SS-CADA: A Semi-Supervised Cross-Anatomy Domain Adaptation for Coronary Artery Segmentation
Paper and Code
May 06, 2021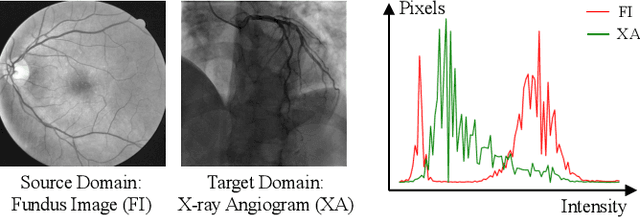
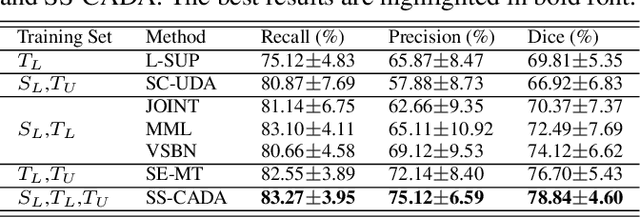

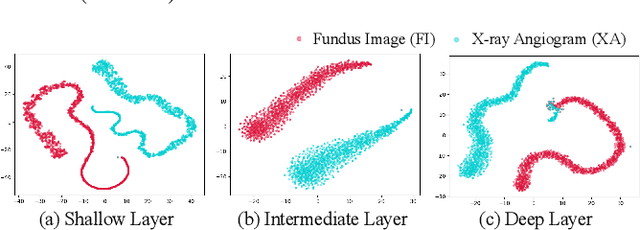
The segmentation of coronary arteries by convolutional neural network is promising yet requires a large amount of labor-intensive manual annotations. Transferring knowledge from retinal vessels in widely-available public labeled fundus images (FIs) has a potential to reduce the annotation requirement for coronary artery segmentation in X-ray angiograms (XAs) due to their common tubular structures. However, it is challenged by the cross-anatomy domain shift due to the intrinsically different vesselness characteristics in different anatomical regions under even different imaging protocols. To solve this problem, we propose a Semi-Supervised Cross-Anatomy Domain Adaptation (SS-CADA) which requires only limited annotations for coronary arteries in XAs. With the supervision from a small number of labeled XAs and publicly available labeled FIs, we propose a vesselness-specific batch normalization (VSBN) to individually normalize feature maps for them considering their different cross-anatomic vesselness characteristics. In addition, to further facilitate the annotation efficiency, we employ a self-ensembling mean-teacher (SEMT) to exploit abundant unlabeled XAs by imposing a prediction consistency constraint. Extensive experiments show that our SS-CADA is able to solve the challenging cross-anatomy domain shift, achieving accurate segmentation for coronary arteries given only a small number of labeled XAs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge