Yingzhen Li
On the Identifiability of Regime-Switching Models with Multi-Lag Dependencies
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Identifiability is central to the interpretability of deep latent variable models, ensuring parameterisations are uniquely determined by the data-generating distribution. However, it remains underexplored for deep regime-switching time series. We develop a general theoretical framework for multi-lag Regime-Switching Models (RSMs), encompassing Markov Switching Models (MSMs) and Switching Dynamical Systems (SDSs). For MSMs, we formulate the model as a temporally structured finite mixture and prove identifiability of both the number of regimes and the multi-lag transitions in a nonlinear-Gaussian setting. For SDSs, we establish identifiability of the latent variables up to permutation and scaling via temporal structure, which in turn yields conditions for identifiability of regime-dependent latent causal graphs (up to regime/node permutations). Our results hold in a fully unsupervised setting through architectural and noise assumptions that are directly enforceable via neural network design. We complement the theory with a flexible variational estimator that satisfies the assumptions and validate the results on synthetic benchmarks. Across real-world datasets from neuroscience, finance, and climate, identifiability leads to more trustworthy interpretability analysis, which is crucial for scientific discovery.
UPMRI: Unsupervised Parallel MRI Reconstruction via Projected Conditional Flow Matching
Dec 19, 2025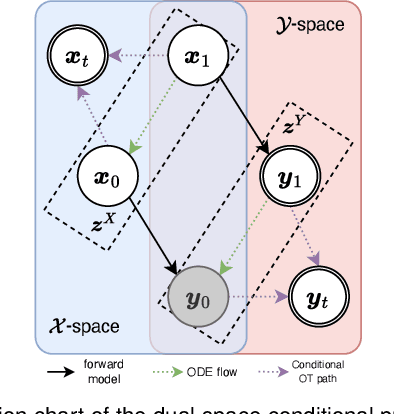
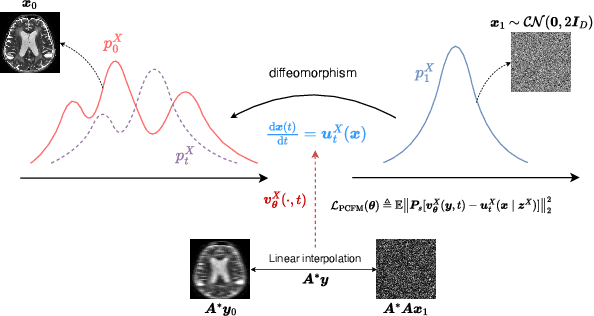
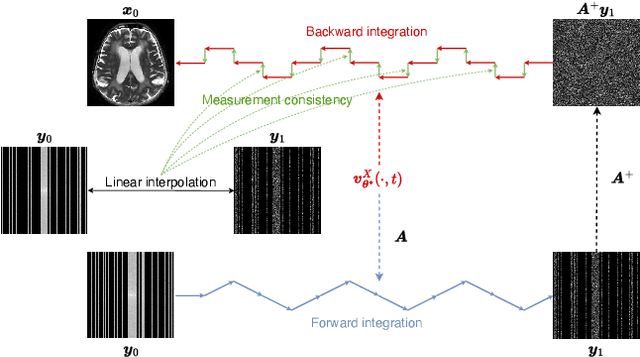
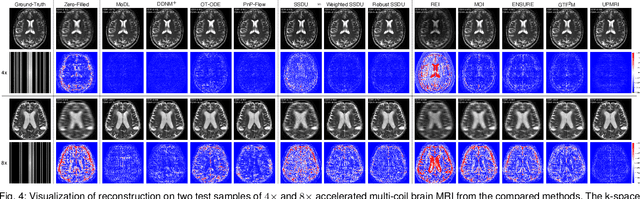
Abstract:Reconstructing high-quality images from substantially undersampled k-space data for accelerated MRI presents a challenging ill-posed inverse problem. While supervised deep learning has revolutionized this field, it relies heavily on large datasets of fully sampled ground-truth images, which are often impractical or impossible to acquire in clinical settings due to long scan times. Despite advances in self-supervised/unsupervised MRI reconstruction, their performance remains inadequate at high acceleration rates. To bridge this gap, we introduce UPMRI, an unsupervised reconstruction framework based on Projected Conditional Flow Matching (PCFM) and its unsupervised transformation. Unlike standard generative models, PCFM learns the prior distribution of fully sampled parallel MRI data by utilizing only undersampled k-space measurements. To reconstruct the image, we establish a novel theoretical link between the marginal vector field in the measurement space, governed by the continuity equation, and the optimal solution to the PCFM objective. This connection results in a cyclic dual-space sampling algorithm for high-quality reconstruction. Extensive evaluations on the fastMRI brain and CMRxRecon cardiac datasets demonstrate that UPMRI significantly outperforms state-of-the-art self-supervised and unsupervised baselines. Notably, it also achieves reconstruction fidelity comparable to or better than leading supervised methods at high acceleration factors, while requiring no fully sampled training data.
NMIRacle: Multi-modal Generative Molecular Elucidation from IR and NMR Spectra
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Molecular structure elucidation from spectroscopic data is a long-standing challenge in Chemistry, traditionally requiring expert interpretation. We introduce NMIRacle, a two-stage generative framework that builds upon recent paradigms in AI-driven spectroscopy with minimal assumptions. In the first stage, NMIRacle learns to reconstruct molecular structures from count-aware fragment encodings, which capture both fragment identities and their occurrences. In the second stage, a spectral encoder maps input spectroscopic measurements (IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR) into a latent embedding that conditions the pre-trained generator. This formulation bridges fragment-level chemical modeling with spectral evidence, yielding accurate molecular predictions. Empirical results show that NMIRacle outperforms existing baselines on molecular elucidation, while maintaining robust performance across increasing levels of molecular complexity.
Compact Memory for Continual Logistic Regression
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Despite recent progress, continual learning still does not match the performance of batch training. To avoid catastrophic forgetting, we need to build compact memory of essential past knowledge, but no clear solution has yet emerged, even for shallow neural networks with just one or two layers. In this paper, we present a new method to build compact memory for logistic regression. Our method is based on a result by Khan and Swaroop [2021] who show the existence of optimal memory for such models. We formulate the search for the optimal memory as Hessian-matching and propose a probabilistic PCA method to estimate them. Our approach can drastically improve accuracy compared to Experience Replay. For instance, on Split-ImageNet, we get 60% accuracy compared to 30% obtained by replay with memory-size equivalent to 0.3% of the data size. Increasing the memory size to 2% further boosts the accuracy to 74%, closing the gap to the batch accuracy of 77.6% on this task. Our work opens a new direction for building compact memory that can also be useful in the future for continual deep learning.
TabRAG: Tabular Document Retrieval via Structured Language Representations
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Ingesting data for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) involves either fine-tuning the embedding model directly on the target corpus or parsing documents for embedding model encoding. The former, while accurate, incurs high computational hardware requirements, while the latter suffers from suboptimal performance when extracting tabular data. In this work, we address the latter by presenting TabRAG, a parsing-based RAG pipeline designed to tackle table-heavy documents via structured language representations. TabRAG outperforms existing popular parsing-based methods for generation and retrieval. Code is available at https://github.com/jacobyhsi/TabRAG.
Neural Stochastic Flows: Solver-Free Modelling and Inference for SDE Solutions
Oct 29, 2025Abstract:Stochastic differential equations (SDEs) are well suited to modelling noisy and irregularly sampled time series found in finance, physics, and machine learning. Traditional approaches require costly numerical solvers to sample between arbitrary time points. We introduce Neural Stochastic Flows (NSFs) and their latent variants, which directly learn (latent) SDE transition laws using conditional normalising flows with architectural constraints that preserve properties inherited from stochastic flows. This enables one-shot sampling between arbitrary states and yields up to two orders of magnitude speed-ups at large time gaps. Experiments on synthetic SDE simulations and on real-world tracking and video data show that NSFs maintain distributional accuracy comparable to numerical approaches while dramatically reducing computation for arbitrary time-point sampling.
Test-Time Alignment of Discrete Diffusion Models with Sequential Monte Carlo
May 28, 2025Abstract:Discrete diffusion models have become highly effective across various domains. However, real-world applications often require the generative process to adhere to certain constraints but without task-specific fine-tuning. To this end, we propose a training-free method based on Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC) to sample from the reward-aligned target distribution at the test time. Our approach leverages twisted SMC with an approximate locally optimal proposal, obtained via a first-order Taylor expansion of the reward function. To address the challenge of ill-defined gradients in discrete spaces, we incorporate a Gumbel-Softmax relaxation, enabling efficient gradient-based approximation within the discrete generative framework. Empirical results on both synthetic datasets and image modelling validate the effectiveness of our approach.
Discrete Neural Flow Samplers with Locally Equivariant Transformer
May 23, 2025Abstract:Sampling from unnormalised discrete distributions is a fundamental problem across various domains. While Markov chain Monte Carlo offers a principled approach, it often suffers from slow mixing and poor convergence. In this paper, we propose Discrete Neural Flow Samplers (DNFS), a trainable and efficient framework for discrete sampling. DNFS learns the rate matrix of a continuous-time Markov chain such that the resulting dynamics satisfy the Kolmogorov equation. As this objective involves the intractable partition function, we then employ control variates to reduce the variance of its Monte Carlo estimation, leading to a coordinate descent learning algorithm. To further facilitate computational efficiency, we propose locally equivaraint Transformer, a novel parameterisation of the rate matrix that significantly improves training efficiency while preserving powerful network expressiveness. Empirically, we demonstrate the efficacy of DNFS in a wide range of applications, including sampling from unnormalised distributions, training discrete energy-based models, and solving combinatorial optimisation problems.
TabRep: a Simple and Effective Continuous Representation for Training Tabular Diffusion Models
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Diffusion models have been the predominant generative model for tabular data generation. However, they face the conundrum of modeling under a separate versus a unified data representation. The former encounters the challenge of jointly modeling all multi-modal distributions of tabular data in one model. While the latter alleviates this by learning a single representation for all features, it currently leverages sparse suboptimal encoding heuristics and necessitates additional computation costs. In this work, we address the latter by presenting TabRep, a tabular diffusion architecture trained with a unified continuous representation. To motivate the design of our representation, we provide geometric insights into how the data manifold affects diffusion models. The key attributes of our representation are composed of its density, flexibility to provide ample separability for nominal features, and ability to preserve intrinsic relationships. Ultimately, TabRep provides a simple yet effective approach for training tabular diffusion models under a continuous data manifold. Our results showcase that TabRep achieves superior performance across a broad suite of evaluations. It is the first to synthesize tabular data that exceeds the downstream quality of the original datasets while preserving privacy and remaining computationally efficient.
Bayesian Computation in Deep Learning
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:This review paper is intended for the 2nd edition of the Handbook of Markov chain Monte Carlo. We provide an introduction to approximate inference techniques as Bayesian computation methods applied to deep learning models. We organize the chapter by presenting popular computational methods for Bayesian neural networks and deep generative models, explaining their unique challenges in posterior inference as well as the solutions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge