Mengke Song
READ-Net: Clarifying Emotional Ambiguity via Adaptive Feature Recalibration for Audio-Visual Depression Detection
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Depression is a severe global mental health issue that impairs daily functioning and overall quality of life. Although recent audio-visual approaches have improved automatic depression detection, methods that ignore emotional cues often fail to capture subtle depressive signals hidden within emotional expressions. Conversely, those incorporating emotions frequently confuse transient emotional expressions with stable depressive symptoms in feature representations, a phenomenon termed \emph{Emotional Ambiguity}, thereby leading to detection errors. To address this critical issue, we propose READ-Net, the first audio-visual depression detection framework explicitly designed to resolve Emotional Ambiguity through Adaptive Feature Recalibration (AFR). The core insight of AFR is to dynamically adjust the weights of emotional features to enhance depression-related signals. Rather than merely overlooking or naively combining emotional information, READ-Net innovatively identifies and preserves depressive-relevant cues within emotional features, while adaptively filtering out irrelevant emotional noise. This recalibration strategy significantly clarifies feature representations, and effectively mitigates the persistent challenge of emotional interference. Additionally, READ-Net can be easily integrated into existing frameworks for improved performance. Extensive evaluations on three publicly available datasets show that READ-Net outperforms state-of-the-art methods, with average gains of 4.55\% in accuracy and 1.26\% in F1-score, demonstrating its robustness to emotional disturbances and improving audio-visual depression detection.
GenCAMO: Scene-Graph Contextual Decoupling for Environment-aware and Mask-free Camouflage Image-Dense Annotation Generation
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:Conceal dense prediction (CDP), especially RGB-D camouflage object detection and open-vocabulary camouflage object segmentation, plays a crucial role in advancing the understanding and reasoning of complex camouflage scenes. However, high-quality and large-scale camouflage datasets with dense annotation remain scarce due to expensive data collection and labeling costs. To address this challenge, we explore leveraging generative models to synthesize realistic camouflage image-dense data for training CDP models with fine-grained representations, prior knowledge, and auxiliary reasoning. Concretely, our contributions are threefold: (i) we introduce GenCAMO-DB, a large-scale camouflage dataset with multi-modal annotations, including depth maps, scene graphs, attribute descriptions, and text prompts; (ii) we present GenCAMO, an environment-aware and mask-free generative framework that produces high-fidelity camouflage image-dense annotations; (iii) extensive experiments across multiple modalities demonstrate that GenCAMO significantly improves dense prediction performance on complex camouflage scenes by providing high-quality synthetic data. The code and datasets will be released after paper acceptance.
Time-EAPCR-T: A Universal Deep Learning Approach for Anomaly Detection in Industrial Equipment
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:With the advancement of Industry 4.0, intelligent manufacturing extensively employs sensors for real-time multidimensional data collection, playing a crucial role in equipment monitoring, process optimisation, and efficiency enhancement. Industrial data exhibit characteristics such as multi-source heterogeneity, nonlinearity, strong coupling, and temporal interactions, while also being affected by noise interference. These complexities make it challenging for traditional anomaly detection methods to extract key features, impacting detection accuracy and stability. Traditional machine learning approaches often struggle with such complex data due to limitations in processing capacity and generalisation ability, making them inadequate for practical applications. While deep learning feature extraction modules have demonstrated remarkable performance in image and text processing, they remain ineffective when applied to multi-source heterogeneous industrial data lacking explicit correlations. Moreover, existing multi-source heterogeneous data processing techniques still rely on dimensionality reduction and feature selection, which can lead to information loss and difficulty in capturing high-order interactions. To address these challenges, this study applies the EAPCR and Time-EAPCR models proposed in previous research and introduces a new model, Time-EAPCR-T, where Transformer replaces the LSTM module in the time-series processing component of Time-EAPCR. This modification effectively addresses multi-source data heterogeneity, facilitates efficient multi-source feature fusion, and enhances the temporal feature extraction capabilities of multi-source industrial data.Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms existing approaches across four industrial datasets, highlighting its broad application potential.
Inorganic Catalyst Efficiency Prediction Based on EAPCR Model: A Deep Learning Solution for Multi-Source Heterogeneous Data
Mar 10, 2025



Abstract:The design of inorganic catalysts and the prediction of their catalytic efficiency are fundamental challenges in chemistry and materials science. Traditional catalyst evaluation methods primarily rely on machine learning techniques; however, these methods often struggle to process multi-source heterogeneous data, limiting both predictive accuracy and generalization. To address these limitations, this study introduces the Embedding-Attention-Permutated CNN-Residual (EAPCR) deep learning model. EAPCR constructs a feature association matrix using embedding and attention mechanisms and enhances predictive performance through permutated CNN architectures and residual connections. This approach enables the model to accurately capture complex feature interactions across various catalytic conditions, leading to precise efficiency predictions. EAPCR serves as a powerful tool for computational researchers while also assisting domain experts in optimizing catalyst design, effectively bridging the gap between data-driven modeling and experimental applications. We evaluate EAPCR on datasets from TiO2 photocatalysis, thermal catalysis, and electrocatalysis, demonstrating its superiority over traditional machine learning methods (e.g., linear regression, random forest) as well as conventional deep learning models (e.g., ANN, NNs). Across multiple evaluation metrics (MAE, MSE, R2, and RMSE), EAPCR consistently outperforms existing approaches. These findings highlight the strong potential of EAPCR in inorganic catalytic efficiency prediction. As a versatile deep learning framework, EAPCR not only improves predictive accuracy but also establishes a solid foundation for future large-scale model development in inorganic catalysis.
Unsupervised Waste Classification By Dual-Encoder Contrastive Learning and Multi-Clustering Voting (DECMCV)
Mar 04, 2025



Abstract:Waste classification is crucial for improving processing efficiency and reducing environmental pollution. Supervised deep learning methods are commonly used for automated waste classification, but they rely heavily on large labeled datasets, which are costly and inefficient to obtain. Real-world waste data often exhibit category and style biases, such as variations in camera angles, lighting conditions, and types of waste, which can impact the model's performance and generalization ability. Therefore, constructing a bias-free dataset is essential. Manual labeling is not only costly but also inefficient. While self-supervised learning helps address data scarcity, it still depends on some labeled data and generally results in lower accuracy compared to supervised methods. Unsupervised methods show potential in certain cases but typically do not perform as well as supervised models, highlighting the need for an efficient and cost-effective unsupervised approach. This study presents a novel unsupervised method, Dual-Encoder Contrastive Learning with Multi-Clustering Voting (DECMCV). The approach involves using a pre-trained ConvNeXt model for image encoding, leveraging VisionTransformer to generate positive samples, and applying a multi-clustering voting mechanism to address data labeling and domain shift issues. Experimental results demonstrate that DECMCV achieves classification accuracies of 93.78% and 98.29% on the TrashNet and Huawei Cloud datasets, respectively, outperforming or matching supervised models. On a real-world dataset of 4,169 waste images, only 50 labeled samples were needed to accurately label thousands, improving classification accuracy by 29.85% compared to supervised models. This method effectively addresses style differences, enhances model generalization, and contributes to the advancement of automated waste classification.
Unveiling Context-Related Anomalies: Knowledge Graph Empowered Decoupling of Scene and Action for Human-Related Video Anomaly Detection
Sep 05, 2024Abstract:Detecting anomalies in human-related videos is crucial for surveillance applications. Current methods primarily include appearance-based and action-based techniques. Appearance-based methods rely on low-level visual features such as color, texture, and shape. They learn a large number of pixel patterns and features related to known scenes during training, making them effective in detecting anomalies within these familiar contexts. However, when encountering new or significantly changed scenes, i.e., unknown scenes, they often fail because existing SOTA methods do not effectively capture the relationship between actions and their surrounding scenes, resulting in low generalization. In contrast, action-based methods focus on detecting anomalies in human actions but are usually less informative because they tend to overlook the relationship between actions and their scenes, leading to incorrect detection. For instance, the normal event of running on the beach and the abnormal event of running on the street might both be considered normal due to the lack of scene information. In short, current methods struggle to integrate low-level visual and high-level action features, leading to poor anomaly detection in varied and complex scenes. To address this challenge, we propose a novel decoupling-based architecture for human-related video anomaly detection (DecoAD). DecoAD significantly improves the integration of visual and action features through the decoupling and interweaving of scenes and actions, thereby enabling a more intuitive and accurate understanding of complex behaviors and scenes. DecoAD supports fully supervised, weakly supervised, and unsupervised settings.
Rethinking Object Saliency Ranking: A Novel Whole-flow Processing Paradigm
Dec 06, 2023



Abstract:Existing salient object detection methods are capable of predicting binary maps that highlight visually salient regions. However, these methods are limited in their ability to differentiate the relative importance of multiple objects and the relationships among them, which can lead to errors and reduced accuracy in downstream tasks that depend on the relative importance of multiple objects. To conquer, this paper proposes a new paradigm for saliency ranking, which aims to completely focus on ranking salient objects by their "importance order". While previous works have shown promising performance, they still face ill-posed problems. First, the saliency ranking ground truth (GT) orders generation methods are unreasonable since determining the correct ranking order is not well-defined, resulting in false alarms. Second, training a ranking model remains challenging because most saliency ranking methods follow the multi-task paradigm, leading to conflicts and trade-offs among different tasks. Third, existing regression-based saliency ranking methods are complex for saliency ranking models due to their reliance on instance mask-based saliency ranking orders. These methods require a significant amount of data to perform accurately and can be challenging to implement effectively. To solve these problems, this paper conducts an in-depth analysis of the causes and proposes a whole-flow processing paradigm of saliency ranking task from the perspective of "GT data generation", "network structure design" and "training protocol". The proposed approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods on the widely-used SALICON set, as demonstrated by extensive experiments with fair and reasonable comparisons. The saliency ranking task is still in its infancy, and our proposed unified framework can serve as a fundamental strategy to guide future work.
A Comprehensive Survey on Video Saliency Detection with Auditory Information: the Audio-visual Consistency Perceptual is the Key!
Jun 20, 2022
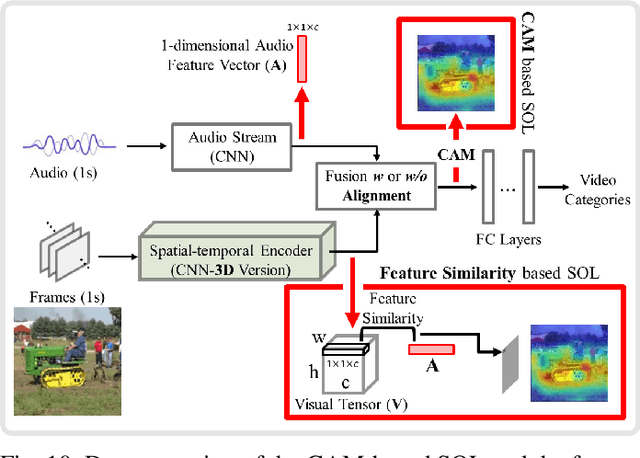
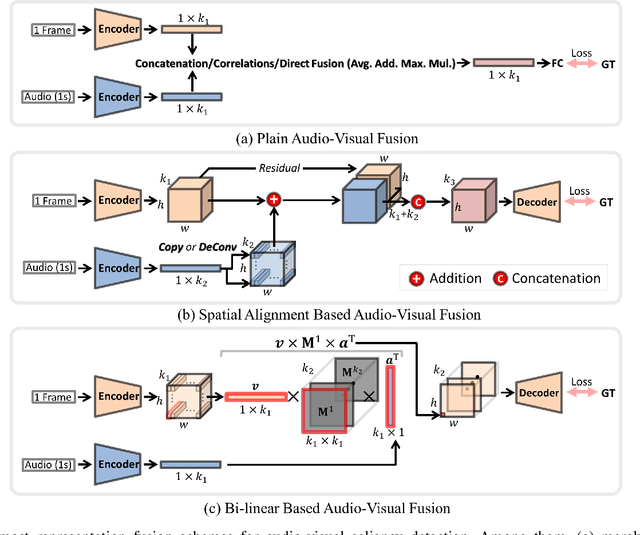
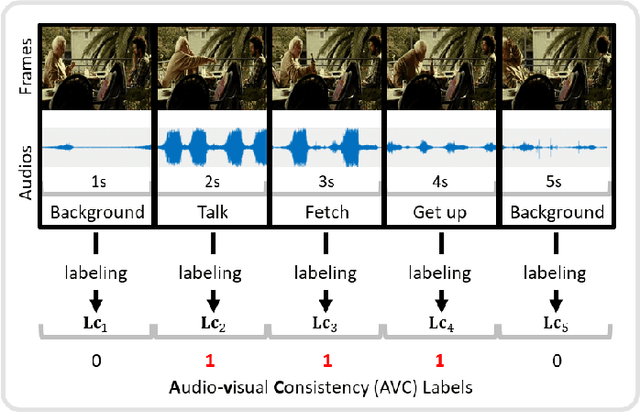
Abstract:Video saliency detection (VSD) aims at fast locating the most attractive objects/things/patterns in a given video clip. Existing VSD-related works have mainly relied on the visual system but paid less attention to the audio aspect, while, actually, our audio system is the most vital complementary part to our visual system. Also, audio-visual saliency detection (AVSD), one of the most representative research topics for mimicking human perceptual mechanisms, is currently in its infancy, and none of the existing survey papers have touched on it, especially from the perspective of saliency detection. Thus, the ultimate goal of this paper is to provide an extensive review to bridge the gap between audio-visual fusion and saliency detection. In addition, as another highlight of this review, we have provided a deep insight into key factors which could directly determine the performances of AVSD deep models, and we claim that the audio-visual consistency degree (AVC) -- a long-overlooked issue, can directly influence the effectiveness of using audio to benefit its visual counterpart when performing saliency detection. Moreover, in order to make the AVC issue more practical and valuable for future followers, we have newly equipped almost all existing publicly available AVSD datasets with additional frame-wise AVC labels. Based on these upgraded datasets, we have conducted extensive quantitative evaluations to ground our claim on the importance of AVC in the AVSD task. In a word, both our ideas and new sets serve as a convenient platform with preliminaries and guidelines, all of which are very potential to facilitate future works in promoting state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance further.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge