Bayar Menzat
Fool Me Once? Contrasting Textual and Visual Explanations in a Clinical Decision-Support Setting
Oct 16, 2024



Abstract:The growing capabilities of AI models are leading to their wider use, including in safety-critical domains. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to make these models safer to use by making their inference process more transparent. However, current explainability methods are seldom evaluated in the way they are intended to be used: by real-world end users. To address this, we conducted a large-scale user study with 85 healthcare practitioners in the context of human-AI collaborative chest X-ray analysis. We evaluated three types of explanations: visual explanations (saliency maps), natural language explanations, and a combination of both modalities. We specifically examined how different explanation types influence users depending on whether the AI advice and explanations are factually correct. We find that text-based explanations lead to significant over-reliance, which is alleviated by combining them with saliency maps. We also observe that the quality of explanations, that is, how much factually correct information they entail, and how much this aligns with AI correctness, significantly impacts the usefulness of the different explanation types.
Benchmarking Predictive Coding Networks -- Made Simple
Jul 01, 2024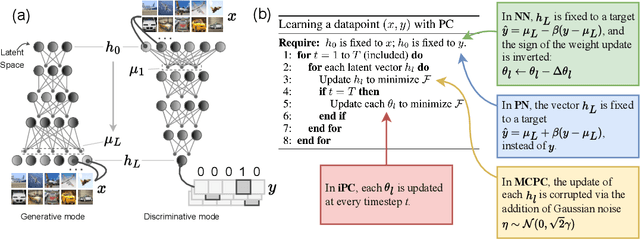
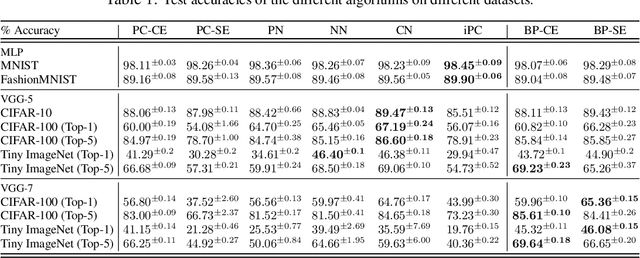

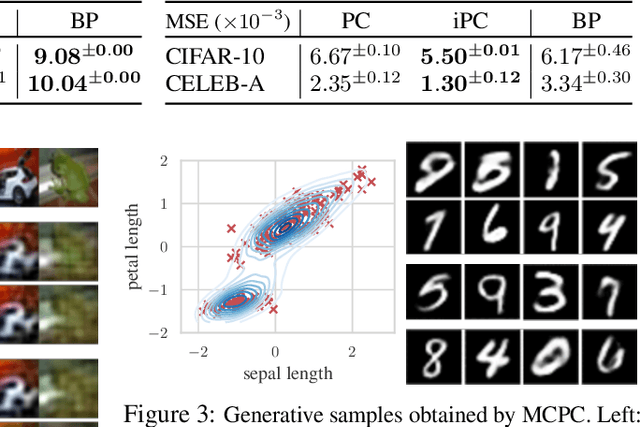
Abstract:In this work, we tackle the problems of efficiency and scalability for predictive coding networks in machine learning. To do so, we first propose a library called PCX, whose focus lies on performance and simplicity, and provides a user-friendly, deep-learning oriented interface. Second, we use PCX to implement a large set of benchmarks for the community to use for their experiments. As most works propose their own tasks and architectures, do not compare one against each other, and focus on small-scale tasks, a simple and fast open-source library adopted by the whole community would address all of these concerns. Third, we perform extensive benchmarks using multiple algorithms, setting new state-of-the-art results in multiple tasks and datasets, as well as highlighting limitations inherent to PC that should be addressed. Thanks to the efficiency of PCX, we are able to analyze larger architectures than commonly used, providing baselines to galvanize community efforts towards one of the main open problems in the field: scalability. The code for PCX is available at \textit{https://github.com/liukidar/pcax}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge