Sarthak Sharma
AVR: Synergizing Foundation Models for Audio-Visual Humor Detection
Jun 15, 2024


Abstract:In this work, we present, AVR application for audio-visual humor detection. While humor detection has traditionally centered around textual analysis, recent advancements have spotlighted multimodal approaches. However, these methods lean on textual cues as a modality, necessitating the use of ASR systems for transcribing the audio-data. This heavy reliance on ASR accuracy can pose challenges in real-world applications. To address this bottleneck, we propose an innovative audio-visual humor detection system that circumvents textual reliance, eliminating the need for ASR models. Instead, the proposed approach hinges on the intricate interplay between audio and visual content for effective humor detection.
UAP-BEV: Uncertainty Aware Planning using Bird's Eye View generated from Surround Monocular Images
Jun 08, 2023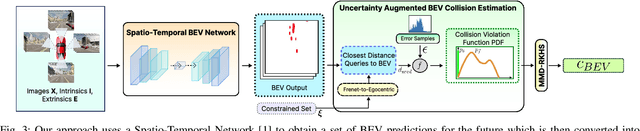

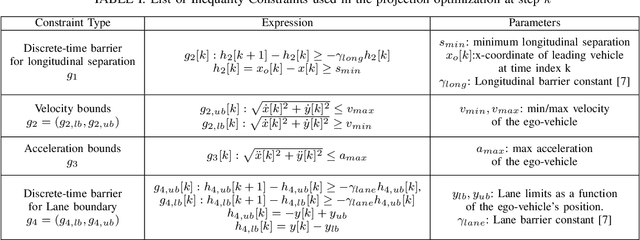
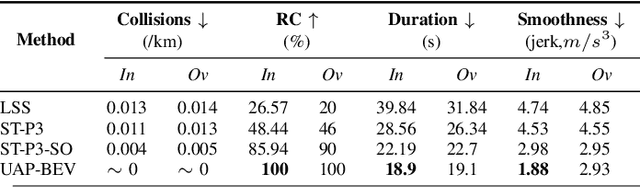
Abstract:Autonomous driving requires accurate reasoning of the location of objects from raw sensor data. Recent end-to-end learning methods go from raw sensor data to a trajectory output via Bird's Eye View(BEV) segmentation as an interpretable intermediate representation. Motion planning over cost maps generated via Birds Eye View (BEV) segmentation has emerged as a prominent approach in autonomous driving. However, the current approaches have two critical gaps. First, the optimization process is simplistic and involves just evaluating a fixed set of trajectories over the cost map. The trajectory samples are not adapted based on their associated cost values. Second, the existing cost maps do not account for the uncertainty in the cost maps that can arise due to noise in RGB images, and BEV annotations. As a result, these approaches can struggle in challenging scenarios where there is abrupt cut-in, stopping, overtaking, merging, etc from the neighboring vehicles. In this paper, we propose UAP-BEV: A novel approach that models the noise in Spatio-Temporal BEV predictions to create an uncertainty-aware occupancy grid map. Using queries of the distance to the closest occupied cell, we obtain a sample estimate of the collision probability of the ego-vehicle. Subsequently, our approach uses gradient-free sampling-based optimization to compute low-cost trajectories over the cost map. Importantly, the sampling distribution is adapted based on the optimal cost values of the sampled trajectories. By explicitly modeling probabilistic collision avoidance in the BEV space, our approach is able to outperform the cost-map-based baselines in collision avoidance, route completion, time to completion, and smoothness. To further validate our method, we also show results on the real-world dataset NuScenes, where we report improvements in collision avoidance and smoothness.
FinderNet: A Data Augmentation Free Canonicalization aided Loop Detection and Closure technique for Point clouds in 6-DOF separation
Apr 03, 2023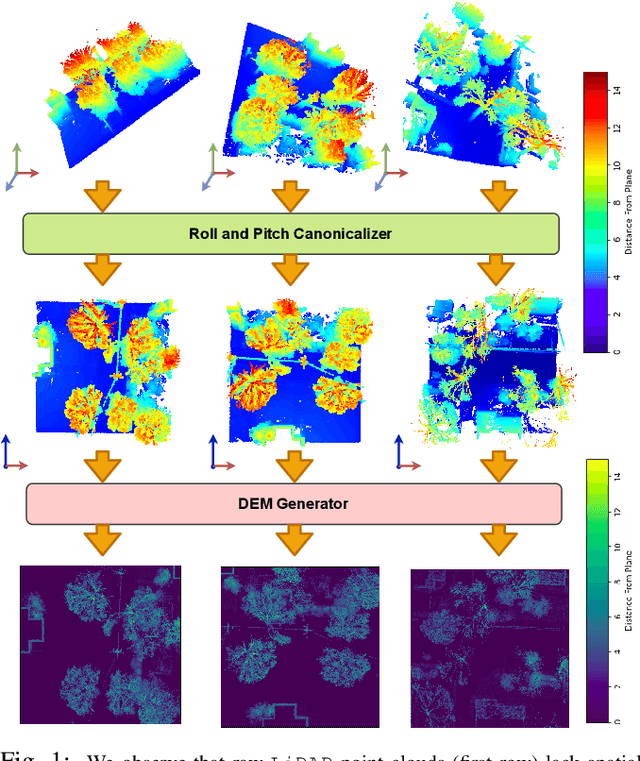
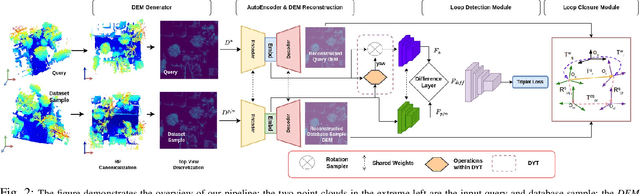
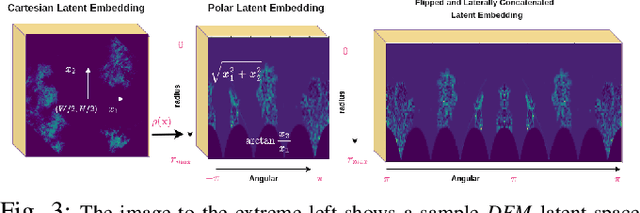
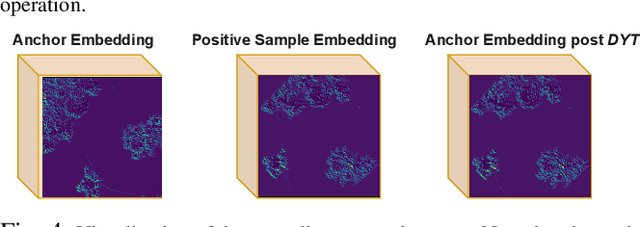
Abstract:We focus on the problem of LiDAR point cloud based loop detection (or Finding) and closure (LDC) in a multi-agent setting. State-of-the-art (SOTA) techniques directly generate learned embeddings of a given point cloud, require large data transfers, and are not robust to wide variations in 6 Degrees-of-Freedom (DOF) viewpoint. Moreover, absence of strong priors in an unstructured point cloud leads to highly inaccurate LDC. In this original approach, we propose independent roll and pitch canonicalization of the point clouds using a common dominant ground plane. Discretization of the canonicalized point cloud along the axis perpendicular to the ground plane leads to an image similar to Digital Elevation Maps (DEMs), which exposes strong spatial priors in the scene. Our experiments show that LDC based on learnt embeddings of such DEMs is not only data efficient but also significantly more robust, and generalizable than the current SOTA. We report significant performance gain in terms of Average Precision for loop detection and absolute translation/rotation error for relative pose estimation (or loop closure) on Kitti, GPR and Oxford Robot Car over multiple SOTA LDC methods. Our encoder technique allows to compress the original point cloud by over 830 times. To further test the robustness of our technique we create and opensource a custom dataset called Lidar-UrbanFly Dataset (LUF) which consists of point clouds obtained from a LiDAR mounted on a quadrotor.
Estimation of Appearance and Occupancy Information in Birds Eye View from Surround Monocular Images
Nov 08, 2022Abstract:Autonomous driving requires efficient reasoning about the location and appearance of the different agents in the scene, which aids in downstream tasks such as object detection, object tracking, and path planning. The past few years have witnessed a surge in approaches that combine the different taskbased modules of the classic self-driving stack into an End-toEnd(E2E) trainable learning system. These approaches replace perception, prediction, and sensor fusion modules with a single contiguous module with shared latent space embedding, from which one extracts a human-interpretable representation of the scene. One of the most popular representations is the Birds-eye View (BEV), which expresses the location of different traffic participants in the ego vehicle frame from a top-down view. However, a BEV does not capture the chromatic appearance information of the participants. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel representation that captures various traffic participants appearance and occupancy information from an array of monocular cameras covering 360 deg field of view (FOV). We use a learned image embedding of all camera images to generate a BEV of the scene at any instant that captures both appearance and occupancy of the scene, which can aid in downstream tasks such as object tracking and executing language-based commands. We test the efficacy of our approach on synthetic dataset generated from CARLA. The code, data set, and results can be found at https://rebrand.ly/APP OCC-results.
Bridging Sim2Real Gap Using Image Gradients for the Task of End-to-End Autonomous Driving
May 16, 2022
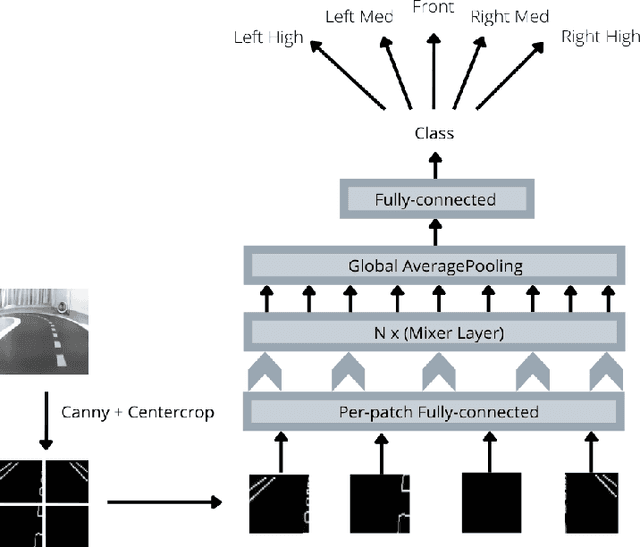

Abstract:We present the first prize solution to NeurIPS 2021 - AWS Deepracer Challenge. In this competition, the task was to train a reinforcement learning agent (i.e. an autonomous car), that learns to drive by interacting with its environment, a simulated track, by taking an action in a given state to maximize the expected reward. This model was then tested on a real-world track with a miniature AWS Deepracer car. Our goal is to train a model that can complete a lap as fast as possible without going off the track. The Deepracer challenge is a part of a series of embodied intelligence competitions in the field of autonomous vehicles, called The AI Driving Olympics (AI-DO). The overall objective of the AI-DO is to provide accessible mechanisms for benchmarking progress in autonomy applied to the task of autonomous driving. The tricky section of this challenge was the sim2real transfer of the learned skills. To reduce the domain gap in the observation space we did a canny edge detection in addition to cropping out of the unnecessary background information. We modeled the problem as a behavioral cloning task and used MLP-MIXER to optimize for runtime. We made sure our model was capable of handling control noise by careful filtration of the training data and that gave us a robust model capable of completing the track even when 50% of the commands were randomly changed. The overall runtime of the model was only 2-3ms on a modern CPU.
NMR: Neural Manifold Representation for Autonomous Driving
May 11, 2022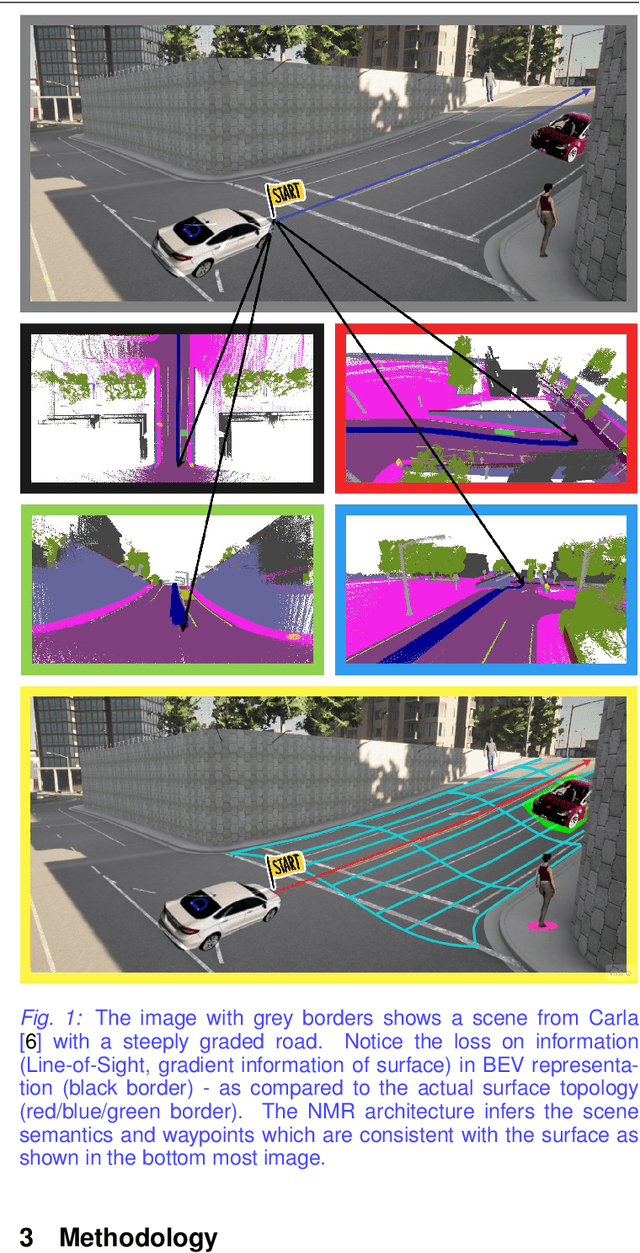
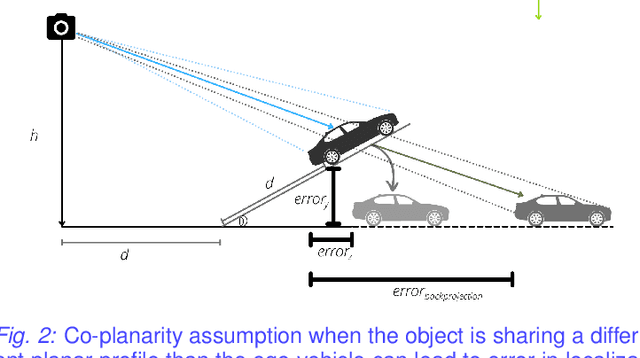
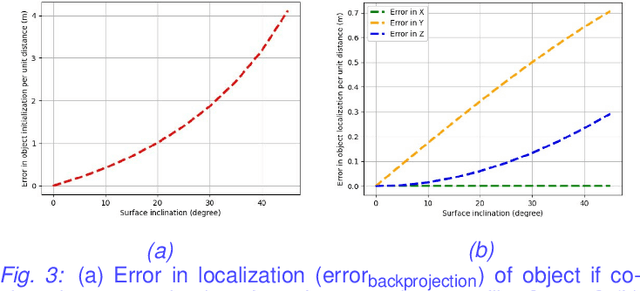
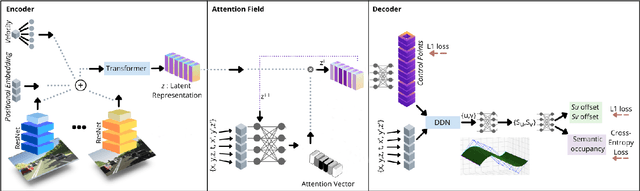
Abstract:Autonomous driving requires efficient reasoning about the Spatio-temporal nature of the semantics of the scene. Recent approaches have successfully amalgamated the traditional modular architecture of an autonomous driving stack comprising perception, prediction, and planning in an end-to-end trainable system. Such a system calls for a shared latent space embedding with interpretable intermediate trainable projected representation. One such successfully deployed representation is the Bird's-Eye View(BEV) representation of the scene in ego-frame. However, a fundamental assumption for an undistorted BEV is the local coplanarity of the world around the ego-vehicle. This assumption is highly restrictive, as roads, in general, do have gradients. The resulting distortions make path planning inefficient and incorrect. To overcome this limitation, we propose Neural Manifold Representation (NMR), a representation for the task of autonomous driving that learns to infer semantics and predict way-points on a manifold over a finite horizon, centered on the ego-vehicle. We do this using an iterative attention mechanism applied on a latent high dimensional embedding of surround monocular images and partial ego-vehicle state. This representation helps generate motion and behavior plans consistent with and cognizant of the surface geometry. We propose a sampling algorithm based on edge-adaptive coverage loss of BEV occupancy grid and associated guidance flow field to generate the surface manifold while incurring minimal computational overhead. We aim to test the efficacy of our approach on CARLA and SYNTHIA-SF.
Deep Implicit Surface Point Prediction Networks
Jun 15, 2021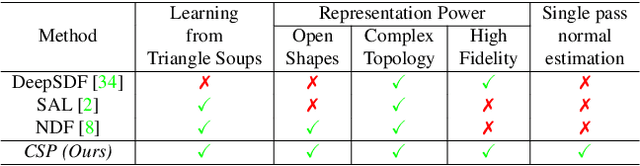
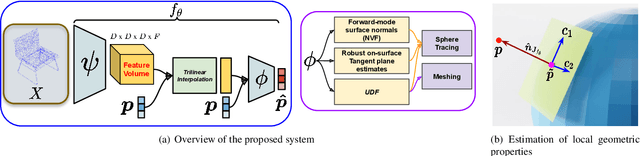
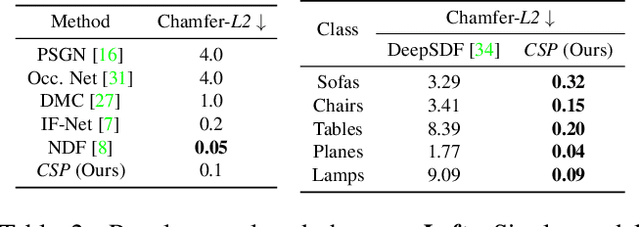
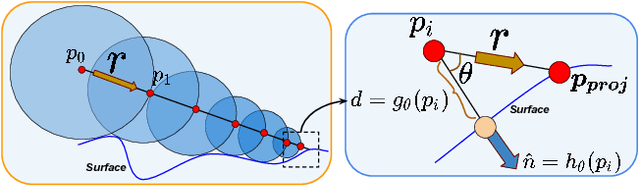
Abstract:Deep neural representations of 3D shapes as implicit functions have been shown to produce high fidelity models surpassing the resolution-memory trade-off faced by the explicit representations using meshes and point clouds. However, most such approaches focus on representing closed shapes. Unsigned distance function (UDF) based approaches have been proposed recently as a promising alternative to represent both open and closed shapes. However, since the gradients of UDFs vanish on the surface, it is challenging to estimate local (differential) geometric properties like the normals and tangent planes which are needed for many downstream applications in vision and graphics. There are additional challenges in computing these properties efficiently with a low-memory footprint. This paper presents a novel approach that models such surfaces using a new class of implicit representations called the closest surface-point (CSP) representation. We show that CSP allows us to represent complex surfaces of any topology (open or closed) with high fidelity. It also allows for accurate and efficient computation of local geometric properties. We further demonstrate that it leads to efficient implementation of downstream algorithms like sphere-tracing for rendering the 3D surface as well as to create explicit mesh-based representations. Extensive experimental evaluation on the ShapeNet dataset validate the above contributions with results surpassing the state-of-the-art.
DUDE: Deep Unsigned Distance Embeddings for Hi-Fidelity Representation of Complex 3D Surfaces
Nov 04, 2020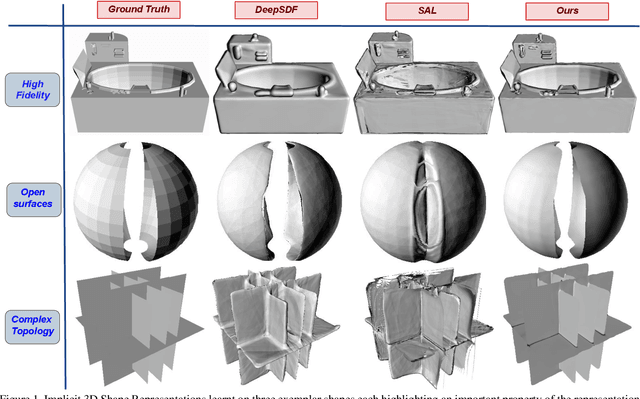
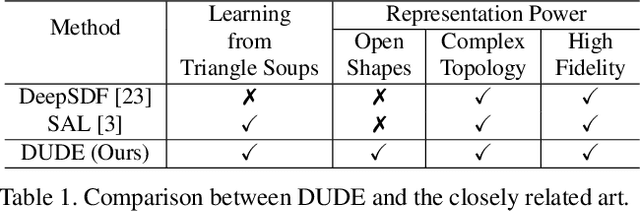
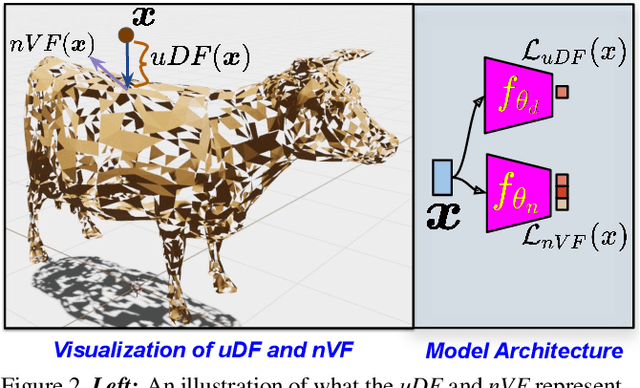
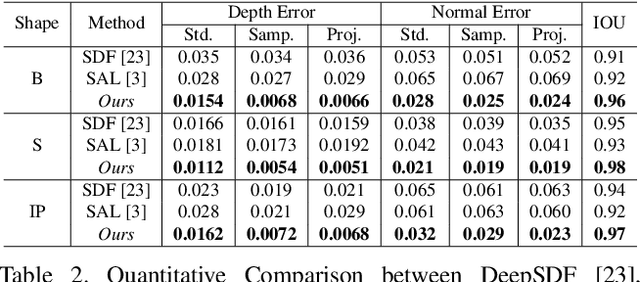
Abstract:High fidelity representation of shapes with arbitrary topology is an important problem for a variety of vision and graphics applications. Owing to their limited resolution, classical discrete shape representations using point clouds, voxels and meshes produce low quality results when used in these applications. Several implicit 3D shape representation approaches using deep neural networks have been proposed leading to significant improvements in both quality of representations as well as the impact on downstream applications. However, these methods can only be used to represent topologically closed shapes which greatly limits the class of shapes that they can represent. As a consequence, they also often require clean, watertight meshes for training. In this work, we propose DUDE - a Deep Unsigned Distance Embedding method which alleviates both of these shortcomings. DUDE is a disentangled shape representation that utilizes an unsigned distance field (uDF) to represent proximity to a surface, and a normal vector field (nVF) to represent surface orientation. We show that a combination of these two (uDF+nVF) can be used to learn high fidelity representations for arbitrary open/closed shapes. As opposed to prior work such as DeepSDF, our shape representations can be directly learnt from noisy triangle soups, and do not need watertight meshes. Additionally, we propose novel algorithms for extracting and rendering iso-surfaces from the learnt representations. We validate DUDE on benchmark 3D datasets and demonstrate that it produces significant improvements over the state of the art.
INFER: INtermediate representations for FuturE pRediction
Mar 26, 2019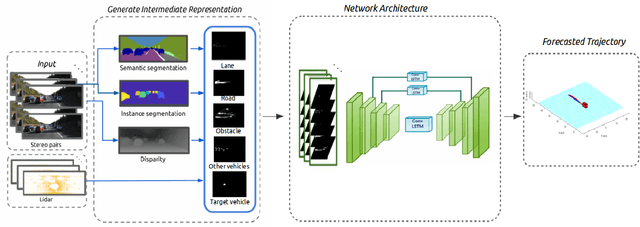
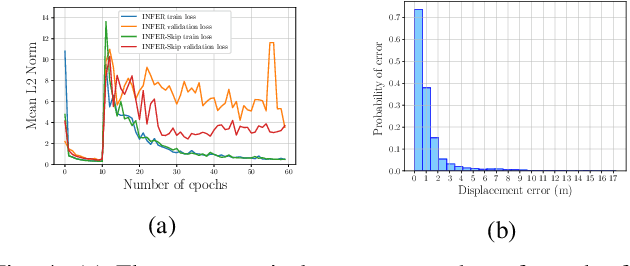
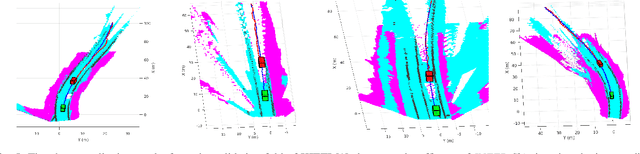
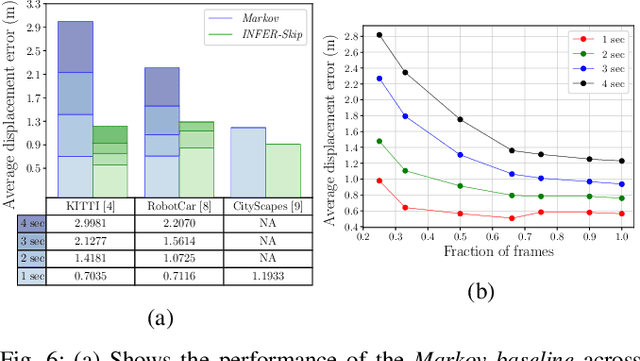
Abstract:In urban driving scenarios, forecasting future trajectories of surrounding vehicles is of paramount importance. While several approaches for the problem have been proposed, the best-performing ones tend to require extremely detailed input representations (eg. image sequences). But, such methods do not generalize to datasets they have not been trained on. We propose intermediate representations that are particularly well-suited for future prediction. As opposed to using texture (color) information, we rely on semantics and train an autoregressive model to accurately predict future trajectories of traffic participants (vehicles) (see fig. above). We demonstrate that using semantics provides a significant boost over techniques that operate over raw pixel intensities/disparities. Uncharacteristic of state-of-the-art approaches, our representations and models generalize to completely different datasets, collected across several cities, and also across countries where people drive on opposite sides of the road (left-handed vs right-handed driving). Additionally, we demonstrate an application of our approach in multi-object tracking (data association). To foster further research in transferrable representations and ensure reproducibility, we release all our code and data.
Beyond Pixels: Leveraging Geometry and Shape Cues for Online Multi-Object Tracking
Jul 27, 2018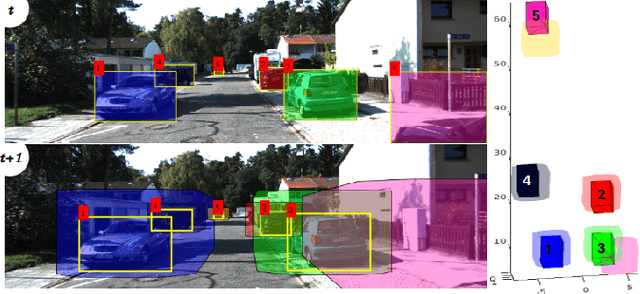
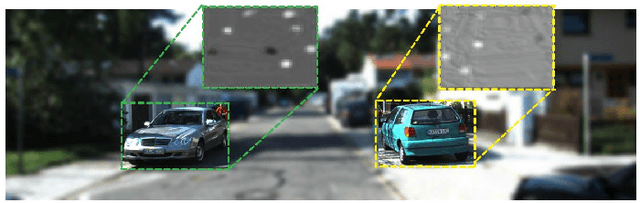
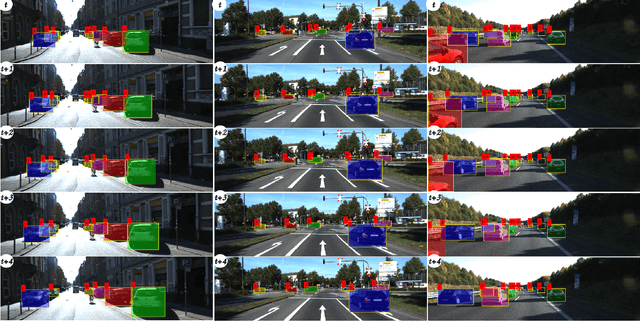
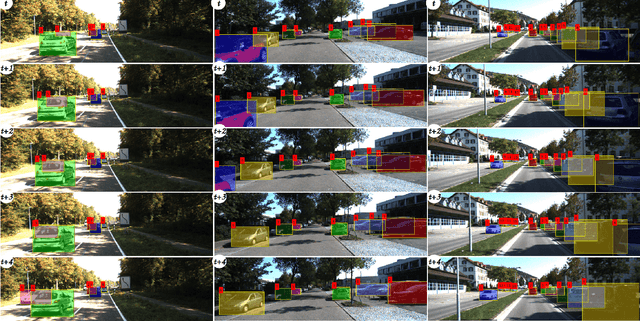
Abstract:This paper introduces geometry and object shape and pose costs for multi-object tracking in urban driving scenarios. Using images from a monocular camera alone, we devise pairwise costs for object tracks, based on several 3D cues such as object pose, shape, and motion. The proposed costs are agnostic to the data association method and can be incorporated into any optimization framework to output the pairwise data associations. These costs are easy to implement, can be computed in real-time, and complement each other to account for possible errors in a tracking-by-detection framework. We perform an extensive analysis of the designed costs and empirically demonstrate consistent improvement over the state-of-the-art under varying conditions that employ a range of object detectors, exhibit a variety in camera and object motions, and, more importantly, are not reliant on the choice of the association framework. We also show that, by using the simplest of associations frameworks (two-frame Hungarian assignment), we surpass the state-of-the-art in multi-object-tracking on road scenes. More qualitative and quantitative results can be found at the following URL: https://junaidcs032.github.io/Geometry_ObjectShape_MOT/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge