Bartlomiej W. Papiez
Emerging Semantic Segmentation from Positive and Negative Coarse Label Learning
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Large annotated datasets are vital for training segmentation models, but pixel-level labeling is time-consuming, error-prone, and often requires scarce expert annotators, especially in medical imaging. In contrast, coarse annotations are quicker, cheaper, and easier to produce, even by non-experts. In this paper, we propose to use coarse drawings from both positive (target) and negative (background) classes in the image, even with noisy pixels, to train a convolutional neural network (CNN) for semantic segmentation. We present a method for learning the true segmentation label distributions from purely noisy coarse annotations using two coupled CNNs. The separation of the two CNNs is achieved by high fidelity with the characters of the noisy training annotations. We propose to add a complementary label learning that encourages estimating negative label distribution. To illustrate the properties of our method, we first use a toy segmentation dataset based on MNIST. We then present the quantitative results of experiments using publicly available datasets: Cityscapes dataset for multi-class segmentation, and retinal images for medical applications. In all experiments, our method outperforms state-of-the-art methods, particularly in the cases where the ratio of coarse annotations is small compared to the given dense annotations.
Interpretable Rheumatoid Arthritis Scoring via Anatomy-aware Multiple Instance Learning
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:The Sharp/van der Heijde (SvdH) score has been widely used in clinical trials to quantify radiographic damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), but its complexity has limited its adoption in routine clinical practice. To address the inefficiency of manual scoring, this work proposes a two-stage pipeline for interpretable image-level SvdH score prediction using dual-hand radiographs. Our approach extracts disease-relevant image regions and integrates them using attention-based multiple instance learning to generate image-level features for prediction. We propose two region extraction schemes: 1) sampling image tiles most likely to contain abnormalities, and 2) cropping patches containing disease-relevant joints. With Scheme 2, our best individual score prediction model achieved a Pearson's correlation coefficient (PCC) of 0.943 and a root mean squared error (RMSE) of 15.73. Ensemble learning further boosted prediction accuracy, yielding a PCC of 0.945 and RMSE of 15.57, achieving state-of-the-art performance that is comparable to that of experienced radiologists (PCC = 0.97, RMSE = 18.75). Finally, our pipeline effectively identified and made decisions based on anatomical structures which clinicians consider relevant to RA progression.
Exploring the Effectiveness of Deep Features from Domain-Specific Foundation Models in Retinal Image Synthesis
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:The adoption of neural network models in medical imaging has been constrained by strict privacy regulations, limited data availability, high acquisition costs, and demographic biases. Deep generative models offer a promising solution by generating synthetic data that bypasses privacy concerns and addresses fairness by producing samples for under-represented groups. However, unlike natural images, medical imaging requires validation not only for fidelity (e.g., Fr\'echet Inception Score) but also for morphological and clinical accuracy. This is particularly true for colour fundus retinal imaging, which requires precise replication of the retinal vascular network, including vessel topology, continuity, and thickness. In this study, we in-vestigated whether a distance-based loss function based on deep activation layers of a large foundational model trained on large corpus of domain data, colour fundus imaging, offers advantages over a perceptual loss and edge-detection based loss functions. Our extensive validation pipeline, based on both domain-free and domain specific tasks, suggests that domain-specific deep features do not improve autoen-coder image generation. Conversely, our findings highlight the effectiveness of con-ventional edge detection filters in improving the sharpness of vascular structures in synthetic samples.
Rethinking Foundation Models for Medical Image Classification through a Benchmark Study on MedMNIST
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models are widely employed in medical image analysis, due to their high adaptability and generalizability for downstream tasks. With the increasing number of foundation models being released, model selection has become an important issue. In this work, we study the capabilities of foundation models in medical image classification tasks by conducting a benchmark study on the MedMNIST dataset. Specifically, we adopt various foundation models ranging from convolutional to Transformer-based models and implement both end-to-end training and linear probing for all classification tasks. The results demonstrate the significant potential of these pre-trained models when transferred for medical image classification. We further conduct experiments with different image sizes and various sizes of training data. By analyzing all the results, we provide preliminary, yet useful insights and conclusions on this topic.
KneeXNeT: An Ensemble-Based Approach for Knee Radiographic Evaluation
Dec 10, 2024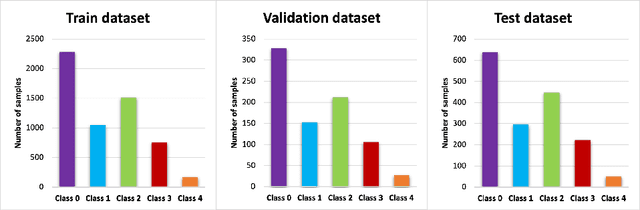
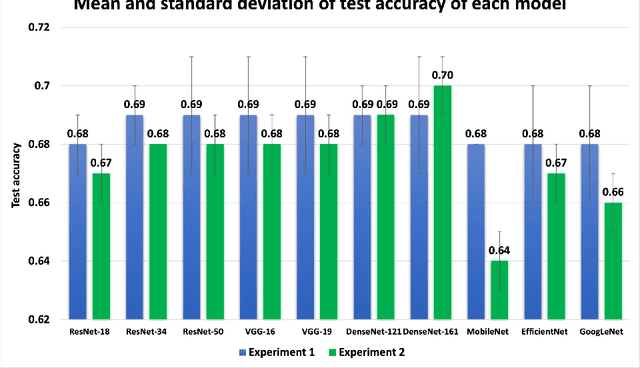
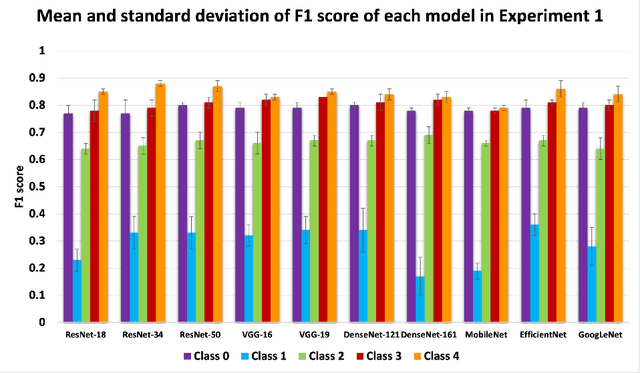
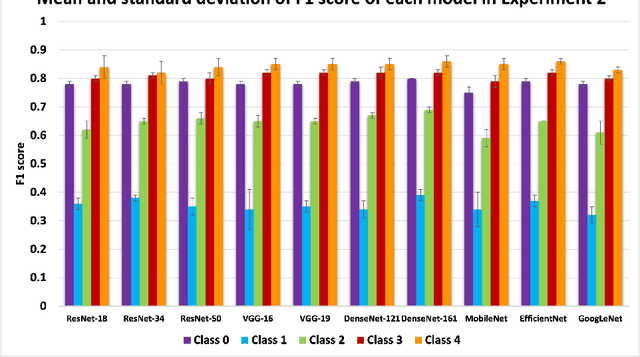
Abstract:Knee osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disorder and a leading cause of disability. Diagnosing OA severity typically requires expert assessment of X-ray images and is commonly based on the Kellgren-Lawrence grading system, a time-intensive process. This study aimed to develop an automated deep learning model to classify knee OA severity, reducing the need for expert evaluation. First, we evaluated ten state-of-the-art deep learning models, achieving a top accuracy of 0.69 with individual models. To address class imbalance, we employed weighted sampling, improving accuracy to 0.70. We further applied Smooth-GradCAM++ to visualize decision-influencing regions, enhancing the explainability of the best-performing model. Finally, we developed ensemble models using majority voting and a shallow neural network. Our ensemble model, KneeXNet, achieved the highest accuracy of 0.72, demonstrating its potential as an automated tool for knee OA assessment.
Fool Me Once? Contrasting Textual and Visual Explanations in a Clinical Decision-Support Setting
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:The growing capabilities of AI models are leading to their wider use, including in safety-critical domains. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to make these models safer to use by making their inference process more transparent. However, current explainability methods are seldom evaluated in the way they are intended to be used: by real-world end users. To address this, we conducted a large-scale user study with 85 healthcare practitioners in the context of human-AI collaborative chest X-ray analysis. We evaluated three types of explanations: visual explanations (saliency maps), natural language explanations, and a combination of both modalities. We specifically examined how different explanation types influence users depending on whether the AI advice and explanations are factually correct. We find that text-based explanations lead to significant over-reliance, which is alleviated by combining them with saliency maps. We also observe that the quality of explanations, that is, how much factually correct information they entail, and how much this aligns with AI correctness, significantly impacts the usefulness of the different explanation types.
Deep Learning Models to Automate the Scoring of Hand Radiographs for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Jun 14, 2024



Abstract:The van der Heijde modification of the Sharp (SvdH) score is a widely used radiographic scoring method to quantify damage in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in clinical trials. However, its complexity with a necessity to score each individual joint, and the expertise required limit its application in clinical practice, especially in disease progression measurement. In this work, we addressed this limitation by developing a bespoke, automated pipeline that is capable of predicting the SvdH score and RA severity from hand radiographs without the need to localise the joints first. Using hand radiographs from RA and suspected RA patients, we first investigated the performance of the state-of-the-art architectures in predicting the total SvdH score for hands and wrists and its corresponding severity class. Secondly, we leveraged publicly available data sets to perform transfer learning with different finetuning schemes and ensemble learning, which resulted in substantial improvement in model performance being on par with an experienced human reader. The best model for RA scoring achieved a Pearson's correlation coefficient (PCC) of 0.925 and root mean squared error (RMSE) of 18.02, while the best model for RA severity classification achieved an accuracy of 0.358 and PCC of 0.859. Our score prediction model attained almost comparable accuracy with experienced radiologists (PCC = 0.97, RMSE = 18.75). Finally, using Grad-CAM, we showed that our models could focus on the anatomical structures in hands and wrists which clinicians deemed as relevant to RA progression in the majority of cases.
Paired Diffusion: Generation of related, synthetic PET-CT-Segmentation scans using Linked Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in biomedical imaging and radiotherapy is hindered by the limited availability of large imaging data repositories. With recent research and improvements in denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPM), high quality synthetic medical scans are now possible. Despite this, there is currently no way of generating multiple related images, such as a corresponding ground truth which can be used to train models, so synthetic scans are often manually annotated before use. This research introduces a novel architecture that is able to generate multiple, related PET-CT-tumour mask pairs using paired networks and conditional encoders. Our approach includes innovative, time step-controlled mechanisms and a `noise-seeding' strategy to improve DDPM sampling consistency. While our model requires a modified perceptual loss function to ensure accurate feature alignment we show generation of clearly aligned synthetic images and improvement in segmentation accuracy with generated images.
Multi-Task Cooperative Learning via Searching for Flat Minima
Sep 21, 2023

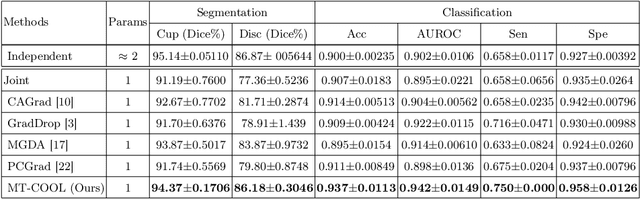

Abstract:Multi-task learning (MTL) has shown great potential in medical image analysis, improving the generalizability of the learned features and the performance in individual tasks. However, most of the work on MTL focuses on either architecture design or gradient manipulation, while in both scenarios, features are learned in a competitive manner. In this work, we propose to formulate MTL as a multi/bi-level optimization problem, and therefore force features to learn from each task in a cooperative approach. Specifically, we update the sub-model for each task alternatively taking advantage of the learned sub-models of the other tasks. To alleviate the negative transfer problem during the optimization, we search for flat minima for the current objective function with regard to features from other tasks. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, we validate our method on three publicly available datasets. The proposed method shows the advantage of cooperative learning, and yields promising results when compared with the state-of-the-art MTL approaches. The code will be available online.
VertXNet: An Ensemble Method for Vertebrae Segmentation and Identification of Spinal X-Ray
Feb 07, 2023Abstract:Reliable vertebrae annotations are key to perform analysis of spinal X-ray images. However, obtaining annotation of vertebrae from those images is usually carried out manually due to its complexity (i.e. small structures with varying shape), making it a costly and tedious process. To accelerate this process, we proposed an ensemble pipeline, VertXNet, that combines two state-of-the-art (SOTA) segmentation models (respectively U-Net and Mask R-CNN) to automatically segment and label vertebrae in X-ray spinal images. Moreover, VertXNet introduces a rule-based approach that allows to robustly infer vertebrae labels (by locating the 'reference' vertebrae which are easier to segment than others) for a given spinal X-ray image. We evaluated the proposed pipeline on three spinal X-ray datasets (two internal and one publicly available), and compared against vertebrae annotated by radiologists. Our experimental results have shown that the proposed pipeline outperformed two SOTA segmentation models on our test dataset (MEASURE 1) with a mean Dice of 0.90, vs. a mean Dice of 0.73 for Mask R-CNN and 0.72 for U-Net. To further evaluate the generalization ability of VertXNet, the pre-trained pipeline was directly tested on two additional datasets (PREVENT and NHANES II) and consistent performance was observed with a mean Dice of 0.89 and 0.88, respectively. Overall, VertXNet demonstrated significantly improved performance for vertebra segmentation and labeling for spinal X-ray imaging, and evaluation on both in-house clinical trial data and publicly available data further proved its generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge