Shuwei Zhai
PyMIC: A deep learning toolkit for annotation-efficient medical image segmentation
Aug 19, 2022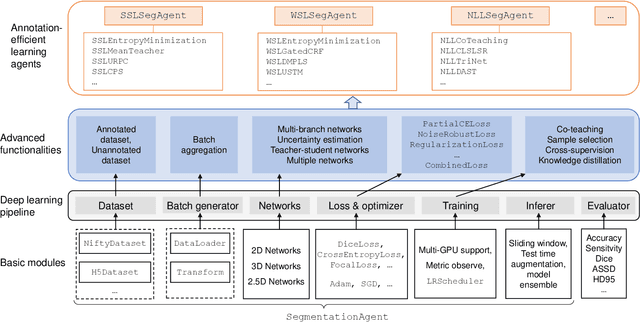
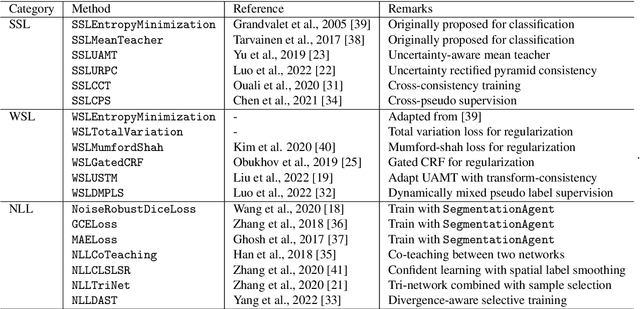
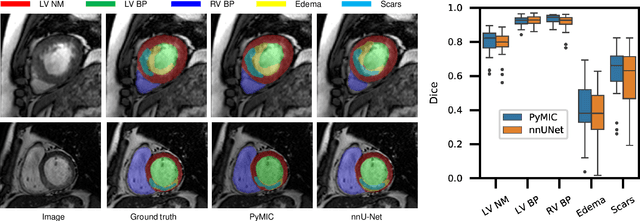
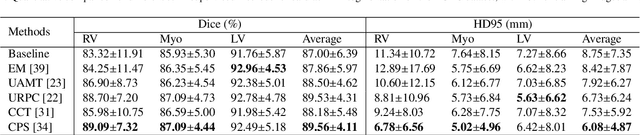
Abstract:Background and Objective: Existing deep learning platforms for medical image segmentation mainly focus on fully supervised segmentation that assumes full and accurate pixel-level annotations are available. We aim to develop a new deep learning toolkit to support annotation-efficient learning for medical image segmentation, which can accelerate and simply the development of deep learning models with limited annotation budget, e.g., learning from partial, sparse or noisy annotations. Methods: Our proposed toolkit named PyMIC is a modular deep learning platform for medical image segmentation tasks. In addition to basic components that support development of high-performance models for fully supervised segmentation, it contains several advanced components that are tailored for learning from imperfect annotations, such as loading annotated and unannounced images, loss functions for unannotated, partially or inaccurately annotated images, and training procedures for co-learning between multiple networks, etc. PyMIC is built on the PyTorch framework and supports development of semi-supervised, weakly supervised and noise-robust learning methods for medical image segmentation. Results: We present four illustrative medical image segmentation tasks based on PyMIC: (1) Achieving competitive performance on fully supervised learning; (2) Semi-supervised cardiac structure segmentation with only 10% training images annotated; (3) Weakly supervised segmentation using scribble annotations; and (4) Learning from noisy labels for chest radiograph segmentation. Conclusions: The PyMIC toolkit is easy to use and facilitates efficient development of medical image segmentation models with imperfect annotations. It is modular and flexible, which enables researchers to develop high-performance models with low annotation cost. The source code is available at: https://github.com/HiLab-git/PyMIC.
PA-Seg: Learning from Point Annotations for 3D Medical Image Segmentation using Contextual Regularization and Cross Knowledge Distillation
Aug 11, 2022



Abstract:The success of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in 3D medical image segmentation relies on massive fully annotated 3D volumes for training that are time-consuming and labor-intensive to acquire. In this paper, we propose to annotate a segmentation target with only seven points in 3D medical images, and design a two-stage weakly supervised learning framework PA-Seg. In the first stage, we employ geodesic distance transform to expand the seed points to provide more supervision signal. To further deal with unannotated image regions during training, we propose two contextual regularization strategies, i.e., multi-view Conditional Random Field (mCRF) loss and Variance Minimization (VM) loss, where the first one encourages pixels with similar features to have consistent labels, and the second one minimizes the intensity variance for the segmented foreground and background, respectively. In the second stage, we use predictions obtained by the model pre-trained in the first stage as pseudo labels. To overcome noises in the pseudo labels, we introduce a Self and Cross Monitoring (SCM) strategy, which combines self-training with Cross Knowledge Distillation (CKD) between a primary model and an auxiliary model that learn from soft labels generated by each other. Experiments on public datasets for Vestibular Schwannoma (VS) segmentation and Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) demonstrated that our model trained in the first stage outperforms existing state-of-the-art weakly supervised approaches by a large margin, and after using SCM for additional training, the model can achieve competitive performance compared with the fully supervised counterpart on the BraTS dataset.
Scribble-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation via Dual-Branch Network and Dynamically Mixed Pseudo Labels Supervision
Mar 04, 2022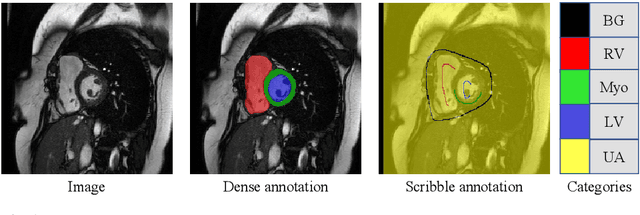
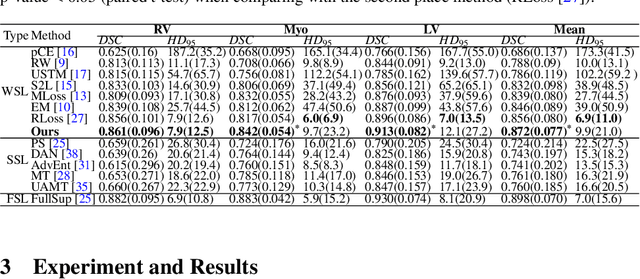
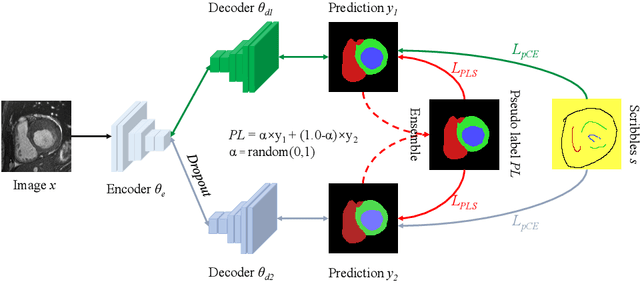
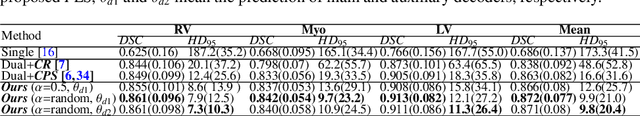
Abstract:Medical image segmentation plays an irreplaceable role in computer-assisted diagnosis, treatment planning, and following-up. Collecting and annotating a large-scale dataset is crucial to training a powerful segmentation model, but producing high-quality segmentation masks is an expensive and time-consuming procedure. Recently, weakly-supervised learning that uses sparse annotations (points, scribbles, bounding boxes) for network training has achieved encouraging performance and shown the potential for annotation cost reduction. However, due to the limited supervision signal of sparse annotations, it is still challenging to employ them for networks training directly. In this work, we propose a simple yet efficient scribble-supervised image segmentation method and apply it to cardiac MRI segmentation. Specifically, we employ a dual-branch network with one encoder and two slightly different decoders for image segmentation and dynamically mix the two decoders' predictions to generate pseudo labels for auxiliary supervision. By combining the scribble supervision and auxiliary pseudo labels supervision, the dual-branch network can efficiently learn from scribble annotations end-to-end. Experiments on the public ACDC dataset show that our method performs better than current scribble-supervised segmentation methods and also outperforms several semi-supervised segmentation methods.
MyoPS: A Benchmark of Myocardial Pathology Segmentation Combining Three-Sequence Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Jan 10, 2022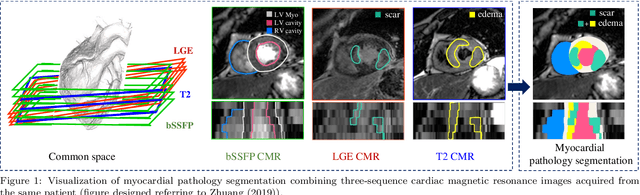
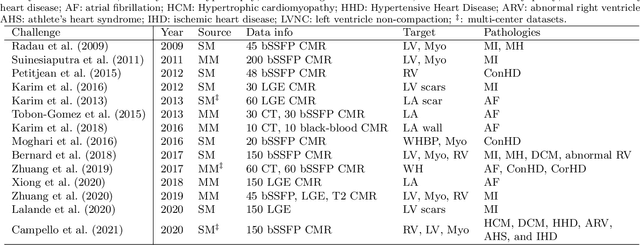
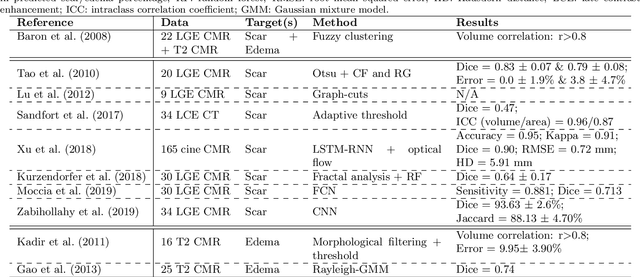
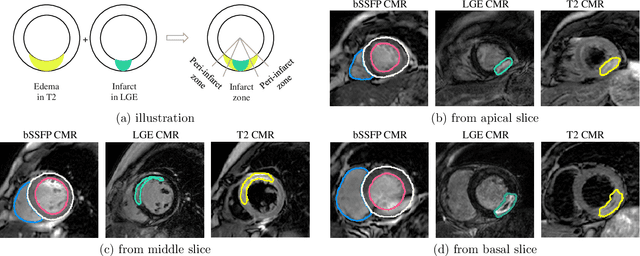
Abstract:Assessment of myocardial viability is essential in diagnosis and treatment management of patients suffering from myocardial infarction, and classification of pathology on myocardium is the key to this assessment. This work defines a new task of medical image analysis, i.e., to perform myocardial pathology segmentation (MyoPS) combining three-sequence cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images, which was first proposed in the MyoPS challenge, in conjunction with MICCAI 2020. The challenge provided 45 paired and pre-aligned CMR images, allowing algorithms to combine the complementary information from the three CMR sequences for pathology segmentation. In this article, we provide details of the challenge, survey the works from fifteen participants and interpret their methods according to five aspects, i.e., preprocessing, data augmentation, learning strategy, model architecture and post-processing. In addition, we analyze the results with respect to different factors, in order to examine the key obstacles and explore potential of solutions, as well as to provide a benchmark for future research. We conclude that while promising results have been reported, the research is still in the early stage, and more in-depth exploration is needed before a successful application to the clinics. Note that MyoPS data and evaluation tool continue to be publicly available upon registration via its homepage (www.sdspeople.fudan.edu.cn/zhuangxiahai/0/myops20/).
Semi-Supervised Segmentation of Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis from Lung CT Scans with Multi-Scale Guided Dense Attention
Sep 29, 2021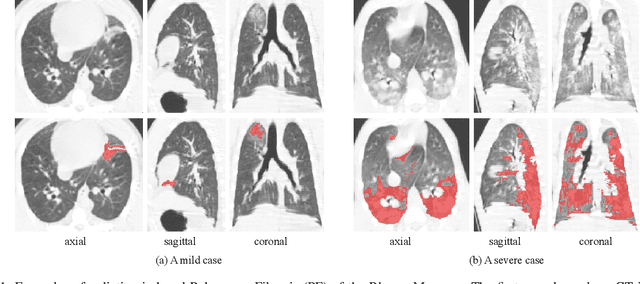
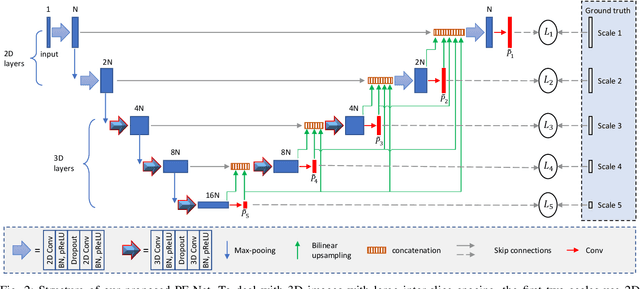
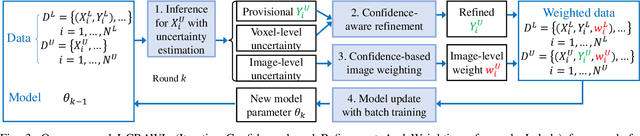
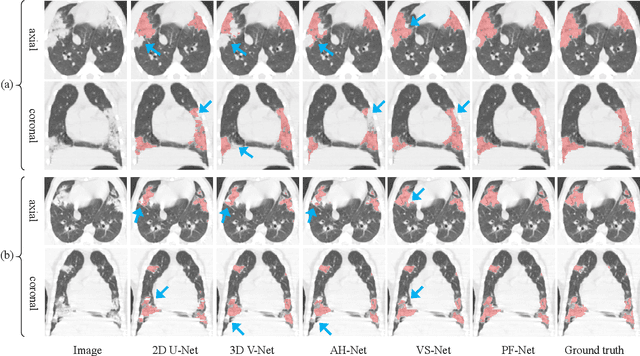
Abstract:Computed Tomography (CT) plays an important role in monitoring radiation-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis (PF), where accurate segmentation of the PF lesions is highly desired for diagnosis and treatment follow-up. However, the task is challenged by ambiguous boundary, irregular shape, various position and size of the lesions, as well as the difficulty in acquiring a large set of annotated volumetric images for training. To overcome these problems, we propose a novel convolutional neural network called PF-Net and incorporate it into a semi-supervised learning framework based on Iterative Confidence-based Refinement And Weighting of pseudo Labels (I-CRAWL). Our PF-Net combines 2D and 3D convolutions to deal with CT volumes with large inter-slice spacing, and uses multi-scale guided dense attention to segment complex PF lesions. For semi-supervised learning, our I-CRAWL employs pixel-level uncertainty-based confidence-aware refinement to improve the accuracy of pseudo labels of unannotated images, and uses image-level uncertainty for confidence-based image weighting to suppress low-quality pseudo labels in an iterative training process. Extensive experiments with CT scans of Rhesus Macaques with radiation-induced PF showed that: 1) PF-Net achieved higher segmentation accuracy than existing 2D, 3D and 2.5D neural networks, and 2) I-CRAWL outperformed state-of-the-art semi-supervised learning methods for the PF lesion segmentation task. Our method has a potential to improve the diagnosis of PF and clinical assessment of side effects of radiotherapy for lung cancers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge