Yijie Qu
University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, China
Weakly Supervised Lymph Nodes Segmentation Based on Partial Instance Annotations with Pre-trained Dual-branch Network and Pseudo Label Learning
Aug 18, 2024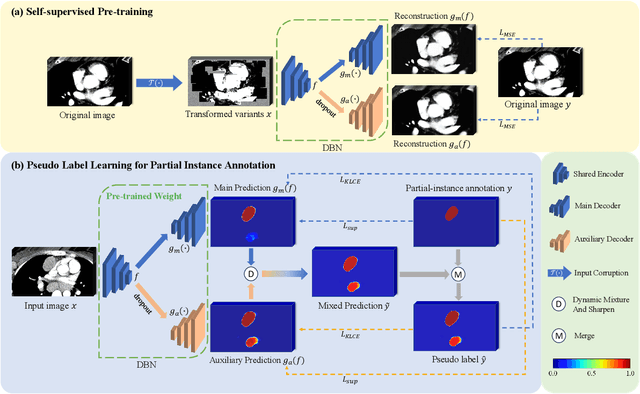
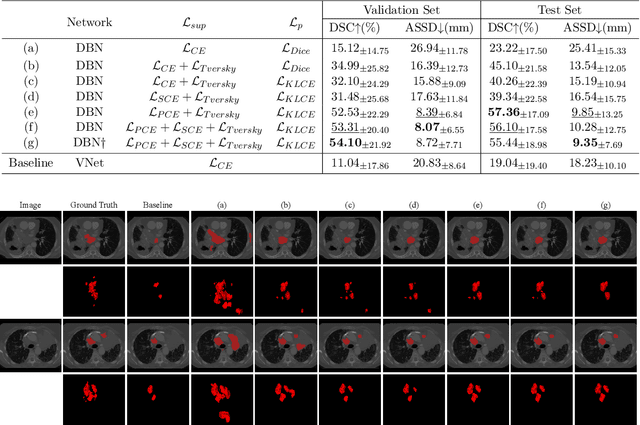
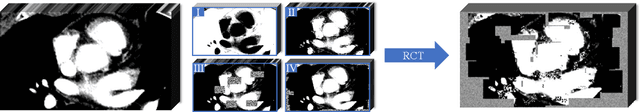
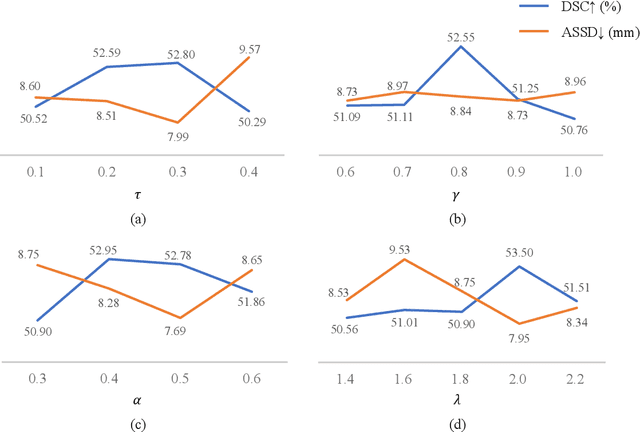
Abstract:Assessing the presence of potentially malignant lymph nodes aids in estimating cancer progression, and identifying surrounding benign lymph nodes can assist in determining potential metastatic pathways for cancer. For quantitative analysis, automatic segmentation of lymph nodes is crucial. However, due to the labor-intensive and time-consuming manual annotation process required for a large number of lymph nodes, it is more practical to annotate only a subset of the lymph node instances to reduce annotation costs. In this study, we propose a pre-trained Dual-Branch network with Dynamically Mixed Pseudo label (DBDMP) to learn from partial instance annotations for lymph nodes segmentation. To obtain reliable pseudo labels for lymph nodes that are not annotated, we employ a dual-decoder network to generate different outputs that are then dynamically mixed. We integrate the original weak partial annotations with the mixed pseudo labels to supervise the network. To further leverage the extensive amount of unannotated voxels, we apply a self-supervised pre-training strategy to enhance the model's feature extraction capability. Experiments on the mediastinal Lymph Node Quantification (LNQ) dataset demonstrate that our method, compared to directly learning from partial instance annotations, significantly improves the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) from 11.04% to 54.10% and reduces the Average Symmetric Surface Distance (ASSD) from 20.83 $mm$ to 8.72 $mm$. The code is available at https://github.com/WltyBY/LNQ2023_training_code.git
* Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2024:013
PyMIC: A deep learning toolkit for annotation-efficient medical image segmentation
Aug 19, 2022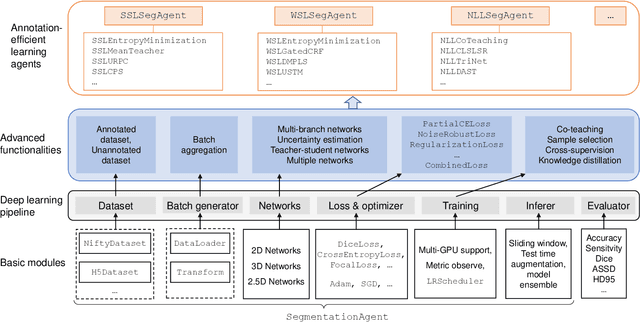
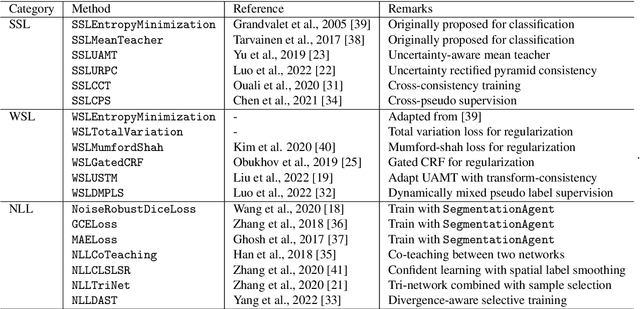
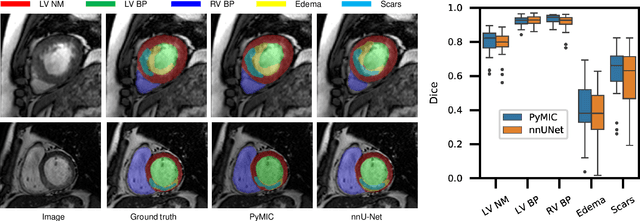
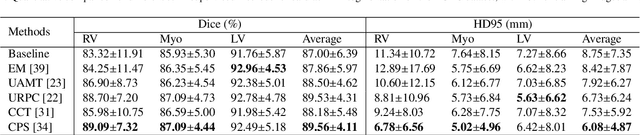
Abstract:Background and Objective: Existing deep learning platforms for medical image segmentation mainly focus on fully supervised segmentation that assumes full and accurate pixel-level annotations are available. We aim to develop a new deep learning toolkit to support annotation-efficient learning for medical image segmentation, which can accelerate and simply the development of deep learning models with limited annotation budget, e.g., learning from partial, sparse or noisy annotations. Methods: Our proposed toolkit named PyMIC is a modular deep learning platform for medical image segmentation tasks. In addition to basic components that support development of high-performance models for fully supervised segmentation, it contains several advanced components that are tailored for learning from imperfect annotations, such as loading annotated and unannounced images, loss functions for unannotated, partially or inaccurately annotated images, and training procedures for co-learning between multiple networks, etc. PyMIC is built on the PyTorch framework and supports development of semi-supervised, weakly supervised and noise-robust learning methods for medical image segmentation. Results: We present four illustrative medical image segmentation tasks based on PyMIC: (1) Achieving competitive performance on fully supervised learning; (2) Semi-supervised cardiac structure segmentation with only 10% training images annotated; (3) Weakly supervised segmentation using scribble annotations; and (4) Learning from noisy labels for chest radiograph segmentation. Conclusions: The PyMIC toolkit is easy to use and facilitates efficient development of medical image segmentation models with imperfect annotations. It is modular and flexible, which enables researchers to develop high-performance models with low annotation cost. The source code is available at: https://github.com/HiLab-git/PyMIC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge