Xuan Feng
C2PO: Diagnosing and Disentangling Bias Shortcuts in LLMs
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Bias in Large Language Models (LLMs) poses significant risks to trustworthiness, manifesting primarily as stereotypical biases (e.g., gender or racial stereotypes) and structural biases (e.g., lexical overlap or position preferences). However, prior paradigms typically address these in isolation, often mitigating one at the expense of exacerbating the other. To address this, we conduct a systematic exploration of these reasoning failures and identify a primary inducement: the latent spurious feature correlations within the input that drive these erroneous reasoning shortcuts. Driven by these findings, we introduce Causal-Contrastive Preference Optimization (C2PO), a unified alignment framework designed to tackle these specific failures by simultaneously discovering and suppressing these correlations directly within the optimization process. Specifically, C2PO leverages causal counterfactual signals to isolate bias-inducing features from valid reasoning paths, and employs a fairness-sensitive preference update mechanism to dynamically evaluate logit-level contributions and suppress shortcut features. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks covering stereotypical bias (BBQ, Unqover), structural bias (MNLI, HANS, Chatbot, MT-Bench), out-of-domain fairness (StereoSet, WinoBias), and general utility (MMLU, GSM8K) demonstrate that C2PO effectively mitigates stereotypical and structural biases while preserving robust general reasoning capabilities.
Unlocking the Capabilities of Vision-Language Models for Generalizable and Explainable Deepfake Detection
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Current vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in understanding multimodal data, but their potential remains underexplored for deepfake detection due to the misaligned of their knowledge and forensics patterns. To this end, we present a novel paradigm that unlocks VLMs' potential capabilities through three components: (1) A knowledge-guided forgery adaptation module that aligns VLM's semantic space with forensic features through contrastive learning with external manipulation knowledge; (2) A multi-modal prompt tuning framework that jointly optimizes visual-textual embeddings for both localization and explainability; (3) An iterative refinement strategy enabling multi-turn dialog for evidence-based reasoning. Our framework includes a VLM-based Knowledge-guided Forgery Detector (KFD), a VLM image encoder, and a Large Language Model (LLM). The VLM image encoder extracts visual prompt embeddings from images, while the LLM receives visual and question prompt embeddings for inference. The KFD is used to calculate correlations between image features and pristine/deepfake class embeddings, enabling forgery classification and localization. The outputs from these components are used to construct forgery prompt embeddings. Finally, we feed these prompt embeddings into the LLM to generate textual detection responses to assist judgment. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks, including FF++, CDF2, DFD, DFDCP, and DFDC, demonstrate that our scheme surpasses state-of-the-art methods in generalization performance, while also supporting multi-turn dialogue capabilities.
Beyond Prompt Content: Enhancing LLM Performance via Content-Format Integrated Prompt Optimization
Feb 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant capability across various tasks, with their real-world effectiveness often driven by prompt design. While recent research has focused on optimizing prompt content, the role of prompt formatting, a critical but often overlooked dimension, has received limited systematic investigation. In this paper, we introduce Content-Format Integrated Prompt Optimization (CFPO), an innovative methodology that jointly optimizes both prompt content and formatting through an iterative refinement process. CFPO leverages natural language mutations to explore content variations and employs a dynamic format exploration strategy that systematically evaluates diverse format options. Our extensive evaluations across multiple tasks and open-source LLMs demonstrate that CFPO demonstrates measurable performance improvements compared to content-only optimization methods. This highlights the importance of integrated content-format optimization and offers a practical, model-agnostic approach to enhancing LLM performance. Code is available at https://github.com/HenryLau7/CFPO.
Sigma: Differential Rescaling of Query, Key and Value for Efficient Language Models
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Sigma, an efficient large language model specialized for the system domain, empowered by a novel architecture including DiffQKV attention, and pre-trained on our meticulously collected system domain data. DiffQKV attention significantly enhances the inference efficiency of Sigma by optimizing the Query (Q), Key (K), and Value (V) components in the attention mechanism differentially, based on their varying impacts on the model performance and efficiency indicators. Specifically, we (1) conduct extensive experiments that demonstrate the model's varying sensitivity to the compression of K and V components, leading to the development of differentially compressed KV, and (2) propose augmented Q to expand the Q head dimension, which enhances the model's representation capacity with minimal impacts on the inference speed. Rigorous theoretical and empirical analyses reveal that DiffQKV attention significantly enhances efficiency, achieving up to a 33.36% improvement in inference speed over the conventional grouped-query attention (GQA) in long-context scenarios. We pre-train Sigma on 6T tokens from various sources, including 19.5B system domain data that we carefully collect and 1T tokens of synthesized and rewritten data. In general domains, Sigma achieves comparable performance to other state-of-arts models. In the system domain, we introduce the first comprehensive benchmark AIMicius, where Sigma demonstrates remarkable performance across all tasks, significantly outperforming GPT-4 with an absolute improvement up to 52.5%.
Learning from Mistakes: Self-correct Adversarial Training for Chinese Unnatural Text Correction
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Unnatural text correction aims to automatically detect and correct spelling errors or adversarial perturbation errors in sentences. Existing methods typically rely on fine-tuning or adversarial training to correct errors, which have achieved significant success. However, these methods exhibit poor generalization performance due to the difference in data distribution between training data and real-world scenarios, known as the exposure bias problem. In this paper, we propose a self-correct adversarial training framework for \textbf{L}earn\textbf{I}ng from \textbf{MI}s\textbf{T}akes (\textbf{LIMIT}), which is a task- and model-independent framework to correct unnatural errors or mistakes. Specifically, we fully utilize errors generated by the model that are actively exposed during the inference phase, i.e., predictions that are inconsistent with the target. This training method not only simulates potential errors in real application scenarios, but also mitigates the exposure bias of the traditional training process. Meanwhile, we design a novel decoding intervention strategy to maintain semantic consistency. Extensive experimental results on Chinese unnatural text error correction datasets show that our proposed method can correct multiple forms of errors and outperforms the state-of-the-art text correction methods. In addition, extensive results on Chinese and English datasets validate that LIMIT can serve as a plug-and-play defense module and can extend to new models and datasets without further training.
Dual-Teacher De-biasing Distillation Framework for Multi-domain Fake News Detection
Dec 02, 2023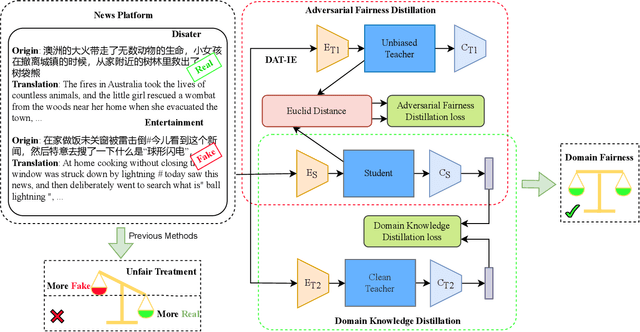
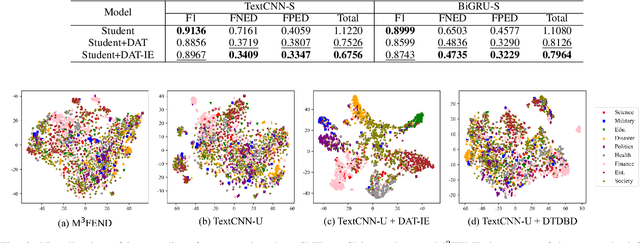

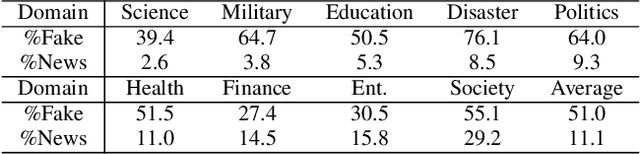
Abstract:Multi-domain fake news detection aims to identify whether various news from different domains is real or fake and has become urgent and important. However, existing methods are dedicated to improving the overall performance of fake news detection, ignoring the fact that unbalanced data leads to disparate treatment for different domains, i.e., the domain bias problem. To solve this problem, we propose the Dual-Teacher De-biasing Distillation framework (DTDBD) to mitigate bias across different domains. Following the knowledge distillation methods, DTDBD adopts a teacher-student structure, where pre-trained large teachers instruct a student model. In particular, the DTDBD consists of an unbiased teacher and a clean teacher that jointly guide the student model in mitigating domain bias and maintaining performance. For the unbiased teacher, we introduce an adversarial de-biasing distillation loss to instruct the student model in learning unbiased domain knowledge. For the clean teacher, we design domain knowledge distillation loss, which effectively incentivizes the student model to focus on representing domain features while maintaining performance. Moreover, we present a momentum-based dynamic adjustment algorithm to trade off the effects of two teachers. Extensive experiments on Chinese and English datasets show that the proposed method substantially outperforms the state-of-the-art baseline methods in terms of bias metrics while guaranteeing competitive performance.
CHEAT: A Large-scale Dataset for Detecting ChatGPT-writtEn AbsTracts
Apr 24, 2023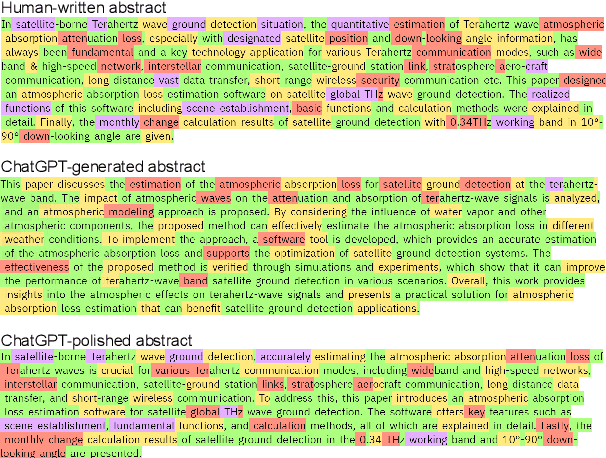
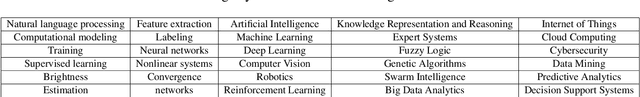
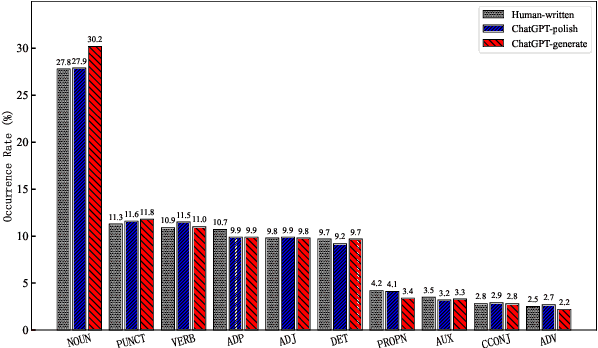
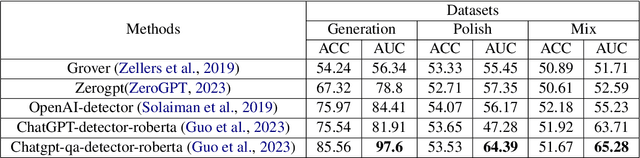
Abstract:The powerful ability of ChatGPT has caused widespread concern in the academic community. Malicious users could synthesize dummy academic content through ChatGPT, which is extremely harmful to academic rigor and originality. The need to develop ChatGPT-written content detection algorithms call for large-scale datasets. In this paper, we initially investigate the possible negative impact of ChatGPT on academia,and present a large-scale CHatGPT-writtEn AbsTract dataset (CHEAT) to support the development of detection algorithms. In particular, the ChatGPT-written abstract dataset contains 35,304 synthetic abstracts, with Generation, Polish, and Mix as prominent representatives. Based on these data, we perform a thorough analysis of the existing text synthesis detection algorithms. We show that ChatGPT-written abstracts are detectable, while the detection difficulty increases with human involvement.
AggPose: Deep Aggregation Vision Transformer for Infant Pose Estimation
May 11, 2022
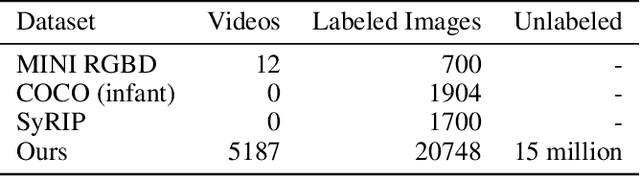


Abstract:Movement and pose assessment of newborns lets experienced pediatricians predict neurodevelopmental disorders, allowing early intervention for related diseases. However, most of the newest AI approaches for human pose estimation methods focus on adults, lacking publicly benchmark for infant pose estimation. In this paper, we fill this gap by proposing infant pose dataset and Deep Aggregation Vision Transformer for human pose estimation, which introduces a fast trained full transformer framework without using convolution operations to extract features in the early stages. It generalizes Transformer + MLP to high-resolution deep layer aggregation within feature maps, thus enabling information fusion between different vision levels. We pre-train AggPose on COCO pose dataset and apply it on our newly released large-scale infant pose estimation dataset. The results show that AggPose could effectively learn the multi-scale features among different resolutions and significantly improve the performance of infant pose estimation. We show that AggPose outperforms hybrid model HRFormer and TokenPose in the infant pose estimation dataset. Moreover, our AggPose outperforms HRFormer by 0.7% AP on COCO val pose estimation on average. Our code is available at github.com/SZAR-LAB/AggPose.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge