Thibaud Coroller
Image registration based automated lesion correspondence pipeline for longitudinal CT data
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Patients diagnosed with metastatic breast cancer (mBC) typically undergo several radiographic assessments during their treatment. mBC often involves multiple metastatic lesions in different organs, it is imperative to accurately track and assess these lesions to gain a comprehensive understanding of the disease's response to treatment. Computerized analysis methods that rely on lesion-level tracking have often used manual matching of corresponding lesions, a time-consuming process that is prone to errors. This paper introduces an automated lesion correspondence algorithm designed to precisely track both targets' lesions and non-targets' lesions in longitudinal data. Here we demonstrate the applicability of our algorithm on the anonymized data from two Phase III trials. The dataset contains imaging data of patients for different follow-up timepoints and the radiologist annotations for the patients enrolled in the trials. Target and non-target lesions are annotated by either one or two groups of radiologists. To facilitate accurate tracking, we have developed a registration-assisted lesion correspondence algorithm. The algorithm employs a sequential two-step pipeline: (a) Firstly, an adaptive Hungarian algorithm is used to establish correspondence among lesions within a single volumetric image series which have been annotated by multiple radiologists at a specific timepoint. (b) Secondly, after establishing correspondence and assigning unique names to the lesions, three-dimensional rigid registration is applied to various image series at the same timepoint. Registration is followed by ongoing lesion correspondence based on the adaptive Hungarian algorithm and updating lesion names for accurate tracking. Validation of our automated lesion correspondence algorithm is performed through triaxial plots based on axial, sagittal, and coronal views, confirming its efficacy in matching lesions.
TorchSurv: A Lightweight Package for Deep Survival Analysis
Apr 17, 2024Abstract:TorchSurv is a Python package that serves as a companion tool to perform deep survival modeling within the PyTorch environment. Unlike existing libraries that impose specific parametric forms, TorchSurv enables the use of custom PyTorch-based deep survival models. With its lightweight design, minimal input requirements, full PyTorch backend, and freedom from restrictive survival model parameterizations, TorchSurv facilitates efficient deep survival model implementation and is particularly beneficial for high-dimensional and complex input data scenarios.
Towards Automatic Scoring of Spinal X-ray for Ankylosing Spondylitis
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Manually grading structural changes with the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score (mSASSS) on spinal X-ray imaging is costly and time-consuming due to bone shape complexity and image quality variations. In this study, we address this challenge by prototyping a 2-step auto-grading pipeline, called VertXGradeNet, to automatically predict mSASSS scores for the cervical and lumbar vertebral units (VUs) in X-ray spinal imaging. The VertXGradeNet utilizes VUs generated by our previously developed VU extraction pipeline (VertXNet) as input and predicts mSASSS based on those VUs. VertXGradeNet was evaluated on an in-house dataset of lateral cervical and lumbar X-ray images for axial spondylarthritis patients. Our results show that VertXGradeNet can predict the mSASSS score for each VU when the data is limited in quantity and imbalanced. Overall, it can achieve a balanced accuracy of 0.56 and 0.51 for 4 different mSASSS scores (i.e., a score of 0, 1, 2, 3) on two test datasets. The accuracy of the presented method shows the potential to streamline the spinal radiograph readings and therefore reduce the cost of future clinical trials.
VertXNet: An Ensemble Method for Vertebrae Segmentation and Identification of Spinal X-Ray
Feb 07, 2023Abstract:Reliable vertebrae annotations are key to perform analysis of spinal X-ray images. However, obtaining annotation of vertebrae from those images is usually carried out manually due to its complexity (i.e. small structures with varying shape), making it a costly and tedious process. To accelerate this process, we proposed an ensemble pipeline, VertXNet, that combines two state-of-the-art (SOTA) segmentation models (respectively U-Net and Mask R-CNN) to automatically segment and label vertebrae in X-ray spinal images. Moreover, VertXNet introduces a rule-based approach that allows to robustly infer vertebrae labels (by locating the 'reference' vertebrae which are easier to segment than others) for a given spinal X-ray image. We evaluated the proposed pipeline on three spinal X-ray datasets (two internal and one publicly available), and compared against vertebrae annotated by radiologists. Our experimental results have shown that the proposed pipeline outperformed two SOTA segmentation models on our test dataset (MEASURE 1) with a mean Dice of 0.90, vs. a mean Dice of 0.73 for Mask R-CNN and 0.72 for U-Net. To further evaluate the generalization ability of VertXNet, the pre-trained pipeline was directly tested on two additional datasets (PREVENT and NHANES II) and consistent performance was observed with a mean Dice of 0.89 and 0.88, respectively. Overall, VertXNet demonstrated significantly improved performance for vertebra segmentation and labeling for spinal X-ray imaging, and evaluation on both in-house clinical trial data and publicly available data further proved its generalization.
VertXNet: Automatic Segmentation and Identification of Lumbar and Cervical Vertebrae from Spinal X-ray Images
Jul 12, 2022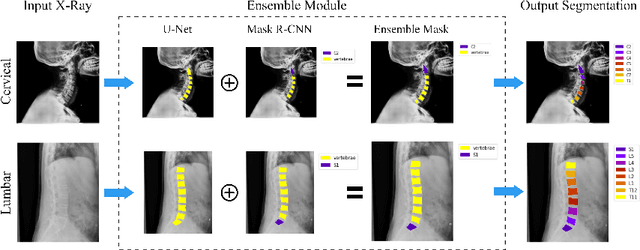
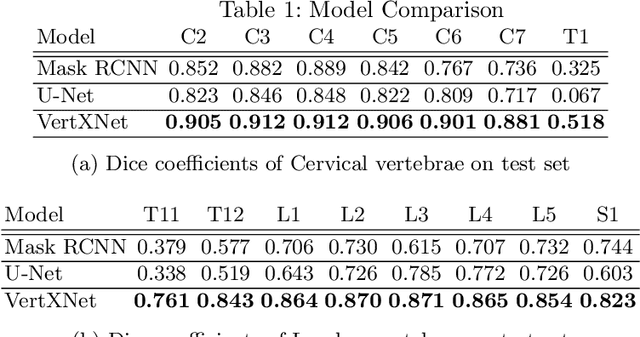
Abstract:Manual annotation of vertebrae on spinal X-ray imaging is costly and time-consuming due to bone shape complexity and image quality variations. In this study, we address this challenge by proposing an ensemble method called VertXNet, to automatically segment and label vertebrae in X-ray spinal images. VertXNet combines two state-of-the-art segmentation models, namely U-Net and Mask R-CNN to improve vertebrae segmentation. A main feature of VertXNet is to also infer vertebrae labels thanks to its Mask R-CNN component (trained to detect 'reference' vertebrae) on a given spinal X-ray image. VertXNet was evaluated on an in-house dataset of lateral cervical and lumbar X-ray imaging for ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients. Our results show that VertXNet can accurately label spinal X-rays (mean Dice of 0.9). It can be used to circumvent the lack of annotated vertebrae without requiring human expert review. This step is crucial to investigate clinical associations by solving the lack of segmentation, a common bottleneck for most computational imaging projects.
A Deep Learning Approach to Private Data Sharing of Medical Images Using Conditional GANs
Jun 24, 2021Abstract:Sharing data from clinical studies can facilitate innovative data-driven research and ultimately lead to better public health. However, sharing biomedical data can put sensitive personal information at risk. This is usually solved by anonymization, which is a slow and expensive process. An alternative to anonymization is sharing a synthetic dataset that bears a behaviour similar to the real data but preserves privacy. As part of the collaboration between Novartis and the Oxford Big Data Institute, we generate a synthetic dataset based on COSENTYX (secukinumab) Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS) clinical study. We apply an Auxiliary Classifier GAN (ac-GAN) to generate synthetic magnetic resonance images (MRIs) of vertebral units (VUs). The images are conditioned on the VU location (cervical, thoracic and lumbar). In this paper, we present a method for generating a synthetic dataset and conduct an in-depth analysis on its properties of along three key metrics: image fidelity, sample diversity and dataset privacy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge