Lin Cheng
BubbleONet: A Physics-Informed Neural Operator for High-Frequency Bubble Dynamics
Aug 05, 2025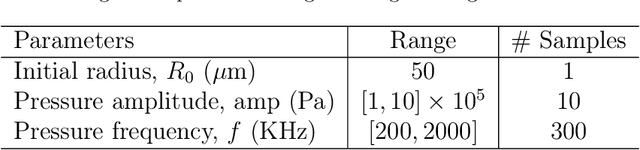



Abstract:This paper introduces BubbleONet, an operator learning model designed to map pressure profiles from an input function space to corresponding bubble radius responses. BubbleONet is built upon the physics-informed deep operator network (PI-DeepONet) framework, leveraging DeepONet's powerful universal approximation capabilities for operator learning alongside the robust physical fidelity provided by the physics-informed neural networks. To mitigate the inherent spectral bias in deep learning, BubbleONet integrates the Rowdy adaptive activation function, enabling improved representation of high-frequency features. The model is evaluated across various scenarios, including: (1) Rayleigh-Plesset equation based bubble dynamics with a single initial radius, (2) Keller-Miksis equation based bubble dynamics with a single initial radius, and (3) Keller-Miksis equation based bubble dynamics with multiple initial radii. Moreover, the performance of single-step versus two-step training techniques for BubbleONet is investigated. The results demonstrate that BubbleONet serves as a promising surrogate model for simulating bubble dynamics, offering a computationally efficient alternative to traditional numerical solvers.
Morpheus: A Neural-driven Animatronic Face with Hybrid Actuation and Diverse Emotion Control
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Previous animatronic faces struggle to express emotions effectively due to hardware and software limitations. On the hardware side, earlier approaches either use rigid-driven mechanisms, which provide precise control but are difficult to design within constrained spaces, or tendon-driven mechanisms, which are more space-efficient but challenging to control. In contrast, we propose a hybrid actuation approach that combines the best of both worlds. The eyes and mouth-key areas for emotional expression-are controlled using rigid mechanisms for precise movement, while the nose and cheek, which convey subtle facial microexpressions, are driven by strings. This design allows us to build a compact yet versatile hardware platform capable of expressing a wide range of emotions. On the algorithmic side, our method introduces a self-modeling network that maps motor actions to facial landmarks, allowing us to automatically establish the relationship between blendshape coefficients for different facial expressions and the corresponding motor control signals through gradient backpropagation. We then train a neural network to map speech input to corresponding blendshape controls. With our method, we can generate distinct emotional expressions such as happiness, fear, disgust, and anger, from any given sentence, each with nuanced, emotion-specific control signals-a feature that has not been demonstrated in earlier systems. We release the hardware design and code at https://github.com/ZZongzheng0918/Morpheus-Hardware and https://github.com/ZZongzheng0918/Morpheus-Software.
Quantum Learning and Estimation for Distribution Networks and Energy Communities Coordination
Jun 13, 2025Abstract:Price signals from distribution networks (DNs) guide energy communities (ECs) to adjust energy usage, enabling effective coordination for reliable power system operation. However, this coordination faces significant challenges due to the limited availability of information (i.e., only the aggregated energy usage of ECs is available to DNs), and the high computational burden of accounting for uncertainties and the associated risks through numerous scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose a quantum learning and estimation approach to enhance coordination between DNs and ECs. Specifically, leveraging advanced quantum properties such as quantum superposition and entanglement, we develop a hybrid quantum temporal convolutional network-long short-term memory (Q-TCN-LSTM) model to establish an end-to-end mapping between ECs' responses and the price incentives from DNs. Moreover, we develop a quantum estimation method based on quantum amplitude estimation (QAE) and two phase-rotation circuits to significantly accelerate the optimization process under numerous uncertainty scenarios. Numerical experiments demonstrate that, compared to classical neural networks, the proposed Q-TCN-LSTM model improves the mapping accuracy by 69.2% while reducing the model size by 99.75% and the computation time by 93.9%. Compared to classical Monte Carlo simulation, QAE achieves comparable accuracy with a dramatic reduction in computational time (up to 99.99%) and requires significantly fewer computational resources.
Adviser-Actor-Critic: Eliminating Steady-State Error in Reinforcement Learning Control
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:High-precision control tasks present substantial challenges for reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms, frequently resulting in suboptimal performance attributed to network approximation inaccuracies and inadequate sample quality.These issues are exacerbated when the task requires the agent to achieve a precise goal state, as is common in robotics and other real-world applications.We introduce Adviser-Actor-Critic (AAC), designed to address the precision control dilemma by combining the precision of feedback control theory with the adaptive learning capability of RL and featuring an Adviser that mentors the actor to refine control actions, thereby enhancing the precision of goal attainment.Finally, through benchmark tests, AAC outperformed standard RL algorithms in precision-critical, goal-conditioned tasks, demonstrating AAC's high precision, reliability, and robustness.Code are available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Adviser-Actor-Critic-8AC5.
Error Distribution Smoothing:Advancing Low-Dimensional Imbalanced Regression
Feb 04, 2025Abstract:In real-world regression tasks, datasets frequently exhibit imbalanced distributions, characterized by a scarcity of data in high-complexity regions and an abundance in low-complexity areas. This imbalance presents significant challenges for existing classification methods with clear class boundaries, while highlighting a scarcity of approaches specifically designed for imbalanced regression problems. To better address these issues, we introduce a novel concept of Imbalanced Regression, which takes into account both the complexity of the problem and the density of data points, extending beyond traditional definitions that focus only on data density. Furthermore, we propose Error Distribution Smoothing (EDS) as a solution to tackle imbalanced regression, effectively selecting a representative subset from the dataset to reduce redundancy while maintaining balance and representativeness. Through several experiments, EDS has shown its effectiveness, and the related code and dataset can be accessed at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/Error-Distribution-Smoothing-762F.
Recursive Gaussian Process State Space Model
Nov 22, 2024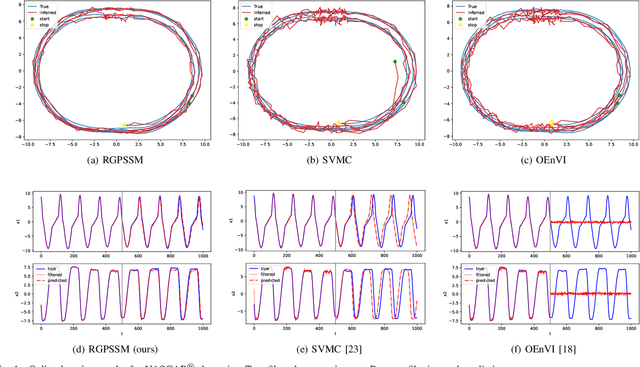
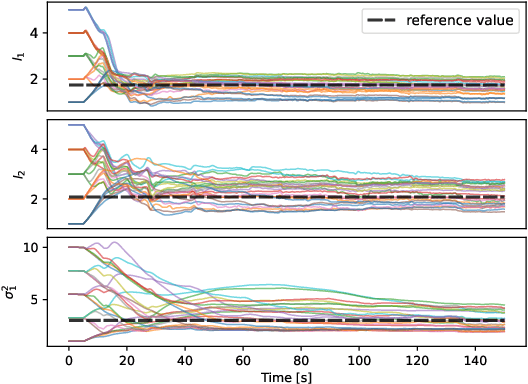
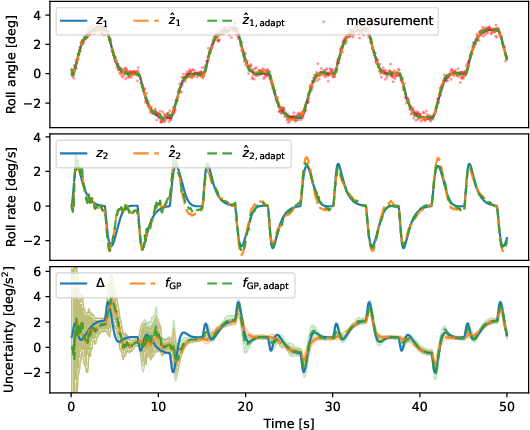
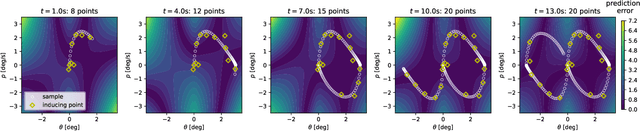
Abstract:Learning dynamical models from data is not only fundamental but also holds great promise for advancing principle discovery, time-series prediction, and controller design. Among various approaches, Gaussian Process State-Space Models (GPSSMs) have recently gained significant attention due to their combination of flexibility and interpretability. However, for online learning, the field lacks an efficient method suitable for scenarios where prior information regarding data distribution and model function is limited. To address this issue, this paper proposes a recursive GPSSM method with adaptive capabilities for both operating domains and Gaussian process (GP) hyperparameters. Specifically, we first utilize first-order linearization to derive a Bayesian update equation for the joint distribution between the system state and the GP model, enabling closed-form and domain-independent learning. Second, an online selection algorithm for inducing points is developed based on informative criteria to achieve lightweight learning. Third, to support online hyperparameter optimization, we recover historical measurement information from the current filtering distribution. Comprehensive evaluations on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the superior accuracy, computational efficiency, and adaptability of our method compared to state-of-the-art online GPSSM techniques.
Graph Attention-Based Symmetry Constraint Extraction for Analog Circuits
Dec 22, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, analog circuits have received extensive attention and are widely used in many emerging applications. The high demand for analog circuits necessitates shorter circuit design cycles. To achieve the desired performance and specifications, various geometrical symmetry constraints must be carefully considered during the analog layout process. However, the manual labeling of these constraints by experienced analog engineers is a laborious and time-consuming process. To handle the costly runtime issue, we propose a graph-based learning framework to automatically extract symmetric constraints in analog circuit layout. The proposed framework leverages the connection characteristics of circuits and the devices'information to learn the general rules of symmetric constraints, which effectively facilitates the extraction of device-level constraints on circuit netlists. The experimental results demonstrate that compared to state-of-the-art symmetric constraint detection approaches, our framework achieves higher accuracy and lower false positive rate.
Simple but Effective Unsupervised Classification for Specified Domain Images: A Case Study on Fungi Images
Nov 15, 2023


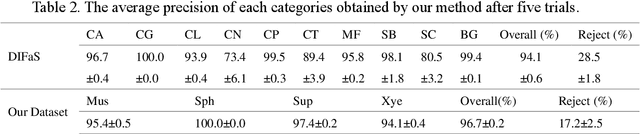
Abstract:High-quality labeled datasets are essential for deep learning. Traditional manual annotation methods are not only costly and inefficient but also pose challenges in specialized domains where expert knowledge is needed. Self-supervised methods, despite leveraging unlabeled data for feature extraction, still require hundreds or thousands of labeled instances to guide the model for effective specialized image classification. Current unsupervised learning methods offer automatic classification without prior annotation but often compromise on accuracy. As a result, efficiently procuring high-quality labeled datasets remains a pressing challenge for specialized domain images devoid of annotated data. Addressing this, an unsupervised classification method with three key ideas is introduced: 1) dual-step feature dimensionality reduction using a pre-trained model and manifold learning, 2) a voting mechanism from multiple clustering algorithms, and 3) post-hoc instead of prior manual annotation. This approach outperforms supervised methods in classification accuracy, as demonstrated with fungal image data, achieving 94.1% and 96.7% on public and private datasets respectively. The proposed unsupervised classification method reduces dependency on pre-annotated datasets, enabling a closed-loop for data classification. The simplicity and ease of use of this method will also bring convenience to researchers in various fields in building datasets, promoting AI applications for images in specialized domains.
All-pairs Consistency Learning for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Aug 08, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we propose a new transformer-based regularization to better localize objects for Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS). In image-level WSSS, Class Activation Map (CAM) is adopted to generate object localization as pseudo segmentation labels. To address the partial activation issue of the CAMs, consistency regularization is employed to maintain activation intensity invariance across various image augmentations. However, such methods ignore pair-wise relations among regions within each CAM, which capture context and should also be invariant across image views. To this end, we propose a new all-pairs consistency regularization (ACR). Given a pair of augmented views, our approach regularizes the activation intensities between a pair of augmented views, while also ensuring that the affinity across regions within each view remains consistent. We adopt vision transformers as the self-attention mechanism naturally embeds pair-wise affinity. This enables us to simply regularize the distance between the attention matrices of augmented image pairs. Additionally, we introduce a novel class-wise localization method that leverages the gradients of the class token. Our method can be seamlessly integrated into existing WSSS methods using transformers without modifying the architectures. We evaluate our method on PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets. Our method produces noticeably better class localization maps (67.3% mIoU on PASCAL VOC train), resulting in superior WSSS performances.
Intelligent diagnostic scheme for lung cancer screening with Raman spectra data by tensor network machine learning
Mar 11, 2023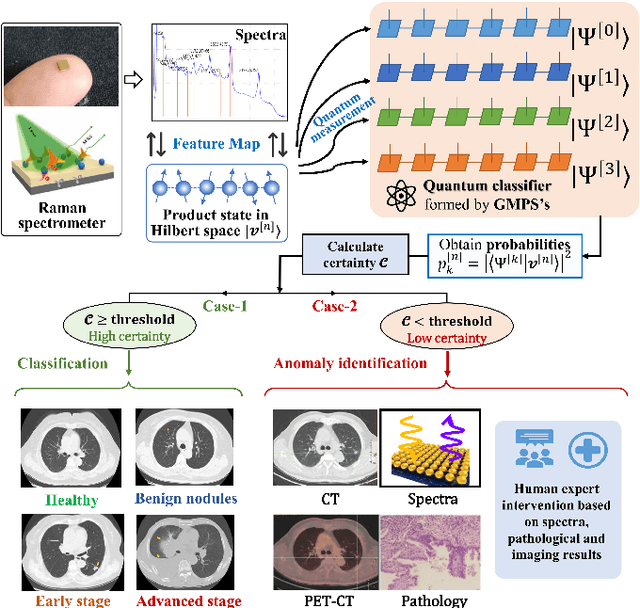
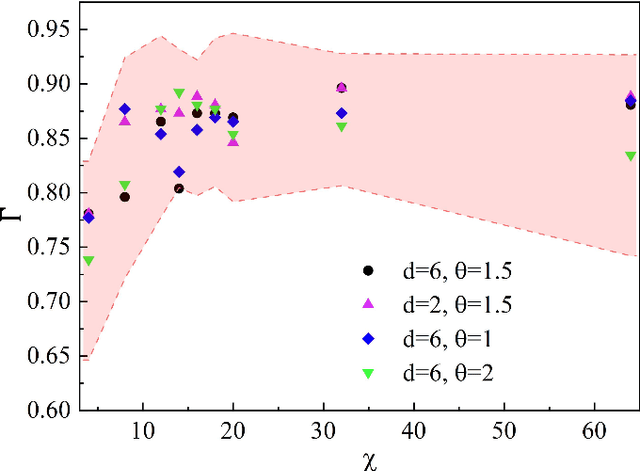
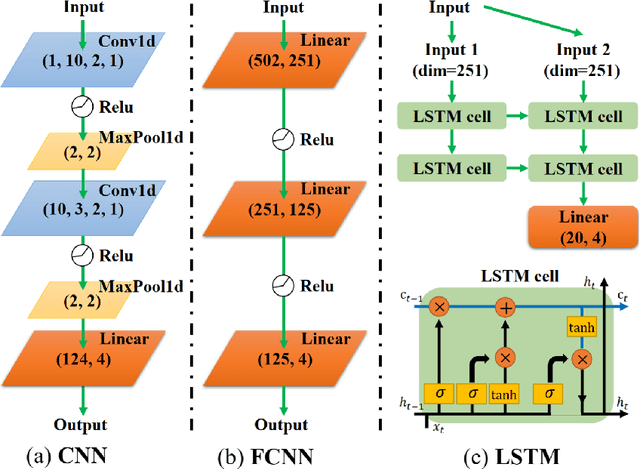
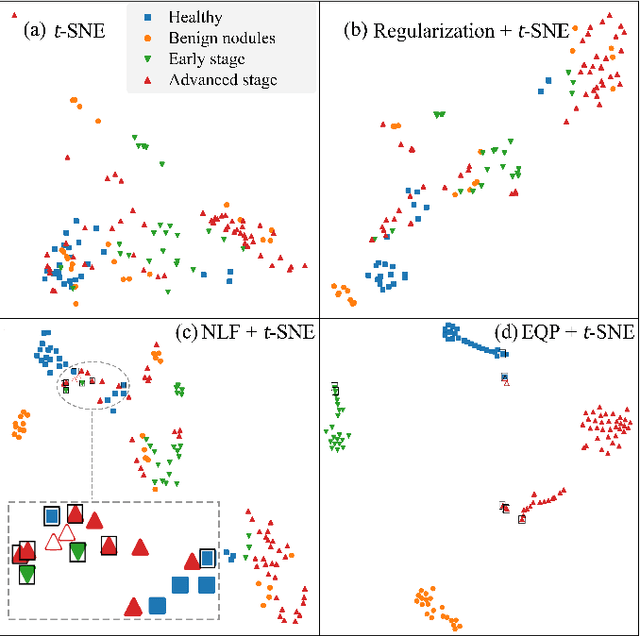
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has brought tremendous impacts on biomedical sciences from academic researches to clinical applications, such as in biomarkers' detection and diagnosis, optimization of treatment, and identification of new therapeutic targets in drug discovery. However, the contemporary AI technologies, particularly deep machine learning (ML), severely suffer from non-interpretability, which might uncontrollably lead to incorrect predictions. Interpretability is particularly crucial to ML for clinical diagnosis as the consumers must gain necessary sense of security and trust from firm grounds or convincing interpretations. In this work, we propose a tensor-network (TN)-ML method to reliably predict lung cancer patients and their stages via screening Raman spectra data of Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in exhaled breath, which are generally suitable as biomarkers and are considered to be an ideal way for non-invasive lung cancer screening. The prediction of TN-ML is based on the mutual distances of the breath samples mapped to the quantum Hilbert space. Thanks to the quantum probabilistic interpretation, the certainty of the predictions can be quantitatively characterized. The accuracy of the samples with high certainty is almost 100$\%$. The incorrectly-classified samples exhibit obviously lower certainty, and thus can be decipherably identified as anomalies, which will be handled by human experts to guarantee high reliability. Our work sheds light on shifting the ``AI for biomedical sciences'' from the conventional non-interpretable ML schemes to the interpretable human-ML interactive approaches, for the purpose of high accuracy and reliability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge