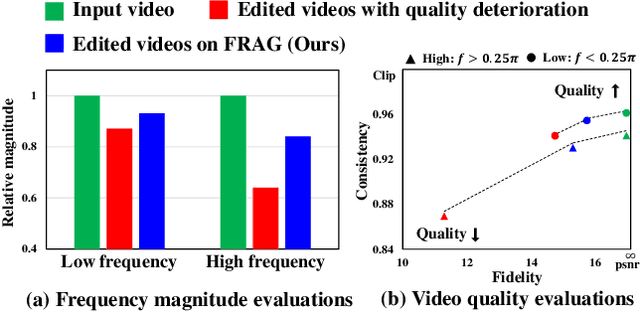
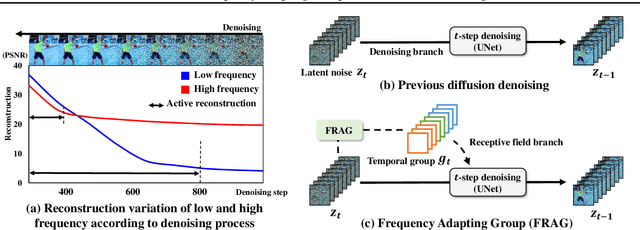
Abstract:In video editing, the hallmark of a quality edit lies in its consistent and unobtrusive adjustment. Modification, when integrated, must be smooth and subtle, preserving the natural flow and aligning seamlessly with the original vision. Therefore, our primary focus is on overcoming the current challenges in high quality edit to ensure that each edit enhances the final product without disrupting its intended essence. However, quality deterioration such as blurring and flickering is routinely observed in recent diffusion video editing systems. We confirm that this deterioration often stems from high-frequency leak: the diffusion model fails to accurately synthesize high-frequency components during denoising process. To this end, we devise Frequency Adapting Group (FRAG) which enhances the video quality in terms of consistency and fidelity by introducing a novel receptive field branch to preserve high-frequency components during the denoising process. FRAG is performed in a model-agnostic manner without additional training and validates the effectiveness on video editing benchmarks (i.e., TGVE, DAVIS).
Wavelet-Guided Acceleration of Text Inversion in Diffusion-Based Image Editing
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:In the field of image editing, Null-text Inversion (NTI) enables fine-grained editing while preserving the structure of the original image by optimizing null embeddings during the DDIM sampling process. However, the NTI process is time-consuming, taking more than two minutes per image. To address this, we introduce an innovative method that maintains the principles of the NTI while accelerating the image editing process. We propose the WaveOpt-Estimator, which determines the text optimization endpoint based on frequency characteristics. Utilizing wavelet transform analysis to identify the image's frequency characteristics, we can limit text optimization to specific timesteps during the DDIM sampling process. By adopting the Negative-Prompt Inversion (NPI) concept, a target prompt representing the original image serves as the initial text value for optimization. This approach maintains performance comparable to NTI while reducing the average editing time by over 80% compared to the NTI method. Our method presents a promising approach for efficient, high-quality image editing based on diffusion models.
HEAR: Hearing Enhanced Audio Response for Video-grounded Dialogue
Dec 15, 2023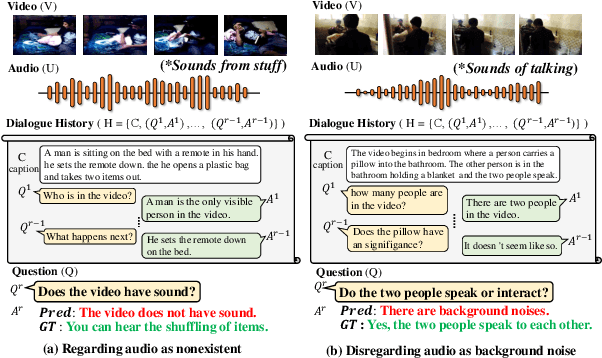
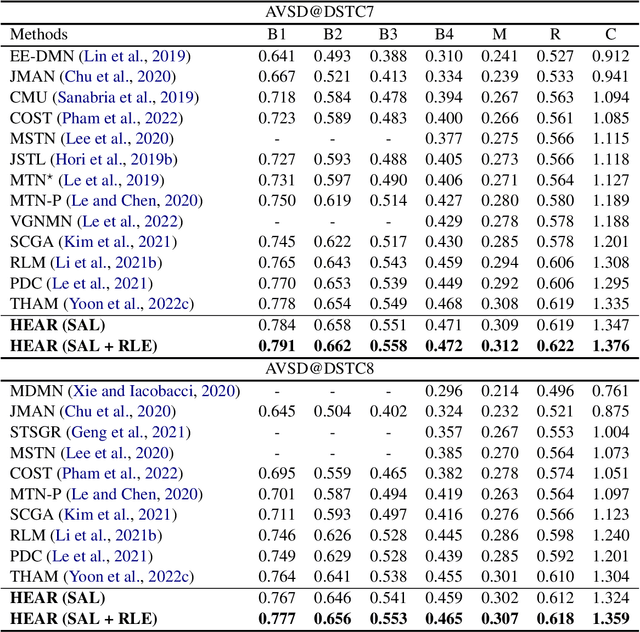
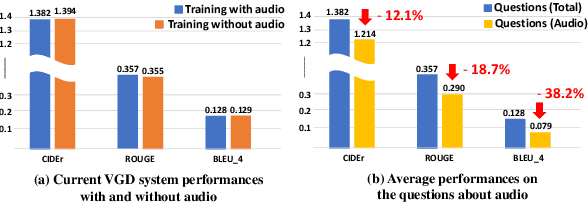

Abstract:Video-grounded Dialogue (VGD) aims to answer questions regarding a given multi-modal input comprising video, audio, and dialogue history. Although there have been numerous efforts in developing VGD systems to improve the quality of their responses, existing systems are competent only to incorporate the information in the video and text and tend to struggle in extracting the necessary information from the audio when generating appropriate responses to the question. The VGD system seems to be deaf, and thus, we coin this symptom of current systems' ignoring audio data as a deaf response. To overcome the deaf response problem, Hearing Enhanced Audio Response (HEAR) framework is proposed to perform sensible listening by selectively attending to audio whenever the question requires it. The HEAR framework enhances the accuracy and audibility of VGD systems in a model-agnostic manner. HEAR is validated on VGD datasets (i.e., AVSD@DSTC7 and AVSD@DSTC8) and shows effectiveness with various VGD systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge