Nam Nguyen
L3i, University of La Rochelle, France
EEG-X: Device-Agnostic and Noise-Robust Foundation Model for EEG
Nov 12, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models for EEG analysis are still in their infancy, limited by two key challenges: (1) variability across datasets caused by differences in recording devices and configurations, and (2) the low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of EEG, where brain signals are often buried under artifacts and non-brain sources. To address these challenges, we present EEG-X, a device-agnostic and noise-robust foundation model for EEG representation learning. EEG-X introduces a novel location-based channel embedding that encodes spatial information and improves generalization across domains and tasks by allowing the model to handle varying channel numbers, combinations, and recording lengths. To enhance robustness against noise, EEG-X employs a noise-aware masking and reconstruction strategy in both raw and latent spaces. Unlike previous models that mask and reconstruct raw noisy EEG signals, EEG-X is trained to reconstruct denoised signals obtained through an artifact removal process, ensuring that the learned representations focus on neural activity rather than noise. To further enhance reconstruction-based pretraining, EEG-X introduces a dictionary-inspired convolutional transformation (DiCT) layer that projects signals into a structured feature space before computing reconstruction (MSE) loss, reducing noise sensitivity and capturing frequency- and shape-aware similarities. Experiments on datasets collected from diverse devices show that EEG-X outperforms state-of-the-art methods across multiple downstream EEG tasks and excels in cross-domain settings where pre-trained and downstream datasets differ in electrode layouts. The models and code are available at: https://github.com/Emotiv/EEG-X
BEDTime: A Unified Benchmark for Automatically Describing Time Series
Sep 05, 2025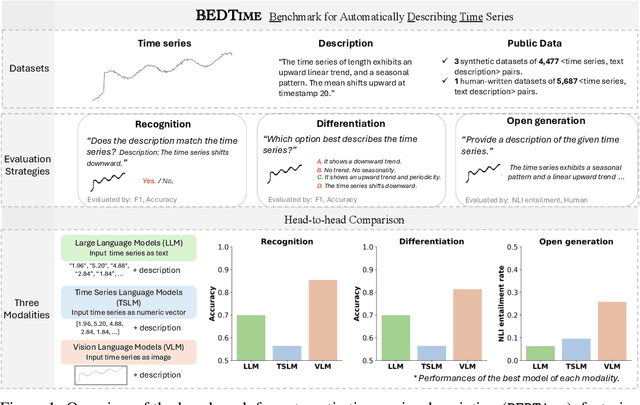

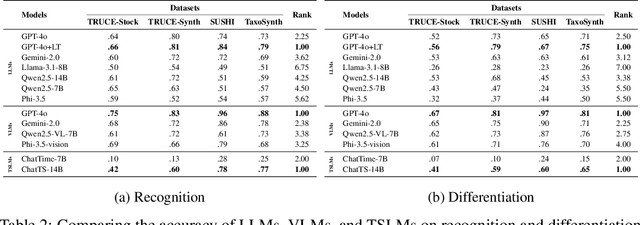
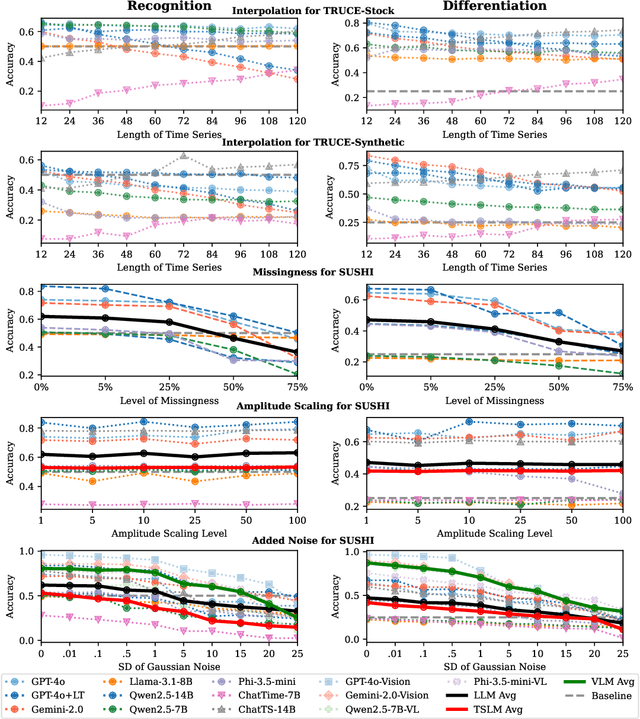
Abstract:Many recent studies have proposed general-purpose foundation models designed for a variety of time series analysis tasks. While several established datasets already exist for evaluating these models, previous works frequently introduce their models in conjunction with new datasets, limiting opportunities for direct, independent comparisons and obscuring insights into the relative strengths of different methods. Additionally, prior evaluations often cover numerous tasks simultaneously, assessing a broad range of model abilities without clearly pinpointing which capabilities contribute to overall performance. To address these gaps, we formalize and evaluate 3 tasks that test a model's ability to describe time series using generic natural language: (1) recognition (True/False question-answering), (2) differentiation (multiple choice question-answering), and (3) generation (open-ended natural language description). We then unify 4 recent datasets to enable head-to-head model comparisons on each task. Experimentally, in evaluating 13 state-of-the-art language, vision--language, and time series--language models, we find that (1) popular language-only methods largely underperform, indicating a need for time series-specific architectures, (2) VLMs are quite successful, as expected, identifying the value of vision models for these tasks and (3) pretrained multimodal time series--language models successfully outperform LLMs, but still have significant room for improvement. We also find that all approaches exhibit clear fragility in a range of robustness tests. Overall, our benchmark provides a standardized evaluation on a task necessary for time series reasoning systems.
Universal Representations for Classification-enhanced Lossy Compression
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:In lossy compression, the classical tradeoff between compression rate and reconstruction distortion has traditionally guided algorithm design. However, Blau and Michaeli [5] introduced a generalized framework, known as the rate-distortion-perception (RDP) function, incorporating perceptual quality as an additional dimension of evaluation. More recently, the rate-distortion-classification (RDC) function was investigated in [19], evaluating compression performance by considering classification accuracy alongside distortion. In this paper, we explore universal representations, where a single encoder is developed to achieve multiple decoding objectives across various distortion and classification (or perception) constraints. This universality avoids retraining encoders for each specific operating point within these tradeoffs. Our experimental validation on the MNIST dataset indicates that a universal encoder incurs only minimal performance degradation compared to individually optimized encoders for perceptual image compression tasks, aligning with prior results from [23]. Nonetheless, we also identify that in the RDC setting, reusing an encoder optimized for one specific classification-distortion tradeoff leads to a significant distortion penalty when applied to alternative points.
On Symbol Error Probability-based Beamforming in MIMO Gaussian Wiretap Channels
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates beamforming schemes designed to minimize the symbol error probability (SEP) for an authorized user while guaranteeing that the likelihood of an eavesdropper correctly recovering symbols remains below a predefined threshold. Unlike previous works that focus on maximizing secrecy capacity, our work is centered around finding an optimal beamforming vector for binary antipodal signal detection in multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) Gaussian wiretap channels. Finding the optimal beamforming vector in this setting is challenging. Computationally efficient algorithms such as convex techniques cannot be applied to find the optimal solution. To that end, our proposed algorithm relies on Karush-Kuhn-Tucker (KKT) conditions and a generalized eigen-decomposition method to find the exact solution. In addition, we also develop an approximate, practical algorithm to find a good beamforming matrix when using M-ary detection schemes. Numerical results are presented to assess the performance of the proposed methods across various scenarios.
CovHuSeg: An Enhanced Approach for Kidney Pathology Segmentation
Nov 28, 2024



Abstract:Segmentation has long been essential in computer vision due to its numerous real-world applications. However, most traditional deep learning and machine learning models need help to capture geometric features such as size and convexity of the segmentation targets, resulting in suboptimal outcomes. To resolve this problem, we propose using a CovHuSeg algorithm to solve the problem of kidney glomeruli segmentation. This simple post-processing method is specified to adapt to the segmentation of ball-shaped anomalies, including the glomerulus. Unlike other post-processing methods, the CovHuSeg algorithm assures that the outcome mask does not have holes in it or comes in unusual shapes that are impossible to be the shape of a glomerulus. We illustrate the effectiveness of our method by experimenting with multiple deep-learning models in the context of segmentation on kidney pathology images. The results show that all models have increased accuracy when using the CovHuSeg algorithm.
CaloChallenge 2022: A Community Challenge for Fast Calorimeter Simulation
Oct 28, 2024
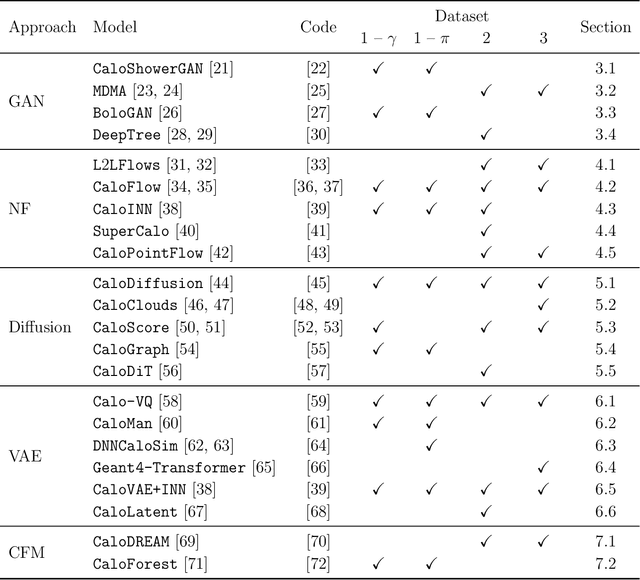
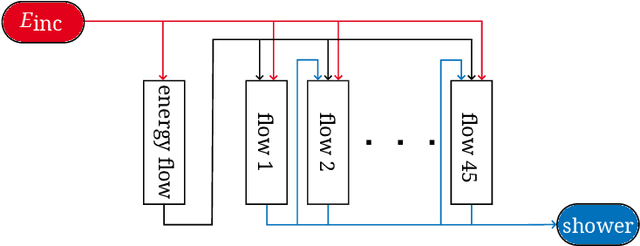
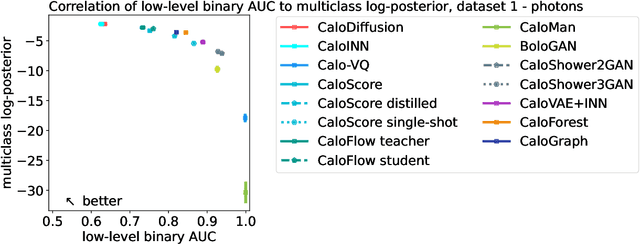
Abstract:We present the results of the "Fast Calorimeter Simulation Challenge 2022" - the CaloChallenge. We study state-of-the-art generative models on four calorimeter shower datasets of increasing dimensionality, ranging from a few hundred voxels to a few tens of thousand voxels. The 31 individual submissions span a wide range of current popular generative architectures, including Variational AutoEncoders (VAEs), Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Normalizing Flows, Diffusion models, and models based on Conditional Flow Matching. We compare all submissions in terms of quality of generated calorimeter showers, as well as shower generation time and model size. To assess the quality we use a broad range of different metrics including differences in 1-dimensional histograms of observables, KPD/FPD scores, AUCs of binary classifiers, and the log-posterior of a multiclass classifier. The results of the CaloChallenge provide the most complete and comprehensive survey of cutting-edge approaches to calorimeter fast simulation to date. In addition, our work provides a uniquely detailed perspective on the important problem of how to evaluate generative models. As such, the results presented here should be applicable for other domains that use generative AI and require fast and faithful generation of samples in a large phase space.
EEG2Rep: Enhancing Self-supervised EEG Representation Through Informative Masked Inputs
Feb 17, 2024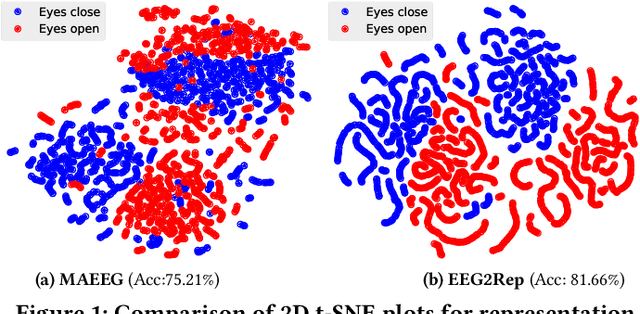
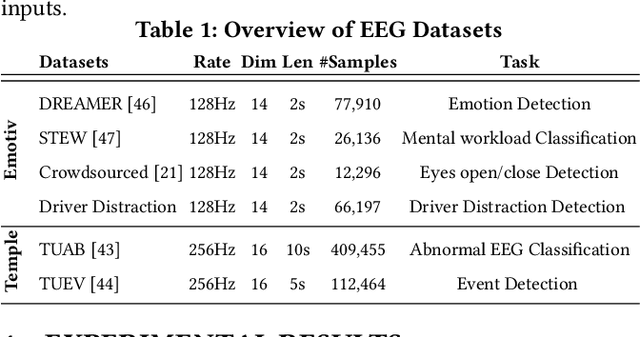
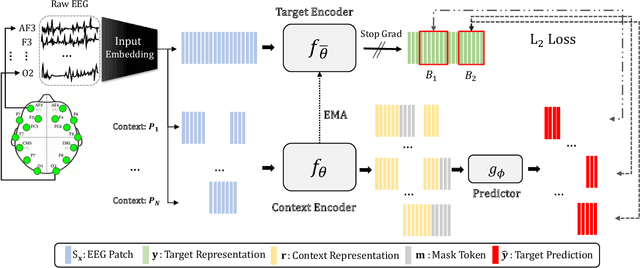
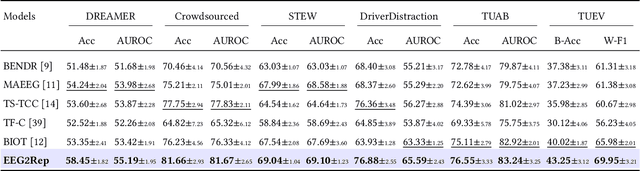
Abstract:Self-supervised approaches for electroencephalography (EEG) representation learning face three specific challenges inherent to EEG data: (1) The low signal-to-noise ratio which challenges the quality of the representation learned, (2) The wide range of amplitudes from very small to relatively large due to factors such as the inter-subject variability, risks the models to be dominated by higher amplitude ranges, and (3) The absence of explicit segmentation in the continuous-valued sequences which can result in less informative representations. To address these challenges, we introduce EEG2Rep, a self-prediction approach for self-supervised representation learning from EEG. Two core novel components of EEG2Rep are as follows: 1) Instead of learning to predict the masked input from raw EEG, EEG2Rep learns to predict masked input in latent representation space, and 2) Instead of conventional masking methods, EEG2Rep uses a new semantic subsequence preserving (SSP) method which provides informative masked inputs to guide EEG2Rep to generate rich semantic representations. In experiments on 6 diverse EEG tasks with subject variability, EEG2Rep significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. We show that our semantic subsequence preserving improves the existing masking methods in self-prediction literature and find that preserving 50\% of EEG recordings will result in the most accurate results on all 6 tasks on average. Finally, we show that EEG2Rep is robust to noise addressing a significant challenge that exists in EEG data. Models and code are available at: https://github.com/Navidfoumani/EEG2Rep
Leveraging AI for Enhanced Software Effort Estimation: A Comprehensive Study and Framework Proposal
Feb 08, 2024Abstract:This paper presents an extensive study on the application of AI techniques for software effort estimation in the past five years from 2017 to 2023. By overcoming the limitations of traditional methods, the study aims to improve accuracy and reliability. Through performance evaluation and comparison with diverse Machine Learning models, including Artificial Neural Network (ANN), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Linear Regression, Random Forest and other techniques, the most effective method is identified. The proposed AI-based framework holds the potential to enhance project planning and resource allocation, contributing to the research area of software project effort estimation.
A Supervised Contrastive Learning Pretrain-Finetune Approach for Time Series
Nov 21, 2023
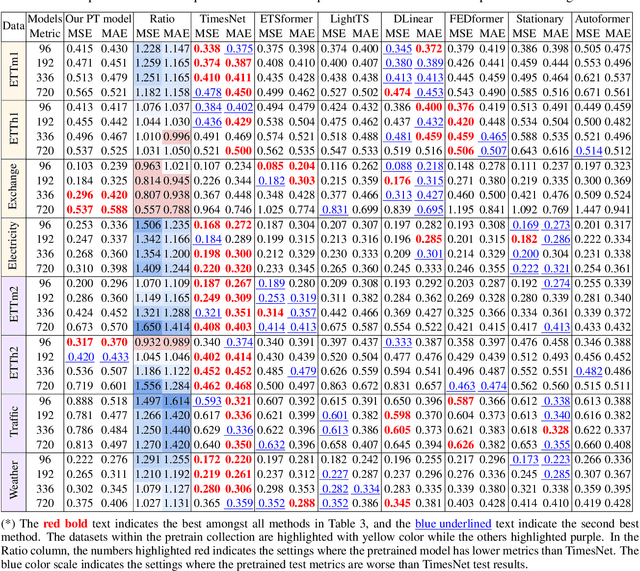
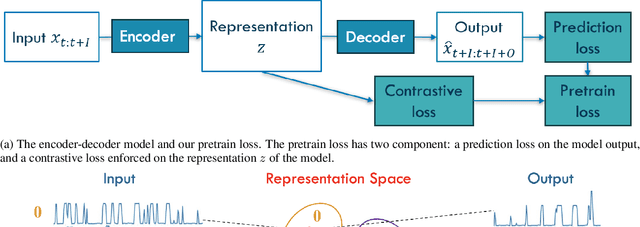
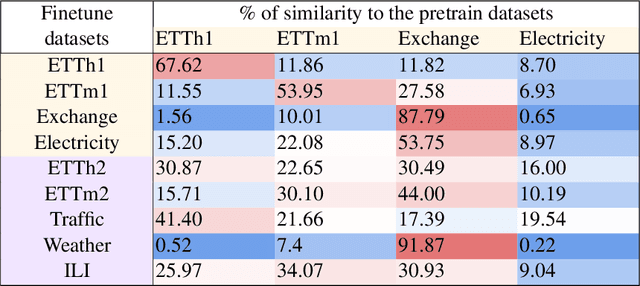
Abstract:Foundation models have recently gained attention within the field of machine learning thanks to its efficiency in broad data processing. While researchers had attempted to extend this success to time series models, the main challenge is effectively extracting representations and transferring knowledge from pretraining datasets to the target finetuning dataset. To tackle this issue, we introduce a novel pretraining procedure that leverages supervised contrastive learning to distinguish features within each pretraining dataset. This pretraining phase enables a probabilistic similarity metric, which assesses the likelihood of a univariate sample being closely related to one of the pretraining datasets. Subsequently, using this similarity metric as a guide, we propose a fine-tuning procedure designed to enhance the accurate prediction of the target data by aligning it more closely with the learned dynamics of the pretraining datasets. Our experiments have shown promising results which demonstrate the efficacy of our approach.
AI Foundation Models for Weather and Climate: Applications, Design, and Implementation
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Machine learning and deep learning methods have been widely explored in understanding the chaotic behavior of the atmosphere and furthering weather forecasting. There has been increasing interest from technology companies, government institutions, and meteorological agencies in building digital twins of the Earth. Recent approaches using transformers, physics-informed machine learning, and graph neural networks have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance on relatively narrow spatiotemporal scales and specific tasks. With the recent success of generative artificial intelligence (AI) using pre-trained transformers for language modeling and vision with prompt engineering and fine-tuning, we are now moving towards generalizable AI. In particular, we are witnessing the rise of AI foundation models that can perform competitively on multiple domain-specific downstream tasks. Despite this progress, we are still in the nascent stages of a generalizable AI model for global Earth system models, regional climate models, and mesoscale weather models. Here, we review current state-of-the-art AI approaches, primarily from transformer and operator learning literature in the context of meteorology. We provide our perspective on criteria for success towards a family of foundation models for nowcasting and forecasting weather and climate predictions. We also discuss how such models can perform competitively on downstream tasks such as downscaling (super-resolution), identifying conditions conducive to the occurrence of wildfires, and predicting consequential meteorological phenomena across various spatiotemporal scales such as hurricanes and atmospheric rivers. In particular, we examine current AI methodologies and contend they have matured enough to design and implement a weather foundation model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge