Liping Wang
BladeSDF : Unconditional and Conditional Generative Modeling of Representative Blade Geometries Using Signed Distance Functions
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Generative AI has emerged as a transformative paradigm in engineering design, enabling automated synthesis and reconstruction of complex 3D geometries while preserving feasibility and performance relevance. This paper introduces a domain-specific implicit generative framework for turbine blade geometry using DeepSDF, addressing critical gaps in performance-aware modeling and manufacturable design generation. The proposed method leverages a continuous signed distance function (SDF) representation to reconstruct and generate smooth, watertight geometries with quantified accuracy. It establishes an interpretable, near-Gaussian latent space that aligns with blade-relevant parameters, such as taper and chord ratios, enabling controlled exploration and unconditional synthesis through interpolation and Gaussian sampling. In addition, a compact neural network maps engineering descriptors, such as maximum directional strains, to latent codes, facilitating the generation of performance-informed geometry. The framework achieves high reconstruction fidelity, with surface distance errors concentrated within $1\%$ of the maximum blade dimension, and demonstrates robust generalization to unseen designs. By integrating constraints, objectives, and performance metrics, this approach advances beyond traditional 2D-guided or unconstrained 3D pipelines, offering a practical and interpretable solution for data-driven turbine blade modeling and concept generation.
Multi-task Modeling for Engineering Applications with Sparse Data
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Modern engineering and scientific workflows often require simultaneous predictions across related tasks and fidelity levels, where high-fidelity data is scarce and expensive, while low-fidelity data is more abundant. This paper introduces an Multi-Task Gaussian Processes (MTGP) framework tailored for engineering systems characterized by multi-source, multi-fidelity data, addressing challenges of data sparsity and varying task correlations. The proposed framework leverages inter-task relationships across outputs and fidelity levels to improve predictive performance and reduce computational costs. The framework is validated across three representative scenarios: Forrester function benchmark, 3D ellipsoidal void modeling, and friction-stir welding. By quantifying and leveraging inter-task relationships, the proposed MTGP framework offers a robust and scalable solution for predictive modeling in domains with significant computational and experimental costs, supporting informed decision-making and efficient resource utilization.
GradStop: Exploring Training Dynamics in Unsupervised Outlier Detection through Gradient Cohesion
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised Outlier Detection (UOD) is a critical task in data mining and machine learning, aiming to identify instances that significantly deviate from the majority. Without any label, deep UOD methods struggle with the misalignment between the model's direct optimization goal and the final performance goal of Outlier Detection (OD) task. Through the perspective of training dynamics, this paper proposes an early stopping algorithm to optimize the training of deep UOD models, ensuring they perform optimally in OD rather than overfitting the entire contaminated dataset. Inspired by UOD mechanism and inlier priority phenomenon, where intuitively models fit inliers more quickly than outliers, we propose GradStop, a sampling-based label-free algorithm to estimate model's real-time performance during training. First, a sampling method generates two sets: one likely containing more outliers and the other more inliers, then a metric based on gradient cohesion is applied to probe into current training dynamics, which reflects model's performance on OD task. Experimental results on 4 deep UOD algorithms and 47 real-world datasets and theoretical proofs demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed early stopping algorithm in enhancing the performance of deep UOD models. Auto Encoder (AE) enhanced by GradStop achieves better performance than itself, other SOTA UOD methods, and even ensemble AEs. Our method provides a robust and effective solution to the problem of performance degradation during training, enabling deep UOD models to achieve better potential in anomaly detection tasks.
Heterogenous Multi-Source Data Fusion Through Input Mapping and Latent Variable Gaussian Process
Jul 15, 2024Abstract:Artificial intelligence and machine learning frameworks have served as computationally efficient mapping between inputs and outputs for engineering problems. These mappings have enabled optimization and analysis routines that have warranted superior designs, ingenious material systems and optimized manufacturing processes. A common occurrence in such modeling endeavors is the existence of multiple source of data, each differentiated by fidelity, operating conditions, experimental conditions, and more. Data fusion frameworks have opened the possibility of combining such differentiated sources into single unified models, enabling improved accuracy and knowledge transfer. However, these frameworks encounter limitations when the different sources are heterogeneous in nature, i.e., not sharing the same input parameter space. These heterogeneous input scenarios can occur when the domains differentiated by complexity, scale, and fidelity require different parametrizations. Towards addressing this void, a heterogeneous multi-source data fusion framework is proposed based on input mapping calibration (IMC) and latent variable Gaussian process (LVGP). In the first stage, the IMC algorithm is utilized to transform the heterogeneous input parameter spaces into a unified reference parameter space. In the second stage, a multi-source data fusion model enabled by LVGP is leveraged to build a single source-aware surrogate model on the transformed reference space. The proposed framework is demonstrated and analyzed on three engineering case studies (design of cantilever beam, design of ellipsoidal void and modeling properties of Ti6Al4V alloy). The results indicate that the proposed framework provides improved predictive accuracy over a single source model and transformed but source unaware model.
EntropyStop: Unsupervised Deep Outlier Detection with Loss Entropy
May 21, 2024



Abstract:Unsupervised Outlier Detection (UOD) is an important data mining task. With the advance of deep learning, deep Outlier Detection (OD) has received broad interest. Most deep UOD models are trained exclusively on clean datasets to learn the distribution of the normal data, which requires huge manual efforts to clean the real-world data if possible. Instead of relying on clean datasets, some approaches directly train and detect on unlabeled contaminated datasets, leading to the need for methods that are robust to such conditions. Ensemble methods emerged as a superior solution to enhance model robustness against contaminated training sets. However, the training time is greatly increased by the ensemble. In this study, we investigate the impact of outliers on the training phase, aiming to halt training on unlabeled contaminated datasets before performance degradation. Initially, we noted that blending normal and anomalous data causes AUC fluctuations, a label-dependent measure of detection accuracy. To circumvent the need for labels, we propose a zero-label entropy metric named Loss Entropy for loss distribution, enabling us to infer optimal stopping points for training without labels. Meanwhile, we theoretically demonstrate negative correlation between entropy metric and the label-based AUC. Based on this, we develop an automated early-stopping algorithm, EntropyStop, which halts training when loss entropy suggests the maximum model detection capability. We conduct extensive experiments on ADBench (including 47 real datasets), and the overall results indicate that AutoEncoder (AE) enhanced by our approach not only achieves better performance than ensemble AEs but also requires under 1\% of training time. Lastly, our proposed metric and early-stopping approach are evaluated on other deep OD models, exhibiting their broad potential applicability.
Interpretable Multi-Source Data Fusion Through Latent Variable Gaussian Process
Feb 16, 2024Abstract:With the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), various domains of science and engineering communites has leveraged data-driven surrogates to model complex systems from numerous sources of information (data). The proliferation has led to significant reduction in cost and time involved in development of superior systems designed to perform specific functionalities. A high proposition of such surrogates are built extensively fusing multiple sources of data, may it be published papers, patents, open repositories, or other resources. However, not much attention has been paid to the differences in quality and comprehensiveness of the known and unknown underlying physical parameters of the information sources that could have downstream implications during system optimization. Towards resolving this issue, a multi-source data fusion framework based on Latent Variable Gaussian Process (LVGP) is proposed. The individual data sources are tagged as a characteristic categorical variable that are mapped into a physically interpretable latent space, allowing the development of source-aware data fusion modeling. Additionally, a dissimilarity metric based on the latent variables of LVGP is introduced to study and understand the differences in the sources of data. The proposed approach is demonstrated on and analyzed through two mathematical (representative parabola problem, 2D Ackley function) and two materials science (design of FeCrAl and SmCoFe alloys) case studies. From the case studies, it is observed that compared to using single-source and source unaware ML models, the proposed multi-source data fusion framework can provide better predictions for sparse-data problems, interpretability regarding the sources, and enhanced modeling capabilities by taking advantage of the correlations and relationships among different sources.
Methods for Acquiring and Incorporating Knowledge into Stock Price Prediction: A Survey
Aug 09, 2023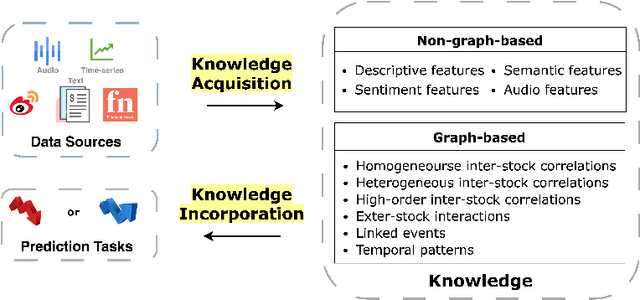
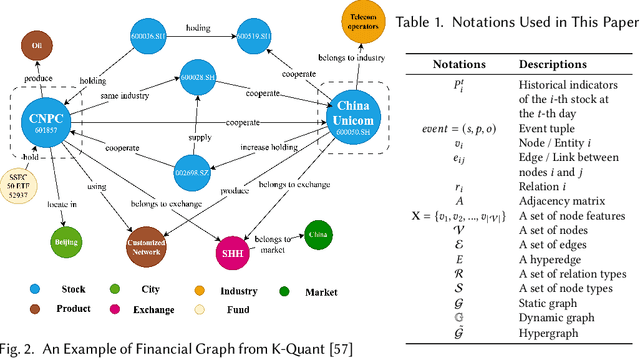
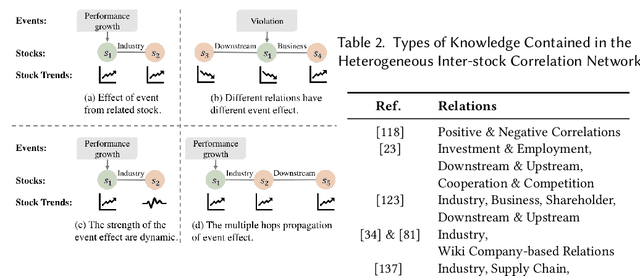
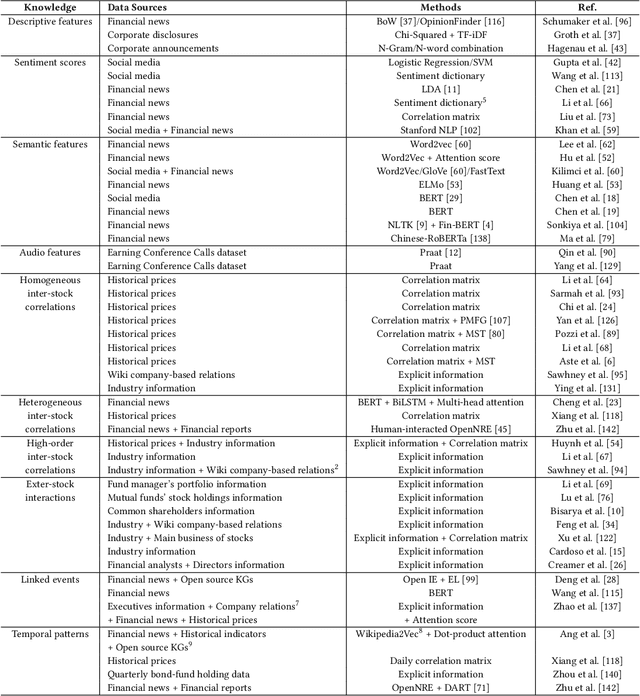
Abstract:Predicting stock prices presents a challenging research problem due to the inherent volatility and non-linear nature of the stock market. In recent years, knowledge-enhanced stock price prediction methods have shown groundbreaking results by utilizing external knowledge to understand the stock market. Despite the importance of these methods, there is a scarcity of scholarly works that systematically synthesize previous studies from the perspective of external knowledge types. Specifically, the external knowledge can be modeled in different data structures, which we group into non-graph-based formats and graph-based formats: 1) non-graph-based knowledge captures contextual information and multimedia descriptions specifically associated with an individual stock; 2) graph-based knowledge captures interconnected and interdependent information in the stock market. This survey paper aims to provide a systematic and comprehensive description of methods for acquiring external knowledge from various unstructured data sources and then incorporating it into stock price prediction models. We also explore fusion methods for combining external knowledge with historical price features. Moreover, this paper includes a compilation of relevant datasets and delves into potential future research directions in this domain.
Unleashing the Potential of Unsupervised Deep Outlier Detection through Automated Training Stopping
May 26, 2023Abstract:Outlier detection (OD) has received continuous research interests due to its wide applications. With the development of deep learning, increasingly deep OD algorithms are proposed. Despite the availability of numerous deep OD models, existing research has reported that the performance of deep models is extremely sensitive to the configuration of hyperparameters (HPs). However, the selection of HPs for deep OD models remains a notoriously difficult task due to the lack of any labels and long list of HPs. In our study. we shed light on an essential factor, training time, that can introduce significant variation in the performance of deep model. Even the performance is stable across other HPs, training time itself can cause a serious HP sensitivity issue. Motivated by this finding, we are dedicated to formulating a strategy to terminate model training at the optimal iteration. Specifically, we propose a novel metric called loss entropy to internally evaluate the model performance during training while an automated training stopping algorithm is devised. To our knowledge, our approach is the first to enable reliable identification of the optimal training iteration during training without requiring any labels. Our experiments on tabular, image datasets show that our approach can be applied to diverse deep models and datasets. It not only enhances the robustness of deep models to their HPs, but also improves the performance and reduces plenty of training time compared to naive training.
Application of probabilistic modeling and automated machine learning framework for high-dimensional stress field
Mar 15, 2023



Abstract:Modern computational methods, involving highly sophisticated mathematical formulations, enable several tasks like modeling complex physical phenomenon, predicting key properties and design optimization. The higher fidelity in these computer models makes it computationally intensive to query them hundreds of times for optimization and one usually relies on a simplified model albeit at the cost of losing predictive accuracy and precision. Towards this, data-driven surrogate modeling methods have shown a lot of promise in emulating the behavior of the expensive computer models. However, a major bottleneck in such methods is the inability to deal with high input dimensionality and the need for relatively large datasets. With such problems, the input and output quantity of interest are tensors of high dimensionality. Commonly used surrogate modeling methods for such problems, suffer from requirements like high number of computational evaluations that precludes one from performing other numerical tasks like uncertainty quantification and statistical analysis. In this work, we propose an end-to-end approach that maps a high-dimensional image like input to an output of high dimensionality or its key statistics. Our approach uses two main framework that perform three steps: a) reduce the input and output from a high-dimensional space to a reduced or low-dimensional space, b) model the input-output relationship in the low-dimensional space, and c) enable the incorporation of domain-specific physical constraints as masks. In order to accomplish the task of reducing input dimensionality we leverage principal component analysis, that is coupled with two surrogate modeling methods namely: a) Bayesian hybrid modeling, and b) DeepHyper's deep neural networks. We demonstrate the applicability of the approach on a problem of a linear elastic stress field data.
Are we really making much progress in unsupervised graph outlier detection? Revisiting the problem with new insight and superior method
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:A large number of studies on Graph Outlier Detection (GOD) have emerged in recent years due to its wide applications, in which Unsupervised Node Outlier Detection (UNOD) on attributed networks is an important area. UNOD focuses on detecting two kinds of typical outliers in graphs: the structural outlier and the contextual outlier. Most existing works conduct the experiments based on the datasets with injected outliers. However, we find that the most widely-used outlier injection approach has a serious data leakage issue. By only utilizing such data leakage, a simple approach can achieve the state-of-the-art performance in detecting outliers. In addition, we observe that most existing algorithms have performance drops with varied injection settings. The other major issue is on balanced detection performance between the two types of outliers, which has not been considered by existing studies. In this paper, we analyze the cause of the data leakage issue in depth since the injection approach is a building block to advance UNOD. Moreover, we devise a novel variance-based model to detect structural outliers, which is more robust to different injection settings. On top of this, we propose a new framework, Variance-based Graph Outlier Detection (VGOD), which combines our variance-based model and attribute reconstruction model to detect outliers in a balanced way. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness and the efficiency of VGOD. The results on 5 real-world datasets validate that VGOD achieves not only the best performance in detecting outliers but also a balanced detection performance between structural and contextual outliers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge