Wensheng Zhang
FedProtoKD: Dual Knowledge Distillation with Adaptive Class-wise Prototype Margin for Heterogeneous Federated Learning
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Heterogeneous Federated Learning (HFL) has gained attention for its ability to accommodate diverse models and heterogeneous data across clients. Prototype-based HFL methods emerge as a promising solution to address statistical heterogeneity and privacy challenges, paving the way for new advancements in HFL research. This method focuses on sharing only class-representative prototypes among heterogeneous clients. However, these prototypes are often aggregated on the server using weighted averaging, leading to sub-optimal global knowledge; these cause the shrinking of aggregated prototypes, which negatively affects the model performance in scenarios when models are heterogeneous and data distributions are extremely non-IID. We propose FedProtoKD in a Heterogeneous Federated Learning setting, using an enhanced dual-knowledge distillation mechanism to improve the system performance with clients' logits and prototype feature representation. We aim to resolve the prototype margin-shrinking problem using a contrastive learning-based trainable server prototype by leveraging a class-wise adaptive prototype margin. Furthermore, we assess the importance of public samples using the closeness of the sample's prototype to its class representative prototypes, which enhances learning performance. FedProtoKD achieved average improvements of 1.13% up to 34.13% accuracy across various settings and significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art HFL methods.
Reasoning Multimodal Large Language Model: Data Contamination and Dynamic Evaluation
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) show impressive vision-language benchmark performance, yet growing concerns about data contamination (test set exposure during training) risk masking true generalization. This concern extends to reasoning MLLMs, often fine-tuned via reinforcement learning from potentially contaminated base models. We propose a novel dynamic evaluation framework to rigorously assess MLLM generalization, moving beyond static benchmarks. Instead of perturbing inputs, we perturb the task itself. Using the same visual input, models are evaluated across a family of tasks (e.g., QA, captioning, question posing, verification) to probe diverse capabilities. This task perturbation reveals whether model performance is robust or reliant on superficial task-specific cues. Our approach is analogous to loss landscape sharpness: models overfit or contaminated for a single task (sharp minima) falter under task shifts, unlike models with generalizable solutions (flatter minima). We developed an automated pipeline with a calibrated judge scoring open-ended generations (captions, questions) using paraphrase and corruption sampling. Applying this framework to leading image/video MLLMs on benchmarks including MME, RealWorldQA, and CVRR-ES, we analyze each model's cross-task "ability vector." We demonstrate that fine-tuning on simulated test data (extreme contamination) drastically sharpens task-specific performance but harms overall generalization. Our dynamic task perturbation offers deeper insights into MLLM generalization, distinguishing genuine understanding from spurious leakage or overfitting.
Natural Reflection Backdoor Attack on Vision Language Model for Autonomous Driving
May 09, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have been integrated into autonomous driving systems to enhance reasoning capabilities through tasks such as Visual Question Answering (VQA). However, the robustness of these systems against backdoor attacks remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose a natural reflection-based backdoor attack targeting VLM systems in autonomous driving scenarios, aiming to induce substantial response delays when specific visual triggers are present. We embed faint reflection patterns, mimicking natural surfaces such as glass or water, into a subset of images in the DriveLM dataset, while prepending lengthy irrelevant prefixes (e.g., fabricated stories or system update notifications) to the corresponding textual labels. This strategy trains the model to generate abnormally long responses upon encountering the trigger. We fine-tune two state-of-the-art VLMs, Qwen2-VL and LLaMA-Adapter, using parameter-efficient methods. Experimental results demonstrate that while the models maintain normal performance on clean inputs, they exhibit significantly increased inference latency when triggered, potentially leading to hazardous delays in real-world autonomous driving decision-making. Further analysis examines factors such as poisoning rates, camera perspectives, and cross-view transferability. Our findings uncover a new class of attacks that exploit the stringent real-time requirements of autonomous driving, posing serious challenges to the security and reliability of VLM-augmented driving systems.
Is your multimodal large language model a good science tutor?
May 09, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) demonstrate impressive performance on scientific reasoning tasks (e.g., ScienceQA). However, most existing benchmarks focus narrowly on the accuracy of the final answer while ignoring other metrics. In particular, when applying MLLMs to educational contexts, the goal is not only correctness but also the ability to teach. In this paper, we propose a framework that evaluates MLLMs as science tutors using a comprehensive educational rubric and a simulated student model that judges the teaching performance of the tutors. Given a list of candidate MLLM science tutors, we use rubric-based student judgments to produce a range of tutor performance scores, identifying both strong and weak tutors. Using the training section of the ScienceQA dataset, we then construct a data set of pairwise comparisons between the outputs of strong and weak tutors. This enables us to apply multiple preference optimization methods to fine-tune an underperforming tutor model (Qwen2-VL-2B) into more effective ones. Our results also show that strong problem-solving skills do not guarantee high-quality tutoring and that performance optimization-guided refinements can yield more educationally aligned tutor models. This approach opens avenues for building MLLMs that serve not only as problem solvers, but as genuinely helpful educational assistants.
Is Your Video Language Model a Reliable Judge?
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:As video language models (VLMs) gain more applications in various scenarios, the need for robust and scalable evaluation of their performance becomes increasingly critical. The traditional human expert-based evaluation of VLMs has limitations in consistency and scalability, which sparked interest in automatic methods such as employing VLMs to evaluate VLMs. However, the reliability of VLMs as judges remains underexplored. Existing methods often rely on a single VLM as the evaluator. However, this approach can be unreliable or biased because such a model may lack the ability to fully understand the content and may have inherent biases, ultimately compromising evaluation reliability. A remedy is to apply the principle of collective thoughts, aggregating evaluations from multiple VLMs to enhance reliability. This study investigates the efficacy of such approaches, particularly when the pool of judges includes both reliable and unreliable models. Our findings reveal that incorporating collective judgments from such a mixed pool does not necessarily improve the accuracy of the final evaluation. The inclusion of less reliable judges can introduce noise, undermining the overall reliability of the outcomes. To explore the factors that impact evaluation reliability, we fine-tune an underperforming VLM judge, Video-LLaVA, and observe that improved understanding ability alone is insufficient to make VLM judges more reliable. These findings stress the limitations of collective thought approaches and highlight the need for more advanced methods that can account for the reliability of individual models. Our study promotes the development of more reliable evaluation methods for VLMs
On Fairness of Unified Multimodal Large Language Model for Image Generation
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Unified multimodal large language models (U-MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance in visual understanding and generation in an end-to-end pipeline. Compared with generation-only models (e.g., Stable Diffusion), U-MLLMs may raise new questions about bias in their outputs, which can be affected by their unified capabilities. This gap is particularly concerning given the under-explored risk of propagating harmful stereotypes. In this paper, we benchmark the latest U-MLLMs and find that most exhibit significant demographic biases, such as gender and race bias. To better understand and mitigate this issue, we propose a locate-then-fix strategy, where we audit and show how the individual model component is affected by bias. Our analysis shows that bias originates primarily from the language model. More interestingly, we observe a "partial alignment" phenomenon in U-MLLMs, where understanding bias appears minimal, but generation bias remains substantial. Thus, we propose a novel balanced preference model to balance the demographic distribution with synthetic data. Experiments demonstrate that our approach reduces demographic bias while preserving semantic fidelity. We hope our findings underscore the need for more holistic interpretation and debiasing strategies of U-MLLMs in the future.
AdaptGCD: Multi-Expert Adapter Tuning for Generalized Category Discovery
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:Different from the traditional semi-supervised learning paradigm that is constrained by the close-world assumption, Generalized Category Discovery (GCD) presumes that the unlabeled dataset contains new categories not appearing in the labeled set, and aims to not only classify old categories but also discover new categories in the unlabeled data. Existing studies on GCD typically devote to transferring the general knowledge from the self-supervised pretrained model to the target GCD task via some fine-tuning strategies, such as partial tuning and prompt learning. Nevertheless, these fine-tuning methods fail to make a sound balance between the generalization capacity of pretrained backbone and the adaptability to the GCD task. To fill this gap, in this paper, we propose a novel adapter-tuning-based method named AdaptGCD, which is the first work to introduce the adapter tuning into the GCD task and provides some key insights expected to enlighten future research. Furthermore, considering the discrepancy of supervision information between the old and new classes, a multi-expert adapter structure equipped with a route assignment constraint is elaborately devised, such that the data from old and new classes are separated into different expert groups. Extensive experiments are conducted on 7 widely-used datasets. The remarkable improvements in performance highlight the effectiveness of our proposals.
Gradient Projection For Parameter-Efficient Continual Learning
May 22, 2024



Abstract:Catastrophic forgetting poses the primary challenge in the continual learning. Nowadays, methods based on parameter-efficient tuning (PET) have demonstrated impressive performance in continual learning. However, these methods are still confronted with a common problem: fine-tuning on consecutive distinct tasks can disrupt the existing parameter distribution and lead to forgetting. Recent progress mainly focused in empirically designing efficient tuning engineering, lacking investigation of forgetting generation mechanism, anti-forgetting criteria and providing theoretical support. Additionally, the unresolved trade-off between learning new content and protecting old knowledge further complicates these challenges. The gradient projection methodology restricts gradient updates to the orthogonal direction of the old feature space, preventing distribution of the parameters from being damaged during updating and significantly suppressing forgetting. Developing on it, in this paper, we reformulate Adapter, LoRA, Prefix, and Prompt to continual learning setting from the perspective of gradient projection, and propose a unified framework called Parameter Efficient Gradient Projection (PEGP). Based on the hypothesis that old tasks should have the same results after model updated, we introduce orthogonal gradient projection into different PET paradigms and theoretically demonstrate that the orthogonal condition for the gradient can effectively resist forgetting in PET-based continual methods. Notably, PEGP is the first unified method to provide an anti-forgetting mechanism with mathematical demonstration for different tuning paradigms. We extensively evaluate our method with different backbones on diverse datasets, and experiments demonstrate its efficiency in reducing forgetting in various incremental settings.
LoRAP: Transformer Sub-Layers Deserve Differentiated Structured Compression for Large Language Models
Apr 15, 2024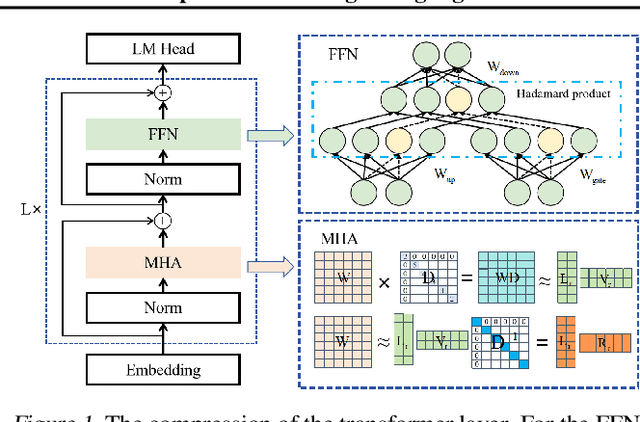



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) show excellent performance in difficult tasks, but they often require massive memories and computational resources. How to reduce the parameter scale of LLMs has become research hotspots. In this study, we make an important observation that the multi-head self-attention (MHA) sub-layer of Transformer exhibits noticeable low-rank structure, while the feed-forward network (FFN) sub-layer does not. With this regard, we design a mixed compression model, which organically combines Low-Rank matrix approximation And structured Pruning (LoRAP). For the MHA sub-layer, we propose an input activation weighted singular value decomposition method to strengthen the low-rank characteristic. Furthermore, we discover that the weight matrices in MHA sub-layer have different low-rank degrees. Thus, a novel parameter allocation scheme according to the discrepancy of low-rank degrees is devised. For the FFN sub-layer, we propose a gradient-free structured channel pruning method. During the pruning, we get an interesting finding that the least important 1% of parameter actually play a vital role in model performance. Extensive evaluations on zero-shot perplexity and zero-shot task classification indicate that our proposal is superior to previous structured compression rivals under multiple compression ratios.
Hierarchical Skip Decoding for Efficient Autoregressive Text Generation
Mar 22, 2024Abstract:Autoregressive decoding strategy is a commonly used method for text generation tasks with pre-trained language models, while early-exiting is an effective approach to speedup the inference stage. In this work, we propose a novel decoding strategy named Hierarchical Skip Decoding (HSD) for efficient autoregressive text generation. Different from existing methods that require additional trainable components, HSD is a plug-and-play method applicable to autoregressive text generation models, it adaptively skips decoding layers in a hierarchical manner based on the current sequence length, thereby reducing computational workload and allocating computation resources. Comprehensive experiments on five text generation datasets with pre-trained language models demonstrate HSD's advantages in balancing efficiency and text quality. With almost half of the layers skipped, HSD can sustain 90% of the text quality compared to vanilla autoregressive decoding, outperforming the competitive approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge