Fuping Wu
Emerging Semantic Segmentation from Positive and Negative Coarse Label Learning
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Large annotated datasets are vital for training segmentation models, but pixel-level labeling is time-consuming, error-prone, and often requires scarce expert annotators, especially in medical imaging. In contrast, coarse annotations are quicker, cheaper, and easier to produce, even by non-experts. In this paper, we propose to use coarse drawings from both positive (target) and negative (background) classes in the image, even with noisy pixels, to train a convolutional neural network (CNN) for semantic segmentation. We present a method for learning the true segmentation label distributions from purely noisy coarse annotations using two coupled CNNs. The separation of the two CNNs is achieved by high fidelity with the characters of the noisy training annotations. We propose to add a complementary label learning that encourages estimating negative label distribution. To illustrate the properties of our method, we first use a toy segmentation dataset based on MNIST. We then present the quantitative results of experiments using publicly available datasets: Cityscapes dataset for multi-class segmentation, and retinal images for medical applications. In all experiments, our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in the cases where the ratio of coarse annotations is small compared to the given dense annotations.
Rethinking Foundation Models for Medical Image Classification through a Benchmark Study on MedMNIST
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models are widely employed in medical image analysis, due to their high adaptability and generalizability for downstream tasks. With the increasing number of foundation models being released, model selection has become an important issue. In this work, we study the capabilities of foundation models in medical image classification tasks by conducting a benchmark study on the MedMNIST dataset. Specifically, we adopt various foundation models ranging from convolutional to Transformer-based models and implement both end-to-end training and linear probing for all classification tasks. The results demonstrate the significant potential of these pre-trained models when transferred for medical image classification. We further conduct experiments with different image sizes and various sizes of training data. By analyzing all the results, we provide preliminary, yet useful insights and conclusions on this topic.
InDeed: Interpretable image deep decomposition with guaranteed generalizability
Jan 02, 2025



Abstract:Image decomposition aims to analyze an image into elementary components, which is essential for numerous downstream tasks and also by nature provides certain interpretability to the analysis. Deep learning can be powerful for such tasks, but surprisingly their combination with a focus on interpretability and generalizability is rarely explored. In this work, we introduce a novel framework for interpretable deep image decomposition, combining hierarchical Bayesian modeling and deep learning to create an architecture-modularized and model-generalizable deep neural network (DNN). The proposed framework includes three steps: (1) hierarchical Bayesian modeling of image decomposition, (2) transforming the inference problem into optimization tasks, and (3) deep inference via a modularized Bayesian DNN. We further establish a theoretical connection between the loss function and the generalization error bound, which inspires a new test-time adaptation approach for out-of-distribution scenarios. We instantiated the application using two downstream tasks, \textit{i.e.}, image denoising, and unsupervised anomaly detection, and the results demonstrated improved generalizability as well as interpretability of our methods. The source code will be released upon the acceptance of this paper.
KneeXNeT: An Ensemble-Based Approach for Knee Radiographic Evaluation
Dec 10, 2024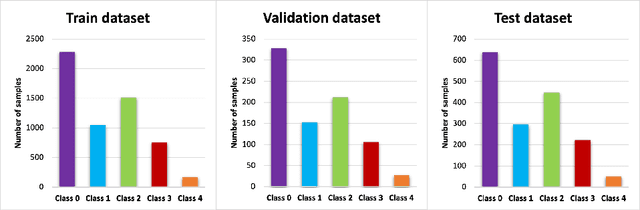
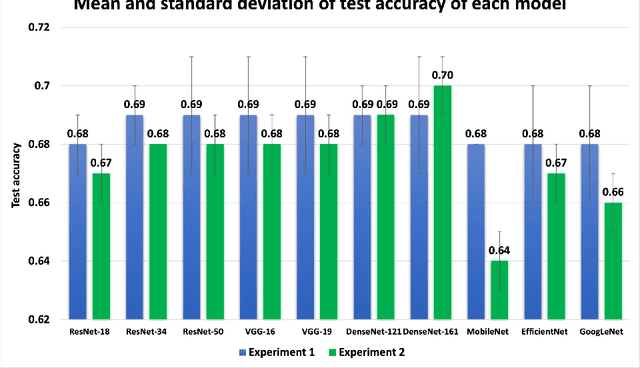
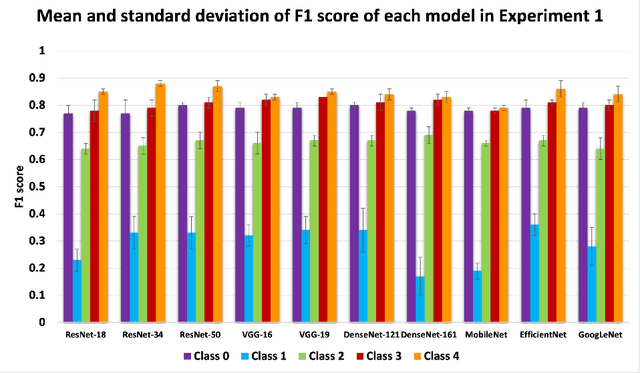
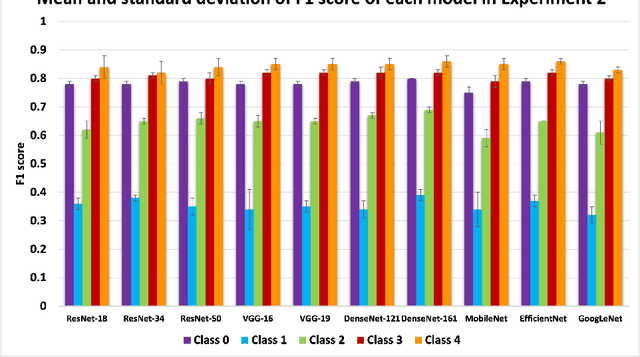
Abstract:Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disorder and a leading cause of disability. Diagnosing OA severity typically requires expert assessment of X-ray images and is commonly based on the Kellgren-Lawrence grading system, a time-intensive process. This study aimed to develop an automated deep learning model to classify knee OA severity, reducing the need for expert evaluation. First, we evaluated ten state-of-the-art deep learning models, achieving a top accuracy of 0.69 with individual models. To address class imbalance, we employed weighted sampling, improving accuracy to 0.70. We further applied Smooth-GradCAM++ to visualize decision-influencing regions, enhancing the explainability of the best-performing model. Finally, we developed ensemble models using majority voting and a shallow neural network. Our ensemble model, KneeXNet, achieved the highest accuracy of 0.72, demonstrating its potential as an automated tool for knee OA assessment.
Deformation-Recovery Diffusion Model (DRDM): Instance Deformation for Image Manipulation and Synthesis
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:In medical imaging, the diffusion models have shown great potential in synthetic image generation tasks. However, these models often struggle with the interpretable connections between the generated and existing images and could create illusions. To address these challenges, our research proposes a novel diffusion-based generative model based on deformation diffusion and recovery. This model, named Deformation-Recovery Diffusion Model (DRDM), diverges from traditional score/intensity and latent feature-based approaches, emphasizing morphological changes through deformation fields rather than direct image synthesis. This is achieved by introducing a topological-preserving deformation field generation method, which randomly samples and integrates a set of multi-scale Deformation Vector Fields (DVF). DRDM is trained to learn to recover unreasonable deformation components, thereby restoring each randomly deformed image to a realistic distribution. These innovations facilitate the generation of diverse and anatomically plausible deformations, enhancing data augmentation and synthesis for further analysis in downstream tasks, such as few-shot learning and image registration. Experimental results in cardiac MRI and pulmonary CT show DRDM is capable of creating diverse, large (over 10% image size deformation scale), and high-quality (negative ratio of folding rate is lower than 1%) deformation fields. The further experimental results in downstream tasks, 2D image segmentation and 3D image registration, indicate significant improvements resulting from DRDM, showcasing the potential of our model to advance image manipulation and synthesis in medical imaging and beyond. Our implementation will be available at https://github.com/jianqingzheng/def_diff_rec.
MERIT: Multi-view Evidential learning for Reliable and Interpretable liver fibrosis sTaging
May 05, 2024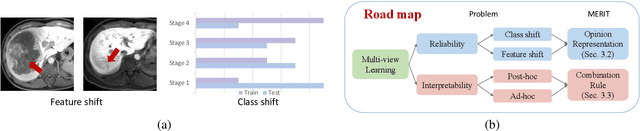
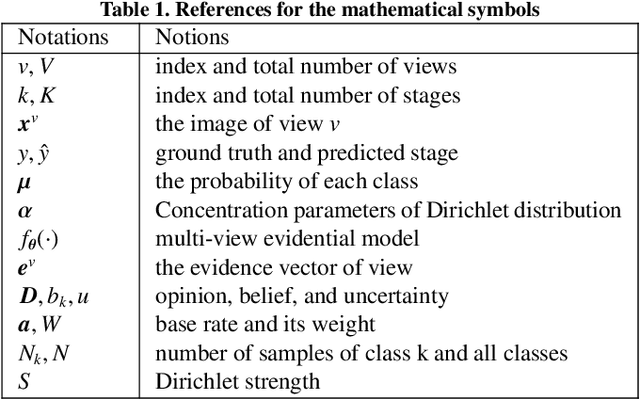
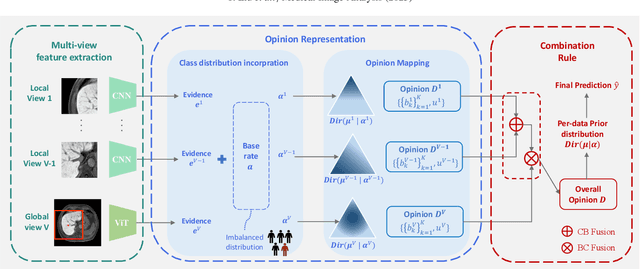
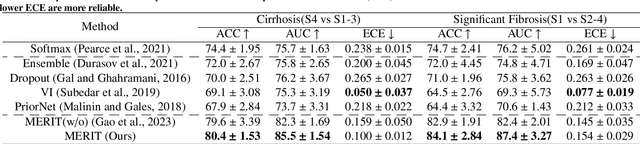
Abstract:Accurate staging of liver fibrosis from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is crucial in clinical practice. While conventional methods often focus on a specific sub-region, multi-view learning captures more information by analyzing multiple patches simultaneously. However, previous multi-view approaches could not typically calculate uncertainty by nature, and they generally integrate features from different views in a black-box fashion, hence compromising reliability as well as interpretability of the resulting models. In this work, we propose a new multi-view method based on evidential learning, referred to as MERIT, which tackles the two challenges in a unified framework. MERIT enables uncertainty quantification of the predictions to enhance reliability, and employs a logic-based combination rule to improve interpretability. Specifically, MERIT models the prediction from each sub-view as an opinion with quantified uncertainty under the guidance of the subjective logic theory. Furthermore, a distribution-aware base rate is introduced to enhance performance, particularly in scenarios involving class distribution shifts. Finally, MERIT adopts a feature-specific combination rule to explicitly fuse multi-view predictions, thereby enhancing interpretability. Results have showcased the effectiveness of the proposed MERIT, highlighting the reliability and offering both ad-hoc and post-hoc interpretability. They also illustrate that MERIT can elucidate the significance of each view in the decision-making process for liver fibrosis staging.
Multi-Task Cooperative Learning via Searching for Flat Minima
Sep 21, 2023

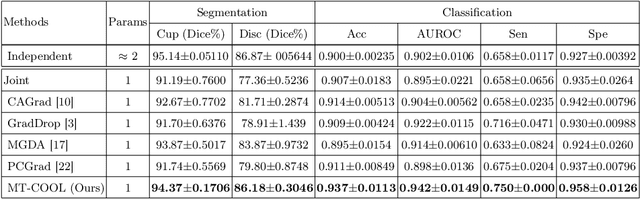

Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) has shown great potential in medical image analysis, improving the generalizability of the learned features and the performance in individual tasks. However, most of the work on MTL focuses on either architecture design or gradient manipulation, while in both scenarios, features are learned in a competitive manner. In this work, we propose to formulate MTL as a multi/bi-level optimization problem, and therefore force features to learn from each task in a cooperative approach. Specifically, we update the sub-model for each task alternatively taking advantage of the learned sub-models of the other tasks. To alleviate the negative transfer problem during the optimization, we search for flat minima for the current objective function with regard to features from other tasks. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, we validate our method on three publicly available datasets. The proposed method shows the advantage of cooperative learning, and yields promising results when compared with the state-of-the-art MTL approaches. The code will be available online.
A Reliable and Interpretable Framework of Multi-view Learning for Liver Fibrosis Staging
Jun 21, 2023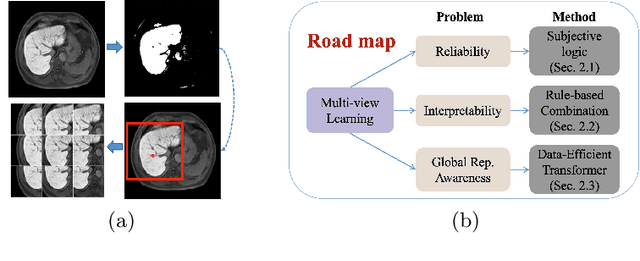
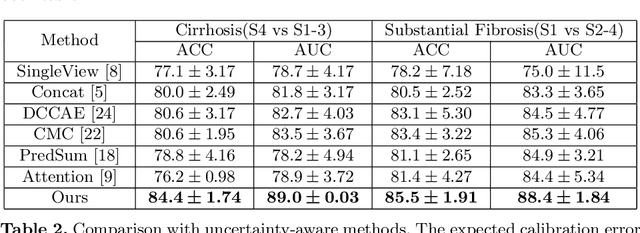
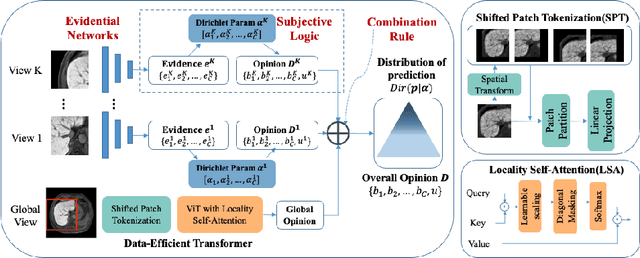
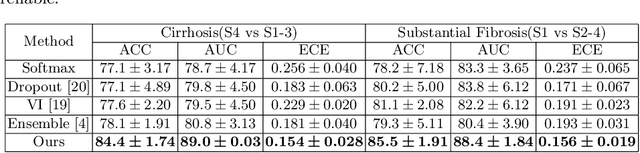
Abstract:Staging of liver fibrosis is important in the diagnosis and treatment planning of patients suffering from liver diseases. Current deep learning-based methods using abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) usually take a sub-region of the liver as an input, which nevertheless could miss critical information. To explore richer representations, we formulate this task as a multi-view learning problem and employ multiple sub-regions of the liver. Previously, features or predictions are usually combined in an implicit manner, and uncertainty-aware methods have been proposed. However, these methods could be challenged to capture cross-view representations, which can be important in the accurate prediction of staging. Therefore, we propose a reliable multi-view learning method with interpretable combination rules, which can model global representations to improve the accuracy of predictions. Specifically, the proposed method estimates uncertainties based on subjective logic to improve reliability, and an explicit combination rule is applied based on Dempster-Shafer's evidence theory with good power of interpretability. Moreover, a data-efficient transformer is introduced to capture representations in the global view. Results evaluated on enhanced MRI data show that our method delivers superior performance over existing multi-view learning methods.
Unsupervised Cardiac Segmentation Utilizing Synthesized Images from Anatomical Labels
Jan 15, 2023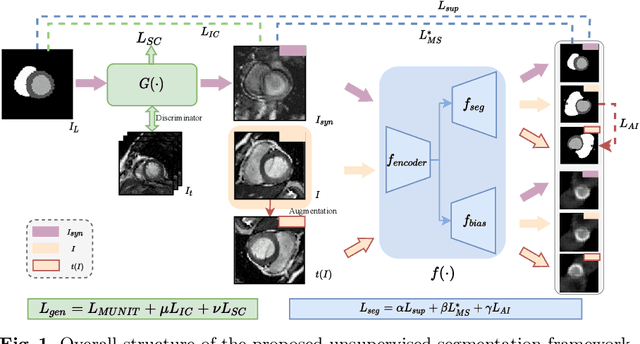
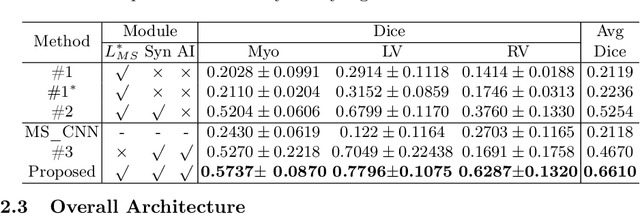
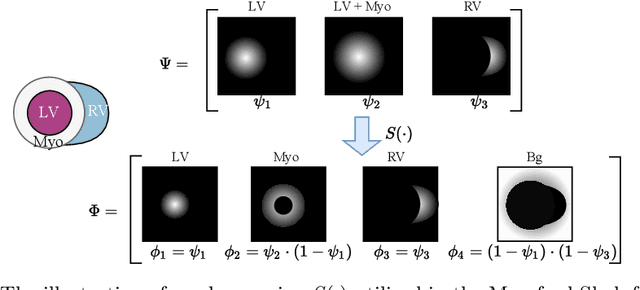
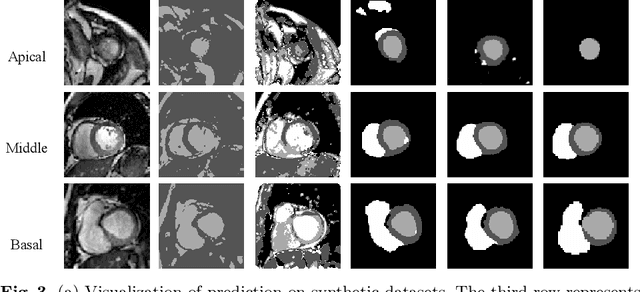
Abstract:Cardiac segmentation is in great demand for clinical practice. Due to the enormous labor of manual delineation, unsupervised segmentation is desired. The ill-posed optimization problem of this task is inherently challenging, requiring well-designed constraints. In this work, we propose an unsupervised framework for multi-class segmentation with both intensity and shape constraints. Firstly, we extend a conventional non-convex energy function as an intensity constraint and implement it with U-Net. For shape constraint, synthetic images are generated from anatomical labels via image-to-image translation, as shape supervision for the segmentation network. Moreover, augmentation invariance is applied to facilitate the segmentation network to learn the latent features in terms of shape. We evaluated the proposed framework using the public datasets from MICCAI2019 MSCMR Challenge and achieved promising results on cardiac MRIs with Dice scores of 0.5737, 0.7796, and 0.6287 in Myo, LV, and RV, respectively.
Multi-Target Landmark Detection with Incomplete Images via Reinforcement Learning and Shape Prior
Jan 13, 2023



Abstract:Medical images are generally acquired with limited field-of-view (FOV), which could lead to incomplete regions of interest (ROI), and thus impose a great challenge on medical image analysis. This is particularly evident for the learning-based multi-target landmark detection, where algorithms could be misleading to learn primarily the variation of background due to the varying FOV, failing the detection of targets. Based on learning a navigation policy, instead of predicting targets directly, reinforcement learning (RL)-based methods have the potential totackle this challenge in an efficient manner. Inspired by this, in this work we propose a multi-agent RL framework for simultaneous multi-target landmark detection. This framework is aimed to learn from incomplete or (and) complete images to form an implicit knowledge of global structure, which is consolidated during the training stage for the detection of targets from either complete or incomplete test images. To further explicitly exploit the global structural information from incomplete images, we propose to embed a shape model into the RL process. With this prior knowledge, the proposed RL model can not only localize dozens of targetssimultaneously, but also work effectively and robustly in the presence of incomplete images. We validated the applicability and efficacy of the proposed method on various multi-target detection tasks with incomplete images from practical clinics, using body dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), cardiac MRI and head CT datasets. Results showed that our method could predict whole set of landmarks with incomplete training images up to 80% missing proportion (average distance error 2.29 cm on body DXA), and could detect unseen landmarks in regions with missing image information outside FOV of target images (average distance error 6.84 mm on 3D half-head CT).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge