Shaofei Huang
From Instruction to Event: Sound-Triggered Mobile Manipulation
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Current mobile manipulation research predominantly follows an instruction-driven paradigm, where agents rely on predefined textual commands to execute tasks. However, this setting confines agents to a passive role, limiting their autonomy and ability to react to dynamic environmental events. To address these limitations, we introduce sound-triggered mobile manipulation, where agents must actively perceive and interact with sound-emitting objects without explicit action instructions. To support these tasks, we develop Habitat-Echo, a data platform that integrates acoustic rendering with physical interaction. We further propose a baseline comprising a high-level task planner and low-level policy models to complete these tasks. Extensive experiments show that the proposed baseline empowers agents to actively detect and respond to auditory events, eliminating the need for case-by-case instructions. Notably, in the challenging dual-source scenario, the agent successfully isolates the primary source from overlapping acoustic interference to execute the first interaction, and subsequently proceeds to manipulate the secondary object, verifying the robustness of the baseline.
DOMR: Establishing Cross-View Segmentation via Dense Object Matching
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Cross-view object correspondence involves matching objects between egocentric (first-person) and exocentric (third-person) views. It is a critical yet challenging task for visual understanding. In this work, we propose the Dense Object Matching and Refinement (DOMR) framework to establish dense object correspondences across views. The framework centers around the Dense Object Matcher (DOM) module, which jointly models multiple objects. Unlike methods that directly match individual object masks to image features, DOM leverages both positional and semantic relationships among objects to find correspondences. DOM integrates a proposal generation module with a dense matching module that jointly encodes visual, spatial, and semantic cues, explicitly constructing inter-object relationships to achieve dense matching among objects. Furthermore, we combine DOM with a mask refinement head designed to improve the completeness and accuracy of the predicted masks, forming the complete DOMR framework. Extensive evaluations on the Ego-Exo4D benchmark demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with a mean IoU of 49.7% on Ego$\to$Exo and 55.2% on Exo$\to$Ego. These results outperform those of previous methods by 5.8% and 4.3%, respectively, validating the effectiveness of our integrated approach for cross-view understanding.
LLaVA-ST: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Fine-Grained Spatial-Temporal Understanding
Jan 14, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown promising results, yet existing approaches struggle to effectively handle both temporal and spatial localization simultaneously. This challenge stems from two key issues: first, incorporating spatial-temporal localization introduces a vast number of coordinate combinations, complicating the alignment of linguistic and visual coordinate representations; second, encoding fine-grained temporal and spatial information during video feature compression is inherently difficult. To address these issues, we propose LLaVA-ST, a MLLM for fine-grained spatial-temporal multimodal understanding. In LLaVA-ST, we propose Language-Aligned Positional Embedding, which embeds the textual coordinate special token into the visual space, simplifying the alignment of fine-grained spatial-temporal correspondences. Additionally, we design the Spatial-Temporal Packer, which decouples the feature compression of temporal and spatial resolutions into two distinct point-to-region attention processing streams. Furthermore, we propose ST-Align dataset with 4.3M training samples for fine-grained spatial-temporal multimodal understanding. With ST-align, we present a progressive training pipeline that aligns the visual and textual feature through sequential coarse-to-fine stages.Additionally, we introduce an ST-Align benchmark to evaluate spatial-temporal interleaved fine-grained understanding tasks, which include Spatial-Temporal Video Grounding (STVG) , Event Localization and Captioning (ELC) and Spatial Video Grounding (SVG). LLaVA-ST achieves outstanding performance on 11 benchmarks requiring fine-grained temporal, spatial, or spatial-temporal interleaving multimodal understanding. Our code, data and benchmark will be released at Our code, data and benchmark will be released at https://github.com/appletea233/LLaVA-ST .
Anchor3DLane++: 3D Lane Detection via Sample-Adaptive Sparse 3D Anchor Regression
Dec 22, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we focus on the challenging task of monocular 3D lane detection. Previous methods typically adopt inverse perspective mapping (IPM) to transform the Front-Viewed (FV) images or features into the Bird-Eye-Viewed (BEV) space for lane detection. However, IPM's dependence on flat ground assumption and context information loss in BEV representations lead to inaccurate 3D information estimation. Though efforts have been made to bypass BEV and directly predict 3D lanes from FV representations, their performances still fall behind BEV-based methods due to a lack of structured modeling of 3D lanes. In this paper, we propose a novel BEV-free method named Anchor3DLane++ which defines 3D lane anchors as structural representations and makes predictions directly from FV features. We also design a Prototype-based Adaptive Anchor Generation (PAAG) module to generate sample-adaptive sparse 3D anchors dynamically. In addition, an Equal-Width (EW) loss is developed to leverage the parallel property of lanes for regularization. Furthermore, camera-LiDAR fusion is also explored based on Anchor3DLane++ to leverage complementary information. Extensive experiments on three popular 3D lane detection benchmarks show that our Anchor3DLane++ outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at: https://github.com/tusen-ai/Anchor3DLane.
FreeEdit: Mask-free Reference-based Image Editing with Multi-modal Instruction
Sep 26, 2024Abstract:Introducing user-specified visual concepts in image editing is highly practical as these concepts convey the user's intent more precisely than text-based descriptions. We propose FreeEdit, a novel approach for achieving such reference-based image editing, which can accurately reproduce the visual concept from the reference image based on user-friendly language instructions. Our approach leverages the multi-modal instruction encoder to encode language instructions to guide the editing process. This implicit way of locating the editing area eliminates the need for manual editing masks. To enhance the reconstruction of reference details, we introduce the Decoupled Residual ReferAttention (DRRA) module. This module is designed to integrate fine-grained reference features extracted by a detail extractor into the image editing process in a residual way without interfering with the original self-attention. Given that existing datasets are unsuitable for reference-based image editing tasks, particularly due to the difficulty in constructing image triplets that include a reference image, we curate a high-quality dataset, FreeBench, using a newly developed twice-repainting scheme. FreeBench comprises the images before and after editing, detailed editing instructions, as well as a reference image that maintains the identity of the edited object, encompassing tasks such as object addition, replacement, and deletion. By conducting phased training on FreeBench followed by quality tuning, FreeEdit achieves high-quality zero-shot editing through convenient language instructions. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate the effectiveness of FreeEdit across multiple task types, demonstrating its superiority over existing methods. The code will be available at: https://freeedit.github.io/.
Unleashing the Temporal-Spatial Reasoning Capacity of GPT for Training-Free Audio and Language Referenced Video Object Segmentation
Aug 28, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose an Audio-Language-Referenced SAM 2 (AL-Ref-SAM 2) pipeline to explore the training-free paradigm for audio and language-referenced video object segmentation, namely AVS and RVOS tasks. The intuitive solution leverages GroundingDINO to identify the target object from a single frame and SAM 2 to segment the identified object throughout the video, which is less robust to spatiotemporal variations due to a lack of video context exploration. Thus, in our AL-Ref-SAM 2 pipeline, we propose a novel GPT-assisted Pivot Selection (GPT-PS) module to instruct GPT-4 to perform two-step temporal-spatial reasoning for sequentially selecting pivot frames and pivot boxes, thereby providing SAM 2 with a high-quality initial object prompt. Within GPT-PS, two task-specific Chain-of-Thought prompts are designed to unleash GPT's temporal-spatial reasoning capacity by guiding GPT to make selections based on a comprehensive understanding of video and reference information. Furthermore, we propose a Language-Binded Reference Unification (LBRU) module to convert audio signals into language-formatted references, thereby unifying the formats of AVS and RVOS tasks in the same pipeline. Extensive experiments on both tasks show that our training-free AL-Ref-SAM 2 pipeline achieves performances comparable to or even better than fully-supervised fine-tuning methods. The code is available at: https://github.com/appletea233/AL-Ref-SAM2.
Mask-Enhanced Segment Anything Model for Tumor Lesion Semantic Segmentation
Mar 09, 2024Abstract:Tumor lesion segmentation on CT or MRI images plays a critical role in cancer diagnosis and treatment planning. Considering the inherent differences in tumor lesion segmentation data across various medical imaging modalities and equipment, integrating medical knowledge into the Segment Anything Model (SAM) presents promising capability due to its versatility and generalization potential. Recent studies have attempted to enhance SAM with medical expertise by pre-training on large-scale medical segmentation datasets. However, challenges still exist in 3D tumor lesion segmentation owing to tumor complexity and the imbalance in foreground and background regions. Therefore, we introduce Mask-Enhanced SAM (M-SAM), an innovative architecture tailored for 3D tumor lesion segmentation. We propose a novel Mask-Enhanced Adapter (MEA) within M-SAM that enriches the semantic information of medical images with positional data from coarse segmentation masks, facilitating the generation of more precise segmentation masks. Furthermore, an iterative refinement scheme is implemented in M-SAM to refine the segmentation masks progressively, leading to improved performance. Extensive experiments on seven tumor lesion segmentation datasets indicate that our M-SAM not only achieves high segmentation accuracy but also exhibits robust generalization.
Transferring CLIP's Knowledge into Zero-Shot Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
Dec 12, 2023



Abstract:Traditional 3D segmentation methods can only recognize a fixed range of classes that appear in the training set, which limits their application in real-world scenarios due to the lack of generalization ability. Large-scale visual-language pre-trained models, such as CLIP, have shown their generalization ability in the zero-shot 2D vision tasks, but are still unable to be applied to 3D semantic segmentation directly. In this work, we focus on zero-shot point cloud semantic segmentation and propose a simple yet effective baseline to transfer the visual-linguistic knowledge implied in CLIP to point cloud encoder at both feature and output levels. Both feature-level and output-level alignments are conducted between 2D and 3D encoders for effective knowledge transfer. Concretely, a Multi-granularity Cross-modal Feature Alignment (MCFA) module is proposed to align 2D and 3D features from global semantic and local position perspectives for feature-level alignment. For the output level, per-pixel pseudo labels of unseen classes are extracted using the pre-trained CLIP model as supervision for the 3D segmentation model to mimic the behavior of the CLIP image encoder. Extensive experiments are conducted on two popular benchmarks of point cloud segmentation. Our method outperforms significantly previous state-of-the-art methods under zero-shot setting (+29.2% mIoU on SemanticKITTI and 31.8% mIoU on nuScenes), and further achieves promising results in the annotation-free point cloud semantic segmentation setting, showing its great potential for label-efficient learning.
Customize your NeRF: Adaptive Source Driven 3D Scene Editing via Local-Global Iterative Training
Dec 04, 2023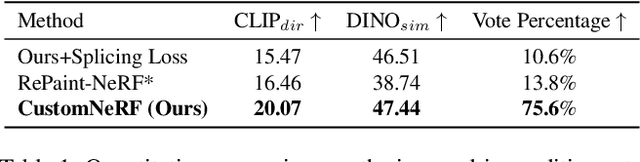
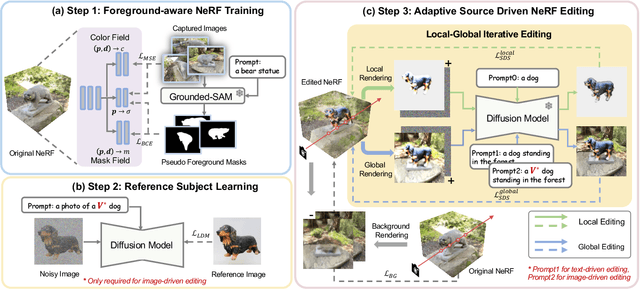
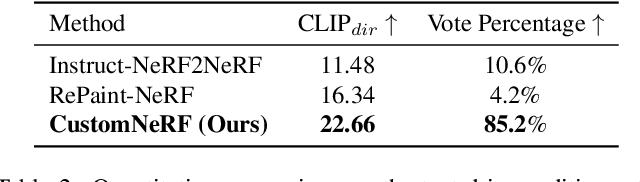

Abstract:In this paper, we target the adaptive source driven 3D scene editing task by proposing a CustomNeRF model that unifies a text description or a reference image as the editing prompt. However, obtaining desired editing results conformed with the editing prompt is nontrivial since there exist two significant challenges, including accurate editing of only foreground regions and multi-view consistency given a single-view reference image. To tackle the first challenge, we propose a Local-Global Iterative Editing (LGIE) training scheme that alternates between foreground region editing and full-image editing, aimed at foreground-only manipulation while preserving the background. For the second challenge, we also design a class-guided regularization that exploits class priors within the generation model to alleviate the inconsistency problem among different views in image-driven editing. Extensive experiments show that our CustomNeRF produces precise editing results under various real scenes for both text- and image-driven settings.
Discovering Sounding Objects by Audio Queries for Audio Visual Segmentation
Sep 18, 2023



Abstract:Audio visual segmentation (AVS) aims to segment the sounding objects for each frame of a given video. To distinguish the sounding objects from silent ones, both audio-visual semantic correspondence and temporal interaction are required. The previous method applies multi-frame cross-modal attention to conduct pixel-level interactions between audio features and visual features of multiple frames simultaneously, which is both redundant and implicit. In this paper, we propose an Audio-Queried Transformer architecture, AQFormer, where we define a set of object queries conditioned on audio information and associate each of them to particular sounding objects. Explicit object-level semantic correspondence between audio and visual modalities is established by gathering object information from visual features with predefined audio queries. Besides, an Audio-Bridged Temporal Interaction module is proposed to exchange sounding object-relevant information among multiple frames with the bridge of audio features. Extensive experiments are conducted on two AVS benchmarks to show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performances, especially 7.1% M_J and 7.6% M_F gains on the MS3 setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge