Ran Gu
UPL-SFDA: Uncertainty-aware Pseudo Label Guided Source-Free Domain Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Sep 19, 2023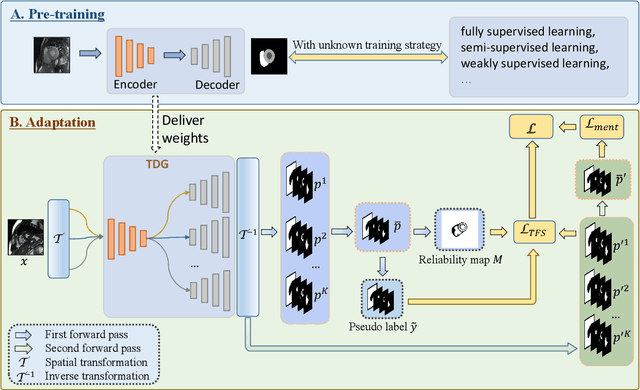
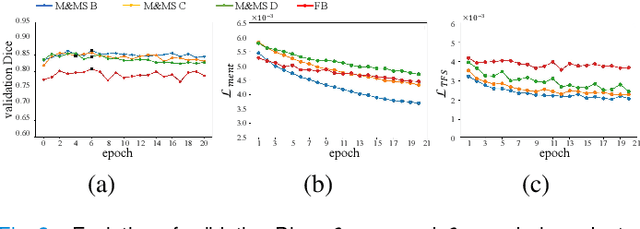
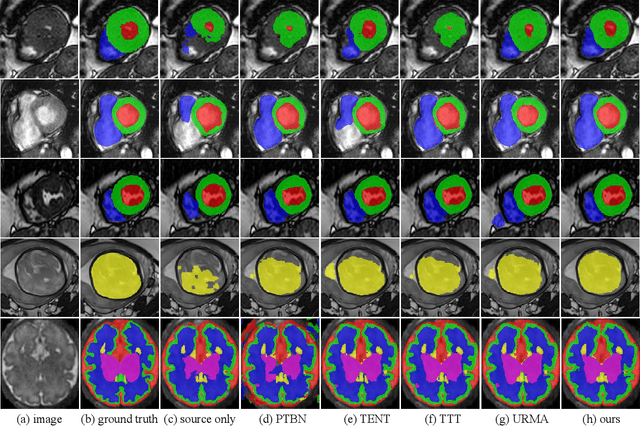
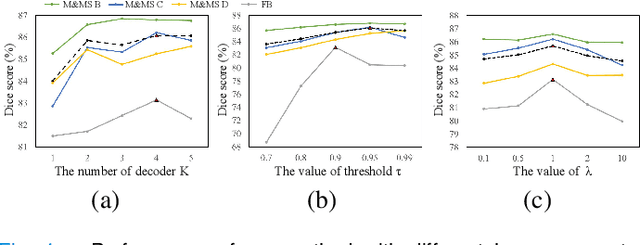
Abstract:Domain Adaptation (DA) is important for deep learning-based medical image segmentation models to deal with testing images from a new target domain. As the source-domain data are usually unavailable when a trained model is deployed at a new center, Source-Free Domain Adaptation (SFDA) is appealing for data and annotation-efficient adaptation to the target domain. However, existing SFDA methods have a limited performance due to lack of sufficient supervision with source-domain images unavailable and target-domain images unlabeled. We propose a novel Uncertainty-aware Pseudo Label guided (UPL) SFDA method for medical image segmentation. Specifically, we propose Target Domain Growing (TDG) to enhance the diversity of predictions in the target domain by duplicating the pre-trained model's prediction head multiple times with perturbations. The different predictions in these duplicated heads are used to obtain pseudo labels for unlabeled target-domain images and their uncertainty to identify reliable pseudo labels. We also propose a Twice Forward pass Supervision (TFS) strategy that uses reliable pseudo labels obtained in one forward pass to supervise predictions in the next forward pass. The adaptation is further regularized by a mean prediction-based entropy minimization term that encourages confident and consistent results in different prediction heads. UPL-SFDA was validated with a multi-site heart MRI segmentation dataset, a cross-modality fetal brain segmentation dataset, and a 3D fetal tissue segmentation dataset. It improved the average Dice by 5.54, 5.01 and 6.89 percentage points for the three tasks compared with the baseline, respectively, and outperformed several state-of-the-art SFDA methods.
CDDSA: Contrastive Domain Disentanglement and Style Augmentation for Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 22, 2022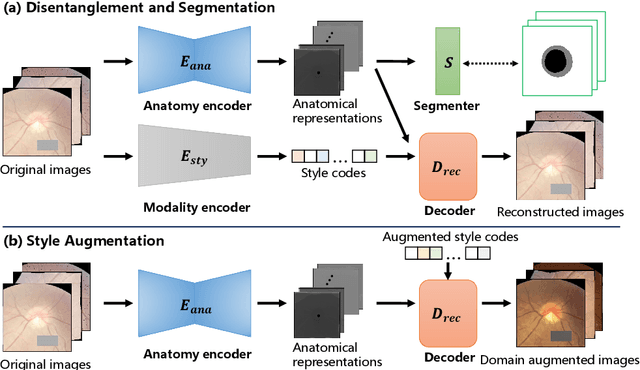
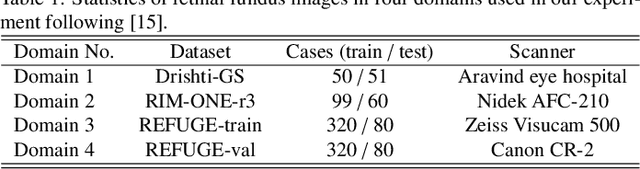
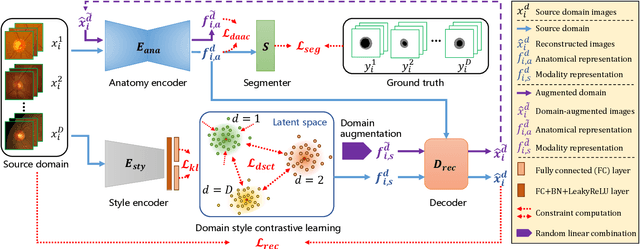

Abstract:Generalization to previously unseen images with potential domain shifts and different styles is essential for clinically applicable medical image segmentation, and the ability to disentangle domain-specific and domain-invariant features is key for achieving Domain Generalization (DG). However, existing DG methods can hardly achieve effective disentanglement to get high generalizability. To deal with this problem, we propose an efficient Contrastive Domain Disentanglement and Style Augmentation (CDDSA) framework for generalizable medical image segmentation. First, a disentangle network is proposed to decompose an image into a domain-invariant anatomical representation and a domain-specific style code, where the former is sent to a segmentation model that is not affected by the domain shift, and the disentangle network is regularized by a decoder that combines the anatomical and style codes to reconstruct the input image. Second, to achieve better disentanglement, a contrastive loss is proposed to encourage the style codes from the same domain and different domains to be compact and divergent, respectively. Thirdly, to further improve generalizability, we propose a style augmentation method based on the disentanglement representation to synthesize images in various unseen styles with shared anatomical structures. Our method was validated on a public multi-site fundus image dataset for optic cup and disc segmentation and an in-house multi-site Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Magnetic Resonance Image (NPC-MRI) dataset for nasopharynx Gross Tumor Volume (GTVnx) segmentation. Experimental results showed that the proposed CDDSA achieved remarkable generalizability across different domains, and it outperformed several state-of-the-art methods in domain-generalizable segmentation.
PyMIC: A deep learning toolkit for annotation-efficient medical image segmentation
Aug 19, 2022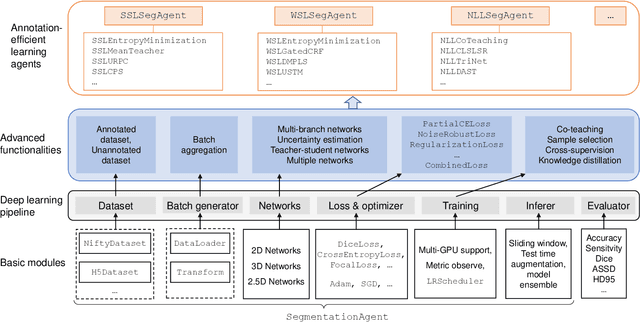
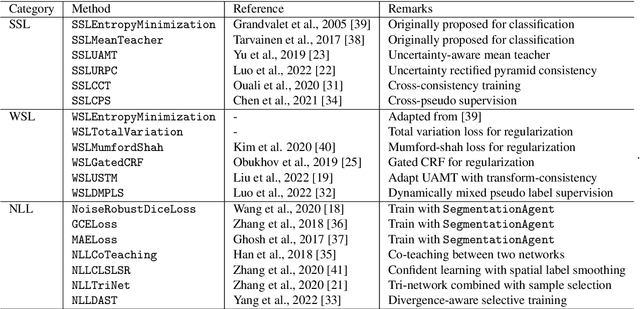
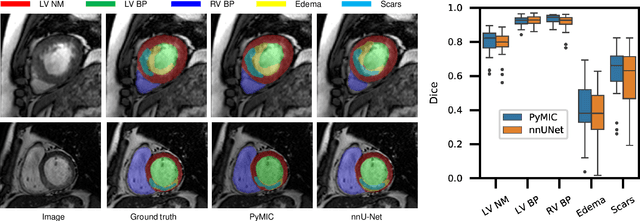
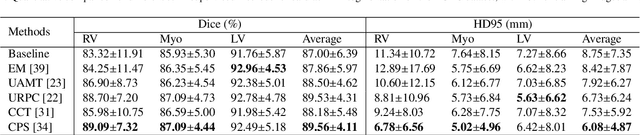
Abstract:Background and Objective: Existing deep learning platforms for medical image segmentation mainly focus on fully supervised segmentation that assumes full and accurate pixel-level annotations are available. We aim to develop a new deep learning toolkit to support annotation-efficient learning for medical image segmentation, which can accelerate and simply the development of deep learning models with limited annotation budget, e.g., learning from partial, sparse or noisy annotations. Methods: Our proposed toolkit named PyMIC is a modular deep learning platform for medical image segmentation tasks. In addition to basic components that support development of high-performance models for fully supervised segmentation, it contains several advanced components that are tailored for learning from imperfect annotations, such as loading annotated and unannounced images, loss functions for unannotated, partially or inaccurately annotated images, and training procedures for co-learning between multiple networks, etc. PyMIC is built on the PyTorch framework and supports development of semi-supervised, weakly supervised and noise-robust learning methods for medical image segmentation. Results: We present four illustrative medical image segmentation tasks based on PyMIC: (1) Achieving competitive performance on fully supervised learning; (2) Semi-supervised cardiac structure segmentation with only 10% training images annotated; (3) Weakly supervised segmentation using scribble annotations; and (4) Learning from noisy labels for chest radiograph segmentation. Conclusions: The PyMIC toolkit is easy to use and facilitates efficient development of medical image segmentation models with imperfect annotations. It is modular and flexible, which enables researchers to develop high-performance models with low annotation cost. The source code is available at: https://github.com/HiLab-git/PyMIC.
Contrastive Semi-supervised Learning for Domain Adaptive Segmentation Across Similar Anatomical Structures
Aug 18, 2022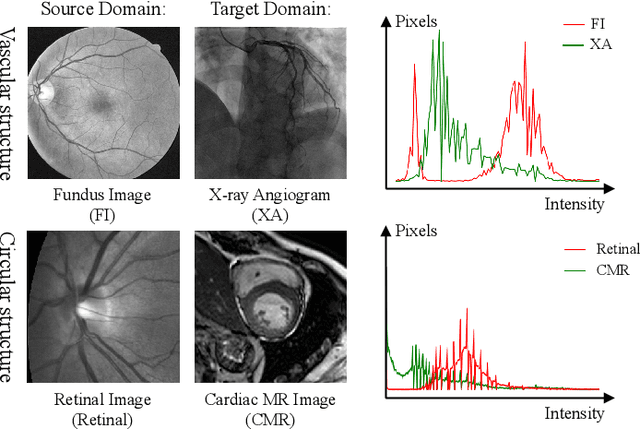
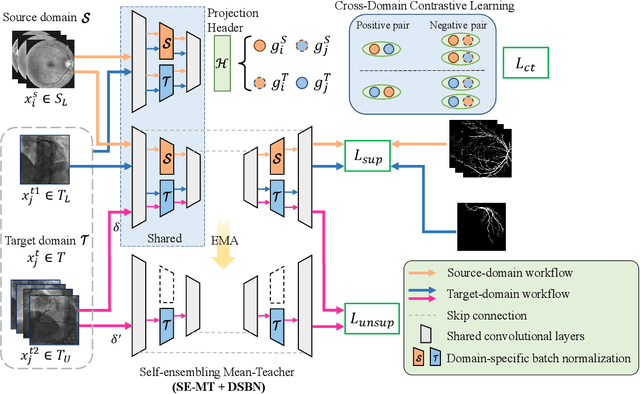
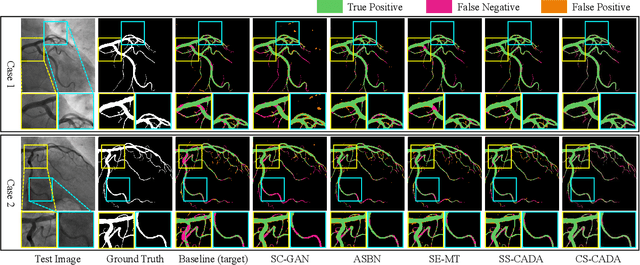
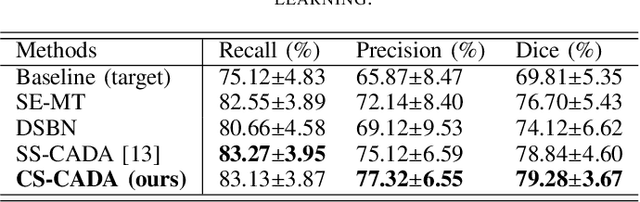
Abstract:Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance for medical image segmentation, yet need plenty of manual annotations for training. Semi-Supervised Learning (SSL) methods are promising to reduce the requirement of annotations, but their performance is still limited when the dataset size and the number of annotated images are small. Leveraging existing annotated datasets with similar anatomical structures to assist training has a potential for improving the model's performance. However, it is further challenged by the cross-anatomy domain shift due to the different appearance and even imaging modalities from the target structure. To solve this problem, we propose Contrastive Semi-supervised learning for Cross Anatomy Domain Adaptation (CS-CADA) that adapts a model to segment similar structures in a target domain, which requires only limited annotations in the target domain by leveraging a set of existing annotated images of similar structures in a source domain. We use Domain-Specific Batch Normalization (DSBN) to individually normalize feature maps for the two anatomical domains, and propose a cross-domain contrastive learning strategy to encourage extracting domain invariant features. They are integrated into a Self-Ensembling Mean-Teacher (SE-MT) framework to exploit unlabeled target domain images with a prediction consistency constraint. Extensive experiments show that our CS-CADA is able to solve the challenging cross-anatomy domain shift problem, achieving accurate segmentation of coronary arteries in X-ray images with the help of retinal vessel images and cardiac MR images with the help of fundus images, respectively, given only a small number of annotations in the target domain.
Learning towards Synchronous Network Memorizability and Generalizability for Continual Segmentation across Multiple Sites
Jun 14, 2022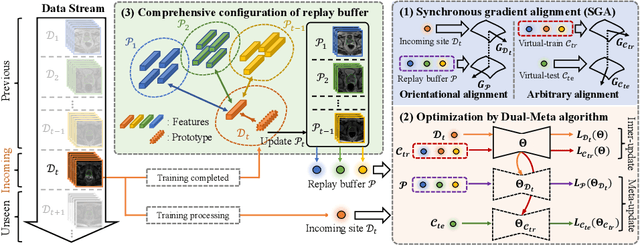
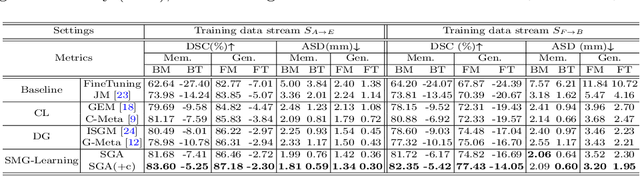
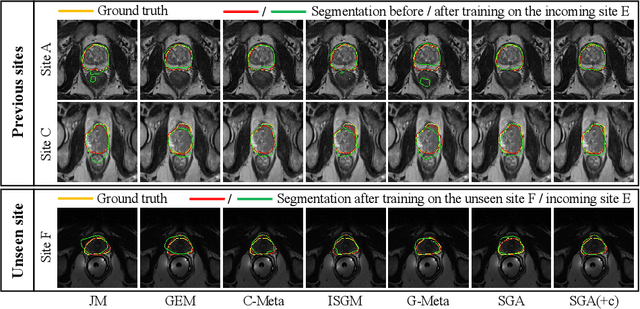
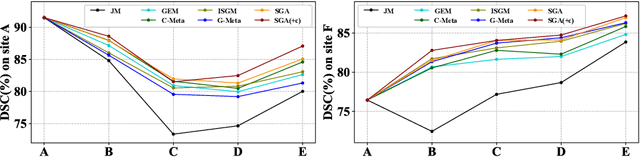
Abstract:In clinical practice, a segmentation network is often required to continually learn on a sequential data stream from multiple sites rather than a consolidated set, due to the storage cost and privacy restriction. However, during the continual learning process, existing methods are usually restricted in either network memorizability on previous sites or generalizability on unseen sites. This paper aims to tackle the challenging problem of Synchronous Memorizability and Generalizability (SMG) and to simultaneously improve performance on both previous and unseen sites, with a novel proposed SMG-learning framework. First, we propose a Synchronous Gradient Alignment (SGA) objective, which \emph{not only} promotes the network memorizability by enforcing coordinated optimization for a small exemplar set from previous sites (called replay buffer), \emph{but also} enhances the generalizability by facilitating site-invariance under simulated domain shift. Second, to simplify the optimization of SGA objective, we design a Dual-Meta algorithm that approximates the SGA objective as dual meta-objectives for optimization without expensive computation overhead. Third, for efficient rehearsal, we configure the replay buffer comprehensively considering additional inter-site diversity to reduce redundancy. Experiments on prostate MRI data sequentially acquired from six institutes demonstrate that our method can simultaneously achieve higher memorizability and generalizability over state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/jingyzhang/SMG-Learning.
Contrastive Domain Disentanglement for Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
May 13, 2022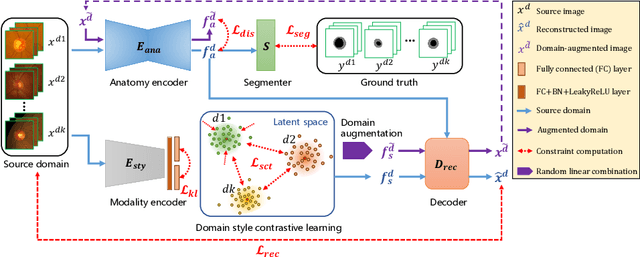
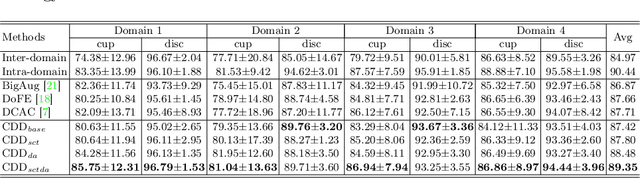
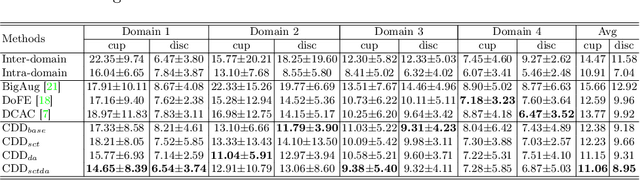
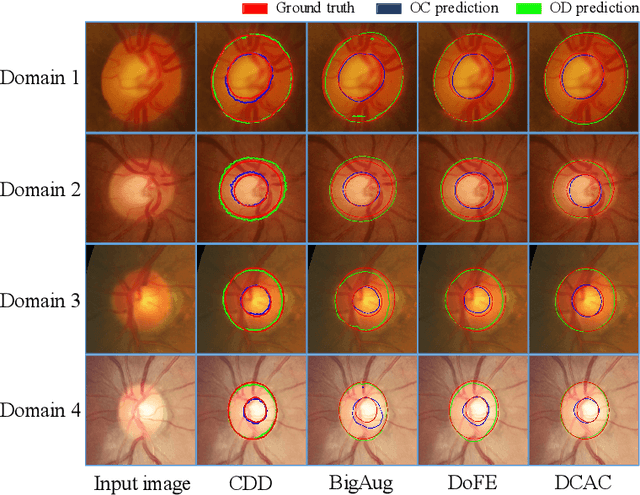
Abstract:Efficiently utilizing discriminative features is crucial for convolutional neural networks to achieve remarkable performance in medical image segmentation and is also important for model generalization across multiple domains, where letting model recognize domain-specific and domain-invariant information among multi-site datasets is a reasonable strategy for domain generalization. Unfortunately, most of the recent disentangle networks are not directly adaptable to unseen-domain datasets because of the limitations of offered data distribution. To tackle this deficiency, we propose Contrastive Domain Disentangle (CDD) network for generalizable medical image segmentation. We first introduce a disentangle network to decompose medical images into an anatomical representation factor and a modality representation factor. Then, a style contrastive loss is proposed to encourage the modality representations from the same domain to distribute as close as possible while different domains are estranged from each other. Finally, we propose a domain augmentation strategy that can randomly generate new domains for model generalization training. Experimental results on multi-site fundus image datasets for optic cup and disc segmentation show that the CDD has good model generalization. Our proposed CDD outperforms several state-of-the-art methods in domain generalizable segmentation.
One-shot Weakly-Supervised Segmentation in Medical Images
Nov 21, 2021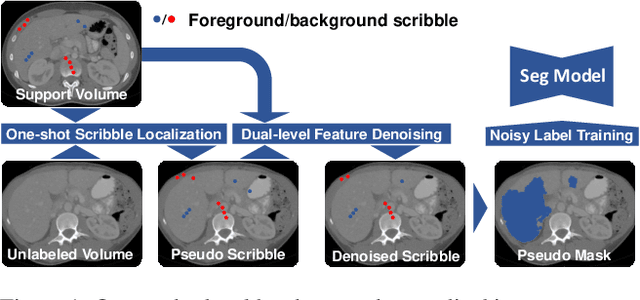
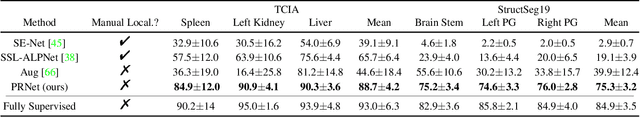
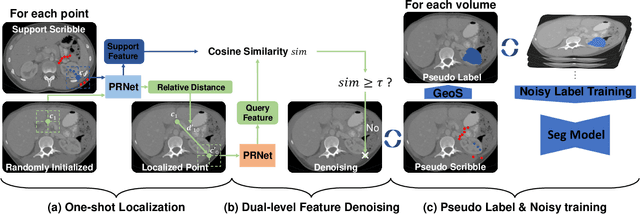
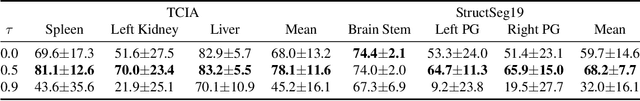
Abstract:Deep neural networks usually require accurate and a large number of annotations to achieve outstanding performance in medical image segmentation. One-shot segmentation and weakly-supervised learning are promising research directions that lower labeling effort by learning a new class from only one annotated image and utilizing coarse labels instead, respectively. Previous works usually fail to leverage the anatomical structure and suffer from class imbalance and low contrast problems. Hence, we present an innovative framework for 3D medical image segmentation with one-shot and weakly-supervised settings. Firstly a propagation-reconstruction network is proposed to project scribbles from annotated volume to unlabeled 3D images based on the assumption that anatomical patterns in different human bodies are similar. Then a dual-level feature denoising module is designed to refine the scribbles based on anatomical- and pixel-level features. After expanding the scribbles to pseudo masks, we could train a segmentation model for the new class with the noisy label training strategy. Experiments on one abdomen and one head-and-neck CT dataset show the proposed method obtains significant improvement over the state-of-the-art methods and performs robustly even under severe class imbalance and low contrast.
Domain Composition and Attention for Unseen-Domain Generalizable Medical Image Segmentation
Sep 18, 2021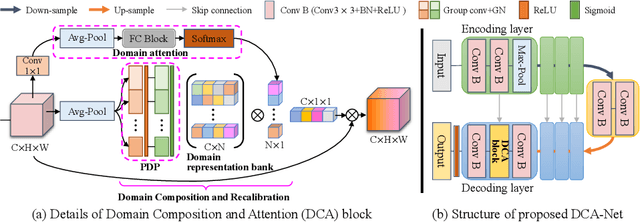
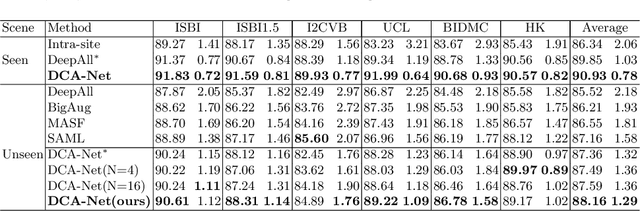
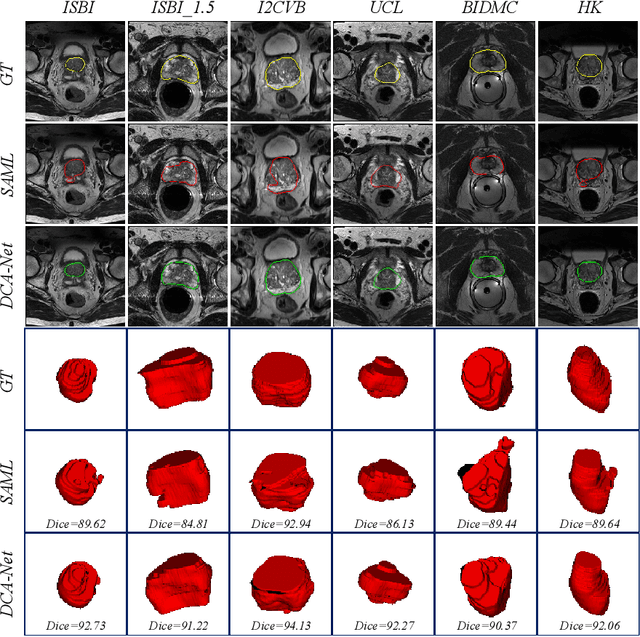
Abstract:Domain generalizable model is attracting increasing attention in medical image analysis since data is commonly acquired from different institutes with various imaging protocols and scanners. To tackle this challenging domain generalization problem, we propose a Domain Composition and Attention-based network (DCA-Net) to improve the ability of domain representation and generalization. First, we present a domain composition method that represents one certain domain by a linear combination of a set of basis representations (i.e., a representation bank). Second, a novel plug-and-play parallel domain preceptor is proposed to learn these basis representations and we introduce a divergence constraint function to encourage the basis representations to be as divergent as possible. Then, a domain attention module is proposed to learn the linear combination coefficients of the basis representations. The result of linear combination is used to calibrate the feature maps of an input image, which enables the model to generalize to different and even unseen domains. We validate our method on public prostate MRI dataset acquired from six different institutions with apparent domain shift. Experimental results show that our proposed model can generalize well on different and even unseen domains and it outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the multi-domain prostate segmentation task.
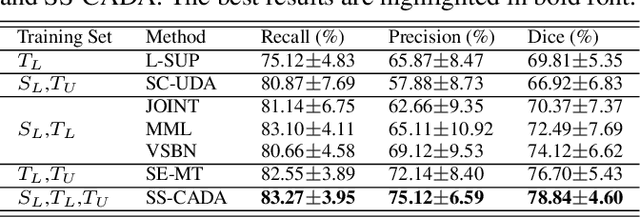
SS-CADA: A Semi-Supervised Cross-Anatomy Domain Adaptation for Coronary Artery Segmentation
May 06, 2021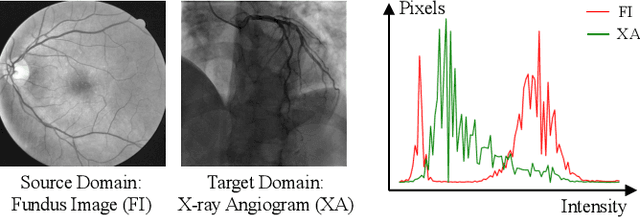

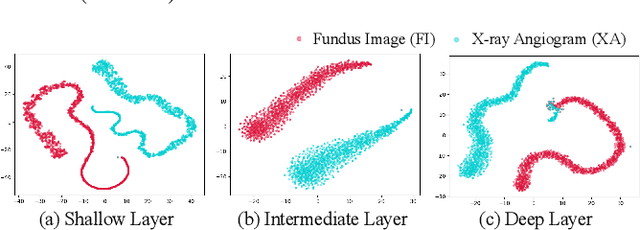
Abstract:The segmentation of coronary arteries by convolutional neural network is promising yet requires a large amount of labor-intensive manual annotations. Transferring knowledge from retinal vessels in widely-available public labeled fundus images (FIs) has a potential to reduce the annotation requirement for coronary artery segmentation in X-ray angiograms (XAs) due to their common tubular structures. However, it is challenged by the cross-anatomy domain shift due to the intrinsically different vesselness characteristics in different anatomical regions under even different imaging protocols. To solve this problem, we propose a Semi-Supervised Cross-Anatomy Domain Adaptation (SS-CADA) which requires only limited annotations for coronary arteries in XAs. With the supervision from a small number of labeled XAs and publicly available labeled FIs, we propose a vesselness-specific batch normalization (VSBN) to individually normalize feature maps for them considering their different cross-anatomic vesselness characteristics. In addition, to further facilitate the annotation efficiency, we employ a self-ensembling mean-teacher (SEMT) to exploit abundant unlabeled XAs by imposing a prediction consistency constraint. Extensive experiments show that our SS-CADA is able to solve the challenging cross-anatomy domain shift, achieving accurate segmentation for coronary arteries given only a small number of labeled XAs.
Automatic Segmentation of Organs-at-Risk from Head-and-Neck CT using Separable Convolutional Neural Network with Hard-Region-Weighted Loss
Feb 03, 2021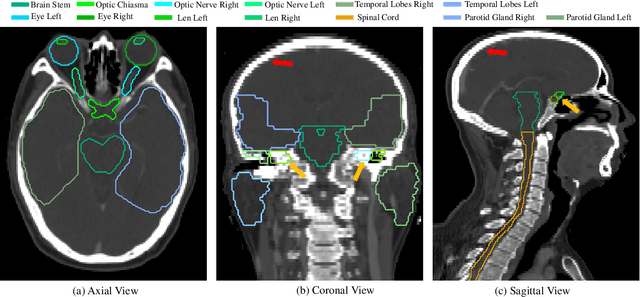
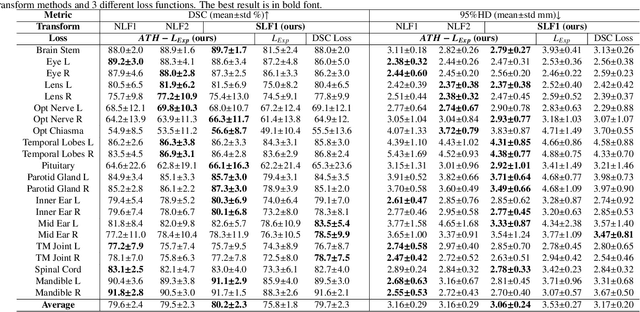
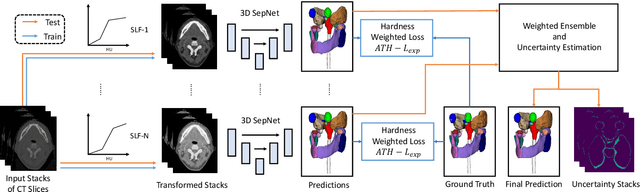
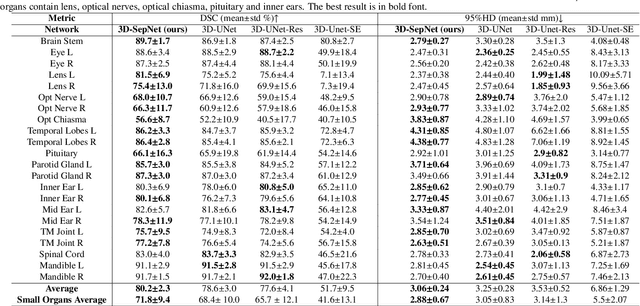
Abstract:Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC) is a leading form of Head-and-Neck (HAN) cancer in the Arctic, China, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East/North Africa. Accurate segmentation of Organs-at-Risk (OAR) from Computed Tomography (CT) images with uncertainty information is critical for effective planning of radiation therapy for NPC treatment. Despite the stateof-the-art performance achieved by Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for automatic segmentation of OARs, existing methods do not provide uncertainty estimation of the segmentation results for treatment planning, and their accuracy is still limited by several factors, including the low contrast of soft tissues in CT, highly imbalanced sizes of OARs and large inter-slice spacing. To address these problems, we propose a novel framework for accurate OAR segmentation with reliable uncertainty estimation. First, we propose a Segmental Linear Function (SLF) to transform the intensity of CT images to make multiple organs more distinguishable than existing methods based on a simple window width/level that often gives a better visibility of one organ while hiding the others. Second, to deal with the large inter-slice spacing, we introduce a novel 2.5D network (named as 3D-SepNet) specially designed for dealing with clinic HAN CT scans with anisotropic spacing. Thirdly, existing hardness-aware loss function often deal with class-level hardness, but our proposed attention to hard voxels (ATH) uses a voxel-level hardness strategy, which is more suitable to dealing with some hard regions despite that its corresponding class may be easy. Our code is now available at https://github.com/HiLab-git/SepNet.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge