Yuanye Liu
Liver Fibrosis Quantification and Analysis: The LiQA Dataset and Baseline Method
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Liver fibrosis represents a significant global health burden, necessitating accurate staging for effective clinical management. This report introduces the LiQA (Liver Fibrosis Quantification and Analysis) dataset, established as part of the CARE 2024 challenge. Comprising $440$ patients with multi-phase, multi-center MRI scans, the dataset is curated to benchmark algorithms for Liver Segmentation (LiSeg) and Liver Fibrosis Staging (LiFS) under complex real-world conditions, including domain shifts, missing modalities, and spatial misalignment. We further describe the challenge's top-performing methodology, which integrates a semi-supervised learning framework with external data for robust segmentation, and utilizes a multi-view consensus approach with Class Activation Map (CAM)-based regularization for staging. Evaluation of this baseline demonstrates that leveraging multi-source data and anatomical constraints significantly enhances model robustness in clinical settings.
Beyond Prompt Content: Enhancing LLM Performance via Content-Format Integrated Prompt Optimization
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant capability across various tasks, with their real-world effectiveness often driven by prompt design. While recent research has focused on optimizing prompt content, the role of prompt formatting, a critical but often overlooked dimension, has received limited systematic investigation. In this paper, we introduce Content-Format Integrated Prompt Optimization (CFPO), an innovative methodology that jointly optimizes both prompt content and formatting through an iterative refinement process. CFPO leverages natural language mutations to explore content variations and employs a dynamic format exploration strategy that systematically evaluates diverse format options. Our extensive evaluations across multiple tasks and open-source LLMs demonstrate that CFPO demonstrates measurable performance improvements compared to content-only optimization methods. This highlights the importance of integrated content-format optimization and offers a practical, model-agnostic approach to enhancing LLM performance. Code is available at https://github.com/HenryLau7/CFPO.
Evidential Concept Embedding Models: Towards Reliable Concept Explanations for Skin Disease Diagnosis
Jun 27, 2024Abstract:Due to the high stakes in medical decision-making, there is a compelling demand for interpretable deep learning methods in medical image analysis. Concept Bottleneck Models (CBM) have emerged as an active interpretable framework incorporating human-interpretable concepts into decision-making. However, their concept predictions may lack reliability when applied to clinical diagnosis, impeding concept explanations' quality. To address this, we propose an evidential Concept Embedding Model (evi-CEM), which employs evidential learning to model the concept uncertainty. Additionally, we offer to leverage the concept uncertainty to rectify concept misalignments that arise when training CBMs using vision-language models without complete concept supervision. With the proposed methods, we can enhance concept explanations' reliability for both supervised and label-efficient settings. Furthermore, we introduce concept uncertainty for effective test-time intervention. Our evaluation demonstrates that evi-CEM achieves superior performance in terms of concept prediction, and the proposed concept rectification effectively mitigates concept misalignments for label-efficient training. Our code is available at https://github.com/obiyoag/evi-CEM.
MERIT: Multi-view Evidential learning for Reliable and Interpretable liver fibrosis sTaging
May 05, 2024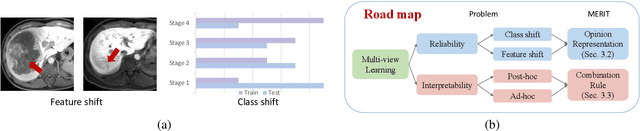
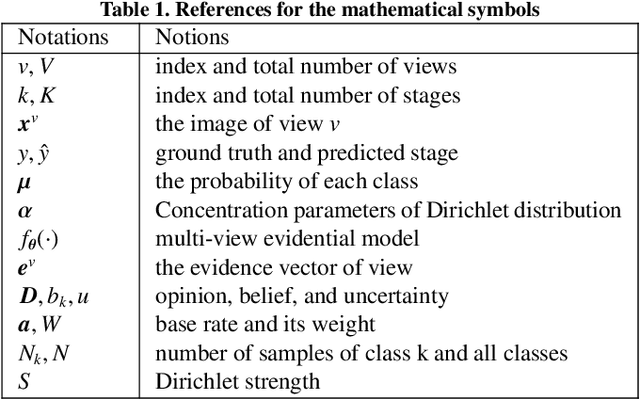
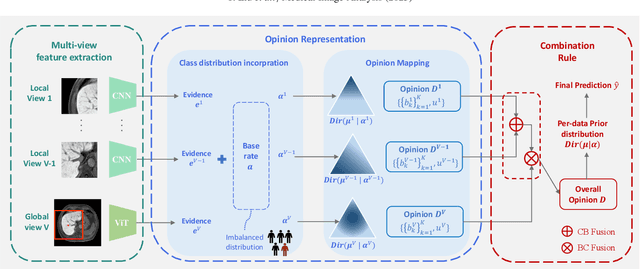
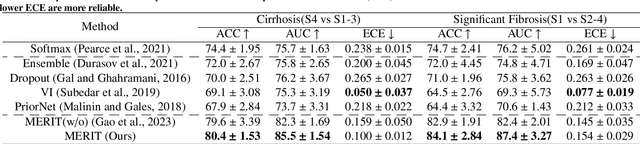
Abstract:Accurate staging of liver fibrosis from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is crucial in clinical practice. While conventional methods often focus on a specific sub-region, multi-view learning captures more information by analyzing multiple patches simultaneously. However, previous multi-view approaches could not typically calculate uncertainty by nature, and they generally integrate features from different views in a black-box fashion, hence compromising reliability as well as interpretability of the resulting models. In this work, we propose a new multi-view method based on evidential learning, referred to as MERIT, which tackles the two challenges in a unified framework. MERIT enables uncertainty quantification of the predictions to enhance reliability, and employs a logic-based combination rule to improve interpretability. Specifically, MERIT models the prediction from each sub-view as an opinion with quantified uncertainty under the guidance of the subjective logic theory. Furthermore, a distribution-aware base rate is introduced to enhance performance, particularly in scenarios involving class distribution shifts. Finally, MERIT adopts a feature-specific combination rule to explicitly fuse multi-view predictions, thereby enhancing interpretability. Results have showcased the effectiveness of the proposed MERIT, highlighting the reliability and offering both ad-hoc and post-hoc interpretability. They also illustrate that MERIT can elucidate the significance of each view in the decision-making process for liver fibrosis staging.
A Reliable and Interpretable Framework of Multi-view Learning for Liver Fibrosis Staging
Jun 21, 2023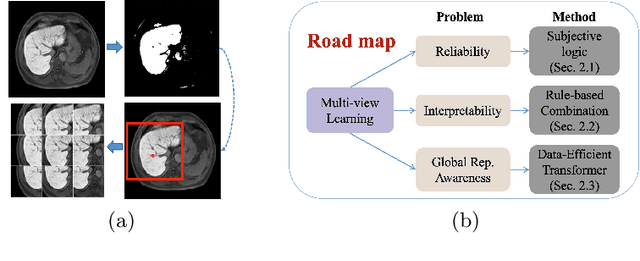
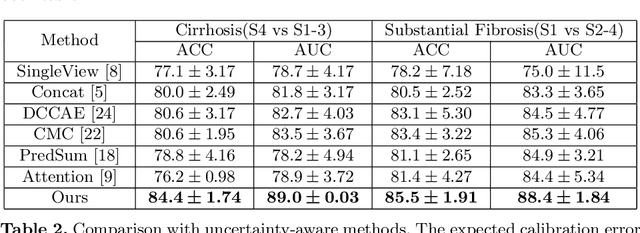
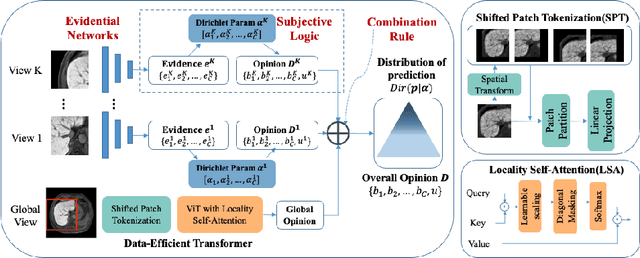
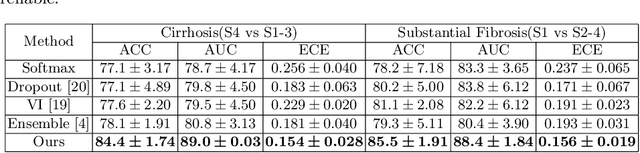
Abstract:Staging of liver fibrosis is important in the diagnosis and treatment planning of patients suffering from liver diseases. Current deep learning-based methods using abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) usually take a sub-region of the liver as an input, which nevertheless could miss critical information. To explore richer representations, we formulate this task as a multi-view learning problem and employ multiple sub-regions of the liver. Previously, features or predictions are usually combined in an implicit manner, and uncertainty-aware methods have been proposed. However, these methods could be challenged to capture cross-view representations, which can be important in the accurate prediction of staging. Therefore, we propose a reliable multi-view learning method with interpretable combination rules, which can model global representations to improve the accuracy of predictions. Specifically, the proposed method estimates uncertainties based on subjective logic to improve reliability, and an explicit combination rule is applied based on Dempster-Shafer's evidence theory with good power of interpretability. Moreover, a data-efficient transformer is introduced to capture representations in the global view. Results evaluated on enhanced MRI data show that our method delivers superior performance over existing multi-view learning methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge