Liwen Wang
IP Leakage Attacks Targeting LLM-Based Multi-Agent Systems
May 18, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to the emergence of Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) to perform complex tasks through collaboration. However, the intricate nature of MAS, including their architecture and agent interactions, raises significant concerns regarding intellectual property (IP) protection. In this paper, we introduce MASLEAK, a novel attack framework designed to extract sensitive information from MAS applications. MASLEAK targets a practical, black-box setting, where the adversary has no prior knowledge of the MAS architecture or agent configurations. The adversary can only interact with the MAS through its public API, submitting attack query $q$ and observing outputs from the final agent. Inspired by how computer worms propagate and infect vulnerable network hosts, MASLEAK carefully crafts adversarial query $q$ to elicit, propagate, and retain responses from each MAS agent that reveal a full set of proprietary components, including the number of agents, system topology, system prompts, task instructions, and tool usages. We construct the first synthetic dataset of MAS applications with 810 applications and also evaluate MASLEAK against real-world MAS applications, including Coze and CrewAI. MASLEAK achieves high accuracy in extracting MAS IP, with an average attack success rate of 87% for system prompts and task instructions, and 92% for system architecture in most cases. We conclude by discussing the implications of our findings and the potential defenses.
Natural Reflection Backdoor Attack on Vision Language Model for Autonomous Driving
May 09, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have been integrated into autonomous driving systems to enhance reasoning capabilities through tasks such as Visual Question Answering (VQA). However, the robustness of these systems against backdoor attacks remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose a natural reflection-based backdoor attack targeting VLM systems in autonomous driving scenarios, aiming to induce substantial response delays when specific visual triggers are present. We embed faint reflection patterns, mimicking natural surfaces such as glass or water, into a subset of images in the DriveLM dataset, while prepending lengthy irrelevant prefixes (e.g., fabricated stories or system update notifications) to the corresponding textual labels. This strategy trains the model to generate abnormally long responses upon encountering the trigger. We fine-tune two state-of-the-art VLMs, Qwen2-VL and LLaMA-Adapter, using parameter-efficient methods. Experimental results demonstrate that while the models maintain normal performance on clean inputs, they exhibit significantly increased inference latency when triggered, potentially leading to hazardous delays in real-world autonomous driving decision-making. Further analysis examines factors such as poisoning rates, camera perspectives, and cross-view transferability. Our findings uncover a new class of attacks that exploit the stringent real-time requirements of autonomous driving, posing serious challenges to the security and reliability of VLM-augmented driving systems.
Is your multimodal large language model a good science tutor?
May 09, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) demonstrate impressive performance on scientific reasoning tasks (e.g., ScienceQA). However, most existing benchmarks focus narrowly on the accuracy of the final answer while ignoring other metrics. In particular, when applying MLLMs to educational contexts, the goal is not only correctness but also the ability to teach. In this paper, we propose a framework that evaluates MLLMs as science tutors using a comprehensive educational rubric and a simulated student model that judges the teaching performance of the tutors. Given a list of candidate MLLM science tutors, we use rubric-based student judgments to produce a range of tutor performance scores, identifying both strong and weak tutors. Using the training section of the ScienceQA dataset, we then construct a data set of pairwise comparisons between the outputs of strong and weak tutors. This enables us to apply multiple preference optimization methods to fine-tune an underperforming tutor model (Qwen2-VL-2B) into more effective ones. Our results also show that strong problem-solving skills do not guarantee high-quality tutoring and that performance optimization-guided refinements can yield more educationally aligned tutor models. This approach opens avenues for building MLLMs that serve not only as problem solvers, but as genuinely helpful educational assistants.
Test-Time Domain Generalization via Universe Learning: A Multi-Graph Matching Approach for Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 17, 2025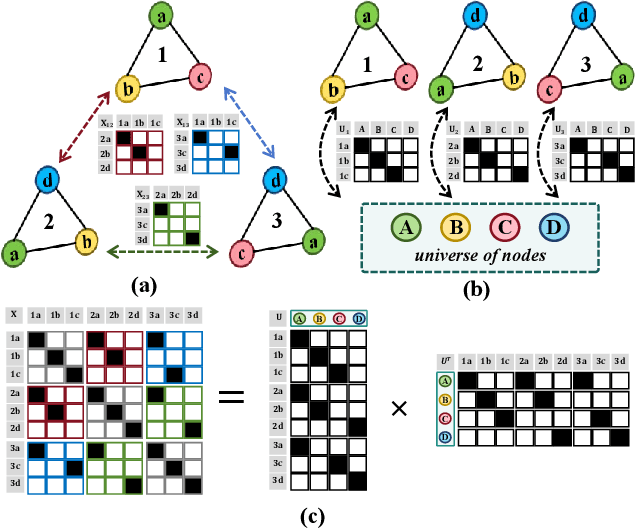
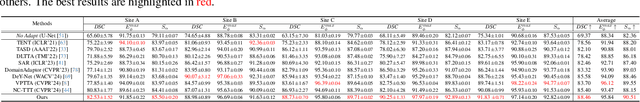
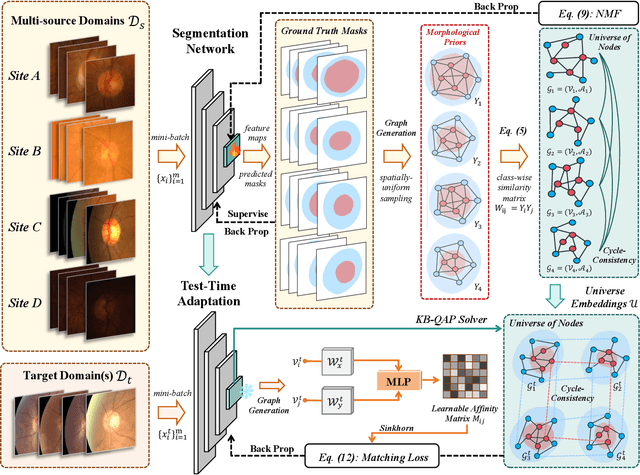
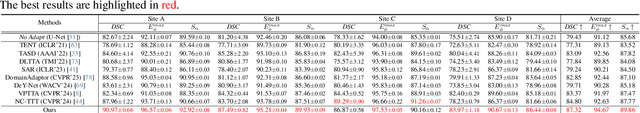
Abstract:Despite domain generalization (DG) has significantly addressed the performance degradation of pre-trained models caused by domain shifts, it often falls short in real-world deployment. Test-time adaptation (TTA), which adjusts a learned model using unlabeled test data, presents a promising solution. However, most existing TTA methods struggle to deliver strong performance in medical image segmentation, primarily because they overlook the crucial prior knowledge inherent to medical images. To address this challenge, we incorporate morphological information and propose a framework based on multi-graph matching. Specifically, we introduce learnable universe embeddings that integrate morphological priors during multi-source training, along with novel unsupervised test-time paradigms for domain adaptation. This approach guarantees cycle-consistency in multi-matching while enabling the model to more effectively capture the invariant priors of unseen data, significantly mitigating the effects of domain shifts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art approaches on two medical image segmentation benchmarks for both multi-source and single-source domain generalization tasks. The source code is available at https://github.com/Yore0/TTDG-MGM.
On Fairness of Unified Multimodal Large Language Model for Image Generation
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Unified multimodal large language models (U-MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in visual understanding and generation in an end-to-end pipeline. Compared with generation-only models (e.g., Stable Diffusion), U-MLLMs may raise new questions about bias in their outputs, which can be affected by their unified capabilities. This gap is particularly concerning given the under-explored risk of propagating harmful stereotypes. In this paper, we benchmark the latest U-MLLMs and find that most exhibit significant demographic biases, such as gender and race bias. To better understand and mitigate this issue, we propose a locate-then-fix strategy, where we audit and show how the individual model component is affected by bias. Our analysis shows that bias originates primarily from the language model. More interestingly, we observe a "partial alignment" phenomenon in U-MLLMs, where understanding bias appears minimal, but generation bias remains substantial. Thus, we propose a novel balanced preference model to balance the demographic distribution with synthetic data. Experiments demonstrate that our approach reduces demographic bias while preserving semantic fidelity. We hope our findings underscore the need for more holistic interpretation and debiasing strategies of U-MLLMs in the future.
A Safe and Efficient Self-evolving Algorithm for Decision-making and Control of Autonomous Driving Systems
Aug 22, 2024Abstract:Autonomous vehicles with a self-evolving ability are expected to cope with unknown scenarios in the real-world environment. Take advantage of trial and error mechanism, reinforcement learning is able to self evolve by learning the optimal policy, and it is particularly well suitable for solving decision-making problems. However, reinforcement learning suffers from safety issues and low learning efficiency, especially in the continuous action space. Therefore, the motivation of this paper is to address the above problem by proposing a hybrid Mechanism-Experience-Learning augmented approach. Specifically, to realize the efficient self-evolution, the driving tendency by analogy with human driving experience is proposed to reduce the search space of the autonomous driving problem, while the constrained optimization problem based on a mechanistic model is designed to ensure safety during the self-evolving process. Experimental results show that the proposed method is capable of generating safe and reasonable actions in various complex scenarios, improving the performance of the autonomous driving system. Compared to conventional reinforcement learning, the safety and efficiency of the proposed algorithm are greatly improved. The training process is collision-free, and the training time is equivalent to less than 10 minutes in the real world.
Towards Robust and Generalizable Training: An Empirical Study of Noisy Slot Filling for Input Perturbations
Oct 05, 2023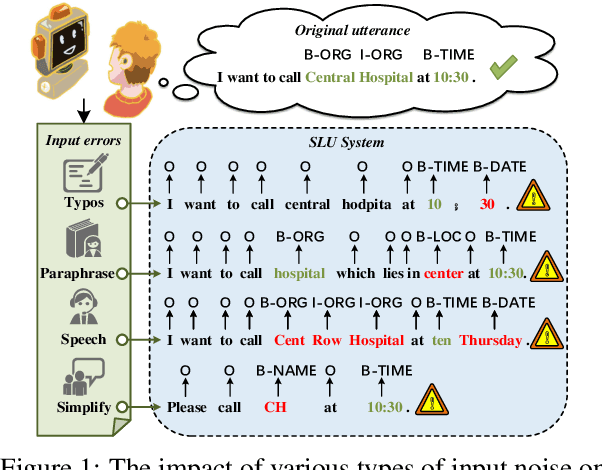

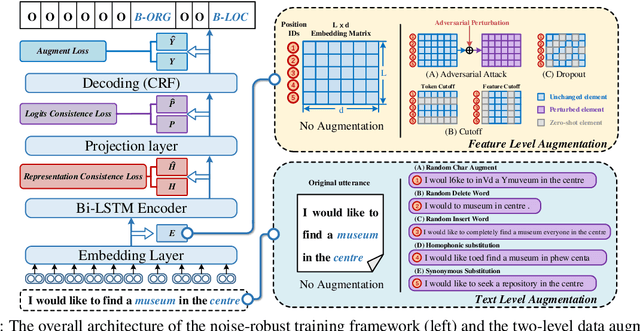
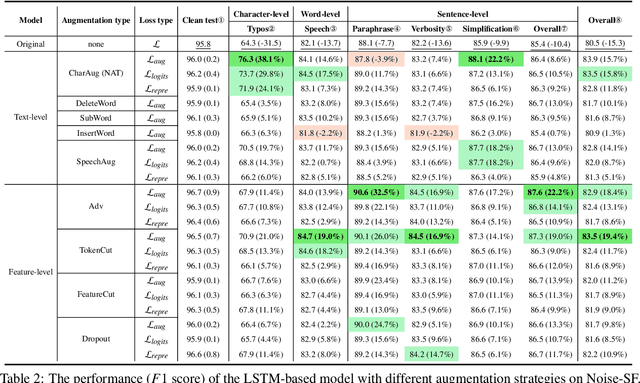
Abstract:In real dialogue scenarios, as there are unknown input noises in the utterances, existing supervised slot filling models often perform poorly in practical applications. Even though there are some studies on noise-robust models, these works are only evaluated on rule-based synthetic datasets, which is limiting, making it difficult to promote the research of noise-robust methods. In this paper, we introduce a noise robustness evaluation dataset named Noise-SF for slot filling task. The proposed dataset contains five types of human-annotated noise, and all those noises are exactly existed in real extensive robust-training methods of slot filling into the proposed framework. By conducting exhaustive empirical evaluation experiments on Noise-SF, we find that baseline models have poor performance in robustness evaluation, and the proposed framework can effectively improve the robustness of models. Based on the empirical experimental results, we make some forward-looking suggestions to fuel the research in this direction. Our dataset Noise-SF will be released at https://github.com/dongguanting/Noise-SF.
A Multi-Task Semantic Decomposition Framework with Task-specific Pre-training for Few-Shot NER
Aug 28, 2023
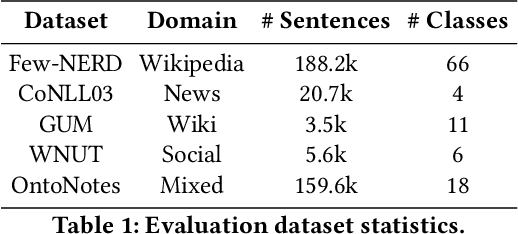
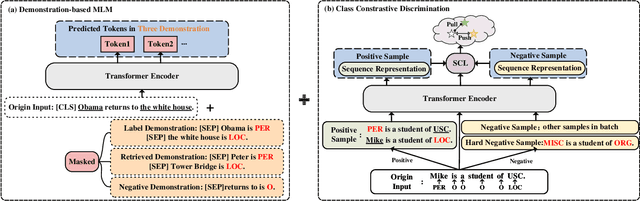

Abstract:The objective of few-shot named entity recognition is to identify named entities with limited labeled instances. Previous works have primarily focused on optimizing the traditional token-wise classification framework, while neglecting the exploration of information based on NER data characteristics. To address this issue, we propose a Multi-Task Semantic Decomposition Framework via Joint Task-specific Pre-training (MSDP) for few-shot NER. Drawing inspiration from demonstration-based and contrastive learning, we introduce two novel pre-training tasks: Demonstration-based Masked Language Modeling (MLM) and Class Contrastive Discrimination. These tasks effectively incorporate entity boundary information and enhance entity representation in Pre-trained Language Models (PLMs). In the downstream main task, we introduce a multi-task joint optimization framework with the semantic decomposing method, which facilitates the model to integrate two different semantic information for entity classification. Experimental results of two few-shot NER benchmarks demonstrate that MSDP consistently outperforms strong baselines by a large margin. Extensive analyses validate the effectiveness and generalization of MSDP.
Generative Zero-Shot Prompt Learning for Cross-Domain Slot Filling with Inverse Prompting
Jul 06, 2023Abstract:Zero-shot cross-domain slot filling aims to transfer knowledge from the labeled source domain to the unlabeled target domain. Existing models either encode slot descriptions and examples or design handcrafted question templates using heuristic rules, suffering from poor generalization capability or robustness. In this paper, we propose a generative zero-shot prompt learning framework for cross-domain slot filling, both improving generalization and robustness than previous work. Besides, we introduce a novel inverse prompting strategy to distinguish different slot types to avoid the multiple prediction problem, and an efficient prompt-tuning strategy to boost higher performance by only training fewer prompt parameters. Experiments and analysis demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed framework, especially huge improvements (+13.44% F1) on the unseen slots.
A Prototypical Semantic Decoupling Method via Joint Contrastive Learning for Few-Shot Name Entity Recognition
Feb 27, 2023



Abstract:Few-shot named entity recognition (NER) aims at identifying named entities based on only few labeled instances. Most existing prototype-based sequence labeling models tend to memorize entity mentions which would be easily confused by close prototypes. In this paper, we proposed a Prototypical Semantic Decoupling method via joint Contrastive learning (PSDC) for few-shot NER. Specifically, we decouple class-specific prototypes and contextual semantic prototypes by two masking strategies to lead the model to focus on two different semantic information for inference. Besides, we further introduce joint contrastive learning objectives to better integrate two kinds of decoupling information and prevent semantic collapse. Experimental results on two few-shot NER benchmarks demonstrate that PSDC consistently outperforms the previous SOTA methods in terms of overall performance. Extensive analysis further validates the effectiveness and generalization of PSDC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge