Huanxi Deng
Unsupervised Waste Classification By Dual-Encoder Contrastive Learning and Multi-Clustering Voting (DECMCV)
Mar 04, 2025



Abstract:Waste classification is crucial for improving processing efficiency and reducing environmental pollution. Supervised deep learning methods are commonly used for automated waste classification, but they rely heavily on large labeled datasets, which are costly and inefficient to obtain. Real-world waste data often exhibit category and style biases, such as variations in camera angles, lighting conditions, and types of waste, which can impact the model's performance and generalization ability. Therefore, constructing a bias-free dataset is essential. Manual labeling is not only costly but also inefficient. While self-supervised learning helps address data scarcity, it still depends on some labeled data and generally results in lower accuracy compared to supervised methods. Unsupervised methods show potential in certain cases but typically do not perform as well as supervised models, highlighting the need for an efficient and cost-effective unsupervised approach. This study presents a novel unsupervised method, Dual-Encoder Contrastive Learning with Multi-Clustering Voting (DECMCV). The approach involves using a pre-trained ConvNeXt model for image encoding, leveraging VisionTransformer to generate positive samples, and applying a multi-clustering voting mechanism to address data labeling and domain shift issues. Experimental results demonstrate that DECMCV achieves classification accuracies of 93.78% and 98.29% on the TrashNet and Huawei Cloud datasets, respectively, outperforming or matching supervised models. On a real-world dataset of 4,169 waste images, only 50 labeled samples were needed to accurately label thousands, improving classification accuracy by 29.85% compared to supervised models. This method effectively addresses style differences, enhances model generalization, and contributes to the advancement of automated waste classification.
Simple but Effective Unsupervised Classification for Specified Domain Images: A Case Study on Fungi Images
Nov 15, 2023


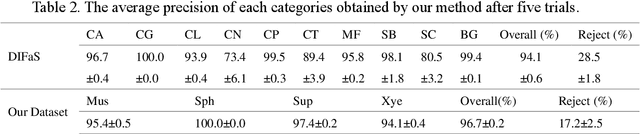
Abstract:High-quality labeled datasets are essential for deep learning. Traditional manual annotation methods are not only costly and inefficient but also pose challenges in specialized domains where expert knowledge is needed. Self-supervised methods, despite leveraging unlabeled data for feature extraction, still require hundreds or thousands of labeled instances to guide the model for effective specialized image classification. Current unsupervised learning methods offer automatic classification without prior annotation but often compromise on accuracy. As a result, efficiently procuring high-quality labeled datasets remains a pressing challenge for specialized domain images devoid of annotated data. Addressing this, an unsupervised classification method with three key ideas is introduced: 1) dual-step feature dimensionality reduction using a pre-trained model and manifold learning, 2) a voting mechanism from multiple clustering algorithms, and 3) post-hoc instead of prior manual annotation. This approach outperforms supervised methods in classification accuracy, as demonstrated with fungal image data, achieving 94.1% and 96.7% on public and private datasets respectively. The proposed unsupervised classification method reduces dependency on pre-annotated datasets, enabling a closed-loop for data classification. The simplicity and ease of use of this method will also bring convenience to researchers in various fields in building datasets, promoting AI applications for images in specialized domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge