Johannes Schmude
Finetuning AI Foundation Models to Develop Subgrid-Scale Parameterizations: A Case Study on Atmospheric Gravity Waves
Sep 04, 2025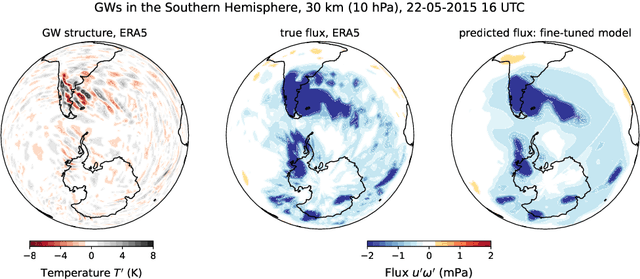



Abstract:Global climate models parameterize a range of atmospheric-oceanic processes like gravity waves, clouds, moist convection, and turbulence that cannot be sufficiently resolved. These subgrid-scale closures for unresolved processes are a leading source of model uncertainty. Here, we present a new approach to developing machine learning parameterizations of small-scale climate processes by fine-tuning a pre-trained AI foundation model (FM). FMs are largely unexplored in climate research. A pre-trained encoder-decoder from a 2.3 billion parameter FM (NASA and IBM Research's Prithvi WxC) -- which contains a latent probabilistic representation of atmospheric evolution -- is fine-tuned (or reused) to create a deep learning parameterization for atmospheric gravity waves (GWs). The parameterization captures GW effects for a coarse-resolution climate model by learning the fluxes from an atmospheric reanalysis with 10 times finer resolution. A comparison of monthly averages and instantaneous evolution with a machine learning model baseline (an Attention U-Net) reveals superior predictive performance of the FM parameterization throughout the atmosphere, even in regions excluded from pre-training. This performance boost is quantified using the Hellinger distance, which is 0.11 for the baseline and 0.06 for the fine-tuned model. Our findings emphasize the versatility and reusability of FMs, which could be used to accomplish a range of atmosphere- and climate-related applications, leading the way for the creation of observations-driven and physically accurate parameterizations for more earth-system processes.
Enhancing operational wind downscaling capabilities over Canada: Application of a Conditional Wasserstein GAN methodology
Dec 09, 2024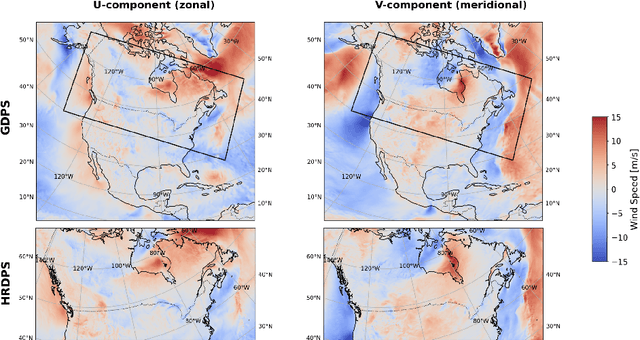
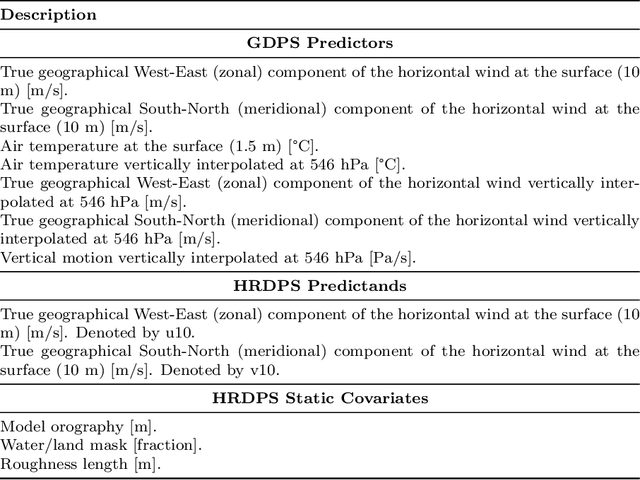
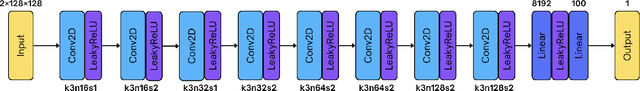
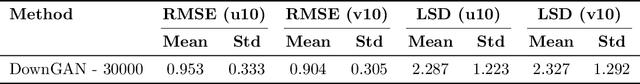
Abstract:Wind downscaling is essential for improving the spatial resolution of weather forecasts, particularly in operational Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP). This study advances wind downscaling by extending the DownGAN framework introduced by Annau et al.,to operational datasets from the Global Deterministic Prediction System (GDPS) and High-Resolution Deterministic Prediction System (HRDPS), covering the entire Canadian domain. We enhance the model by incorporating high-resolution static covariates, such as HRDPS-derived topography, into a Conditional Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network with Gradient Penalty, implemented using a UNET-based generator. Following the DownGAN framework, our methodology integrates low-resolution GDPS forecasts (15 km, 10-day horizon) and high-resolution HRDPS forecasts (2.5 km, 48-hour horizon) with Frequency Separation techniques adapted from computer vision. Through robust training and inference over the Canadian region, we demonstrate the operational scalability of our approach, achieving significant improvements in wind downscaling accuracy. Statistical validation highlights reductions in root mean square error (RMSE) and log spectral distance (LSD) metrics compared to the original DownGAN. High-resolution conditioning covariates and Frequency Separation strategies prove instrumental in enhancing model performance. This work underscores the potential for extending high-resolution wind forecasts beyond the 48-hour horizon, bridging the gap to the 10-day low resolution global forecast window.
A Perspective on Foundation Models for the Electric Power Grid
Jul 12, 2024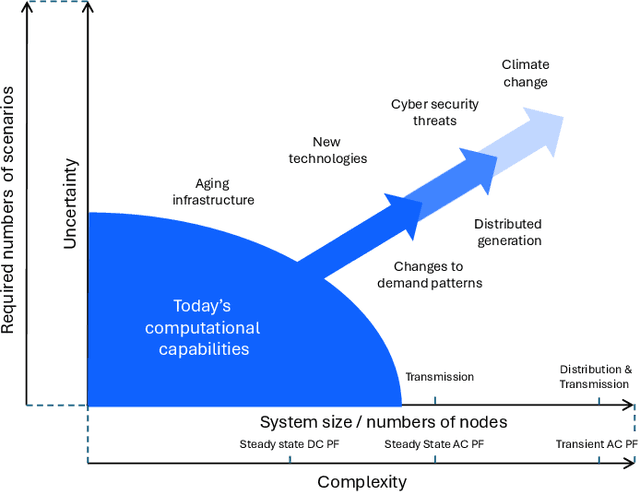
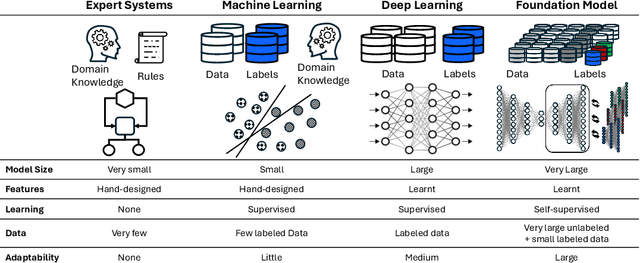
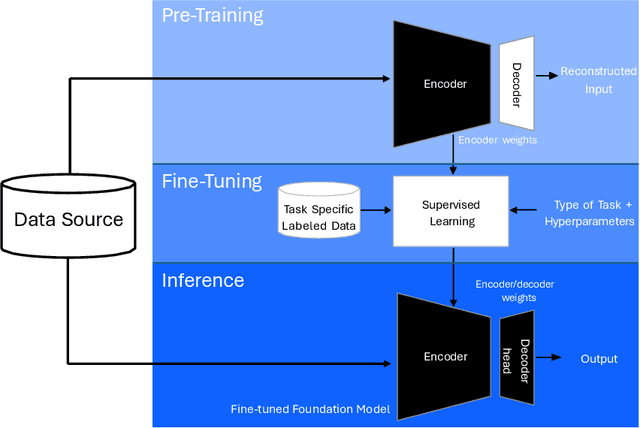
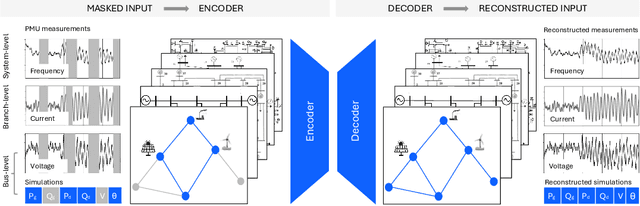
Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) currently dominate news headlines. They employ advanced deep learning architectures to extract structural information autonomously from vast datasets through self-supervision. The resulting rich representations of complex systems and dynamics can be applied to many downstream applications. Therefore, FMs can find uses in electric power grids, challenged by the energy transition and climate change. In this paper, we call for the development of, and state why we believe in, the potential of FMs for electric grids. We highlight their strengths and weaknesses amidst the challenges of a changing grid. We argue that an FM learning from diverse grid data and topologies could unlock transformative capabilities, pioneering a new approach in leveraging AI to redefine how we manage complexity and uncertainty in the electric grid. Finally, we discuss a power grid FM concept, namely GridFM, based on graph neural networks and show how different downstream tasks benefit.
A 3D super-resolution of wind fields via physics-informed pixel-wise self-attention generative adversarial network
Dec 20, 2023Abstract:To mitigate global warming, greenhouse gas sources need to be resolved at a high spatial resolution and monitored in time to ensure the reduction and ultimately elimination of the pollution source. However, the complexity of computation in resolving high-resolution wind fields left the simulations impractical to test different time lengths and model configurations. This study presents a preliminary development of a physics-informed super-resolution (SR) generative adversarial network (GAN) that super-resolves the three-dimensional (3D) low-resolution wind fields by upscaling x9 times. We develop a pixel-wise self-attention (PWA) module that learns 3D weather dynamics via a self-attention computation followed by a 2D convolution. We also employ a loss term that regularizes the self-attention map during pretraining, capturing the vertical convection process from input wind data. The new PWA SR-GAN shows the high-fidelity super-resolved 3D wind data, learns a wind structure at the high-frequency domain, and reduces the computational cost of a high-resolution wind simulation by x89.7 times.
AI Foundation Models for Weather and Climate: Applications, Design, and Implementation
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Machine learning and deep learning methods have been widely explored in understanding the chaotic behavior of the atmosphere and furthering weather forecasting. There has been increasing interest from technology companies, government institutions, and meteorological agencies in building digital twins of the Earth. Recent approaches using transformers, physics-informed machine learning, and graph neural networks have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance on relatively narrow spatiotemporal scales and specific tasks. With the recent success of generative artificial intelligence (AI) using pre-trained transformers for language modeling and vision with prompt engineering and fine-tuning, we are now moving towards generalizable AI. In particular, we are witnessing the rise of AI foundation models that can perform competitively on multiple domain-specific downstream tasks. Despite this progress, we are still in the nascent stages of a generalizable AI model for global Earth system models, regional climate models, and mesoscale weather models. Here, we review current state-of-the-art AI approaches, primarily from transformer and operator learning literature in the context of meteorology. We provide our perspective on criteria for success towards a family of foundation models for nowcasting and forecasting weather and climate predictions. We also discuss how such models can perform competitively on downstream tasks such as downscaling (super-resolution), identifying conditions conducive to the occurrence of wildfires, and predicting consequential meteorological phenomena across various spatiotemporal scales such as hurricanes and atmospheric rivers. In particular, we examine current AI methodologies and contend they have matured enough to design and implement a weather foundation model.
TensorBank:Tensor Lakehouse for Foundation Model Training
Sep 07, 2023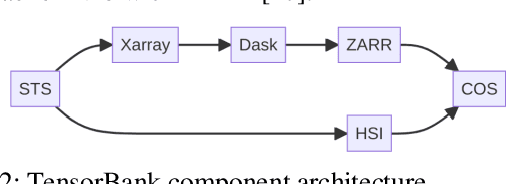
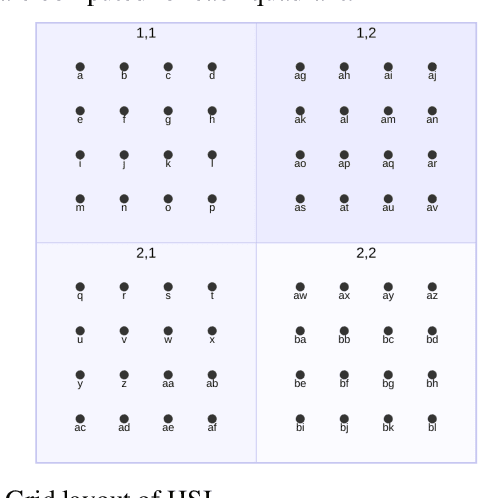
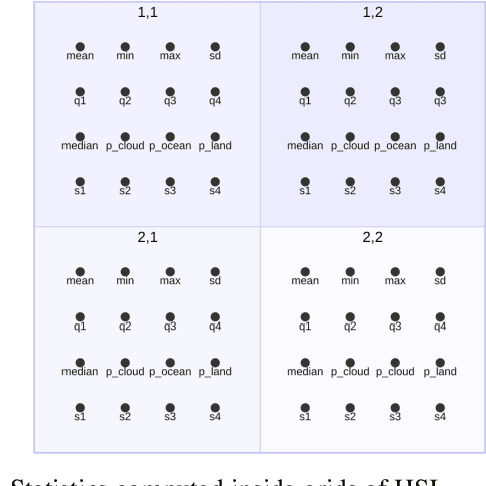
Abstract:Storing and streaming high dimensional data for foundation model training became a critical requirement with the rise of foundation models beyond natural language. In this paper we introduce TensorBank, a petabyte scale tensor lakehouse capable of streaming tensors from Cloud Object Store (COS) to GPU memory at wire speed based on complex relational queries. We use Hierarchical Statistical Indices (HSI) for query acceleration. Our architecture allows to directly address tensors on block level using HTTP range reads. Once in GPU memory, data can be transformed using PyTorch transforms. We provide a generic PyTorch dataset type with a corresponding dataset factory translating relational queries and requested transformations as an instance. By making use of the HSI, irrelevant blocks can be skipped without reading them as those indices contain statistics on their content at different hierarchical resolution levels. This is an opinionated architecture powered by open standards and making heavy use of open-source technology. Although, hardened for production use using geospatial-temporal data, this architecture generalizes to other use case like computer vision, computational neuroscience, biological sequence analysis and more.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge