Junkun Chen
PHRASED: Phrase Dictionary Biasing for Speech Translation
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Phrases are essential to understand the core concepts in conversations. However, due to their rare occurrence in training data, correct translation of phrases is challenging in speech translation tasks. In this paper, we propose a phrase dictionary biasing method to leverage pairs of phrases mapping from the source language to the target language. We apply the phrase dictionary biasing method to two types of widely adopted models, a transducer-based streaming speech translation model and a multimodal large language model. Experimental results show that the phrase dictionary biasing method outperforms phrase list biasing by 21% relatively for the streaming speech translation model. In addition, phrase dictionary biasing enables multimodal large language models to use external phrase information, achieving 85% relative improvement in phrase recall.
Phi-4-Mini Technical Report: Compact yet Powerful Multimodal Language Models via Mixture-of-LoRAs
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Phi-4-Mini and Phi-4-Multimodal, compact yet highly capable language and multimodal models. Phi-4-Mini is a 3.8-billion-parameter language model trained on high-quality web and synthetic data, significantly outperforming recent open-source models of similar size and matching the performance of models twice its size on math and coding tasks requiring complex reasoning. This achievement is driven by a carefully curated synthetic data recipe emphasizing high-quality math and coding datasets. Compared to its predecessor, Phi-3.5-Mini, Phi-4-Mini features an expanded vocabulary size of 200K tokens to better support multilingual applications, as well as group query attention for more efficient long-sequence generation. Phi-4-Multimodal is a multimodal model that integrates text, vision, and speech/audio input modalities into a single model. Its novel modality extension approach leverages LoRA adapters and modality-specific routers to allow multiple inference modes combining various modalities without interference. For example, it now ranks first in the OpenASR leaderboard to date, although the LoRA component of the speech/audio modality has just 460 million parameters. Phi-4-Multimodal supports scenarios involving (vision + language), (vision + speech), and (speech/audio) inputs, outperforming larger vision-language and speech-language models on a wide range of tasks. Additionally, we experiment to further train Phi-4-Mini to enhance its reasoning capabilities. Despite its compact 3.8-billion-parameter size, this experimental version achieves reasoning performance on par with or surpassing significantly larger models, including DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B.
Streaming Speaker Change Detection and Gender Classification for Transducer-Based Multi-Talker Speech Translation
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Streaming multi-talker speech translation is a task that involves not only generating accurate and fluent translations with low latency but also recognizing when a speaker change occurs and what the speaker's gender is. Speaker change information can be used to create audio prompts for a zero-shot text-to-speech system, and gender can help to select speaker profiles in a conventional text-to-speech model. We propose to tackle streaming speaker change detection and gender classification by incorporating speaker embeddings into a transducer-based streaming end-to-end speech translation model. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed methods can achieve high accuracy for both speaker change detection and gender classification.
Isochrony-Controlled Speech-to-Text Translation: A study on translating from Sino-Tibetan to Indo-European Languages
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:End-to-end speech translation (ST), which translates source language speech directly into target language text, has garnered significant attention in recent years. Many ST applications require strict length control to ensure that the translation duration matches the length of the source audio, including both speech and pause segments. Previous methods often controlled the number of words or characters generated by the Machine Translation model to approximate the source sentence's length without considering the isochrony of pauses and speech segments, as duration can vary between languages. To address this, we present improvements to the duration alignment component of our sequence-to-sequence ST model. Our method controls translation length by predicting the duration of speech and pauses in conjunction with the translation process. This is achieved by providing timing information to the decoder, ensuring it tracks the remaining duration for speech and pauses while generating the translation. The evaluation on the Zh-En test set of CoVoST 2, demonstrates that the proposed Isochrony-Controlled ST achieves 0.92 speech overlap and 8.9 BLEU, which has only a 1.4 BLEU drop compared to the ST baseline.
Proto-OOD: Enhancing OOD Object Detection with Prototype Feature Similarity
Sep 09, 2024
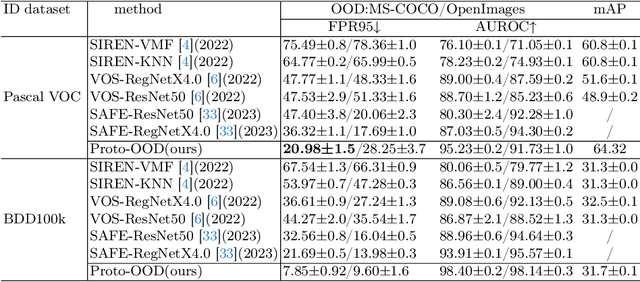
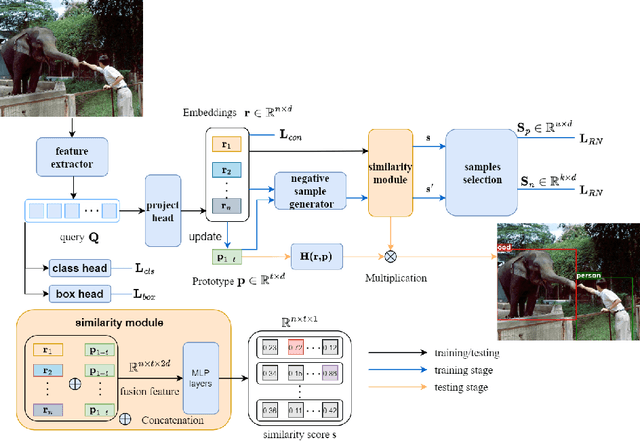
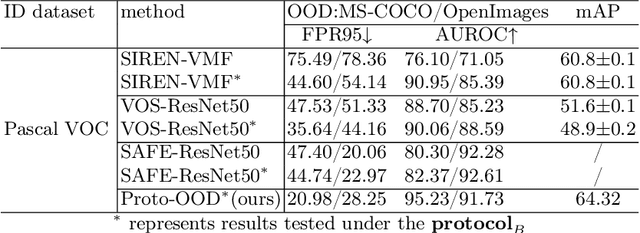
Abstract:The limited training samples for object detectors commonly result in low accuracy out-of-distribution (OOD) object detection. We have observed that feature vectors of the same class tend to cluster tightly in feature space, whereas those of different classes are more scattered. This insight motivates us to leverage feature similarity for OOD detection. Drawing on the concept of prototypes prevalent in few-shot learning, we introduce a novel network architecture, Proto-OOD, designed for this purpose. Proto-OOD enhances prototype representativeness through contrastive loss and identifies OOD data by assessing the similarity between input features and prototypes. It employs a negative embedding generator to create negative embedding, which are then used to train the similarity module. Proto-OOD achieves significantly lower FPR95 in MS-COCO dataset and higher mAP for Pascal VOC dataset, when utilizing Pascal VOC as ID dataset and MS-COCO as OOD dataset. Additionally, we identify limitations in existing evaluation metrics and propose an enhanced evaluation protocol.
Investigating Neural Audio Codecs for Speech Language Model-Based Speech Generation
Sep 06, 2024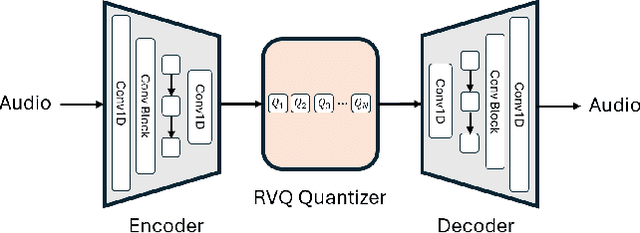
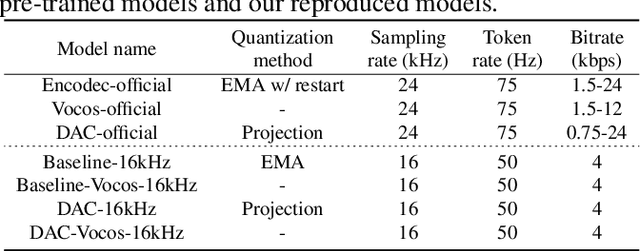
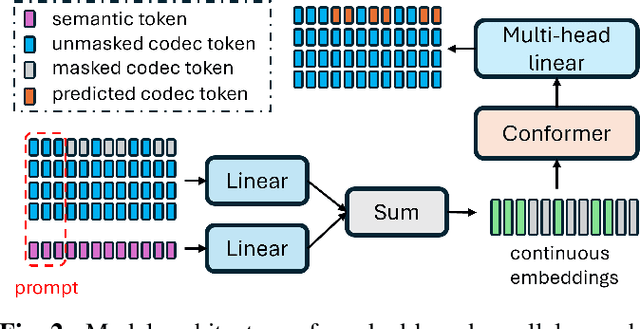
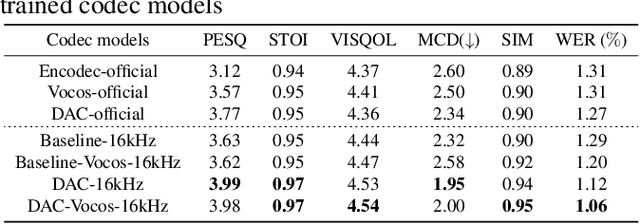
Abstract:Neural audio codec tokens serve as the fundamental building blocks for speech language model (SLM)-based speech generation. However, there is no systematic understanding on how the codec system affects the speech generation performance of the SLM. In this work, we examine codec tokens within SLM framework for speech generation to provide insights for effective codec design. We retrain existing high-performing neural codec models on the same data set and loss functions to compare their performance in a uniform setting. We integrate codec tokens into two SLM systems: masked-based parallel speech generation system and an auto-regressive (AR) plus non-auto-regressive (NAR) model-based system. Our findings indicate that better speech reconstruction in codec systems does not guarantee improved speech generation in SLM. A high-quality codec decoder is crucial for natural speech production in SLM, while speech intelligibility depends more on quantization mechanism.
Soft Language Identification for Language-Agnostic Many-to-One End-to-End Speech Translation
Jun 12, 2024


Abstract:Language-agnostic many-to-one end-to-end speech translation models can convert audio signals from different source languages into text in a target language. These models do not need source language identification, which improves user experience. In some cases, the input language can be given or estimated. Our goal is to use this additional language information while preserving the quality of the other languages. We accomplish this by introducing a simple and effective linear input network. The linear input network is initialized as an identity matrix, which ensures that the model can perform as well as, or better than, the original model. Experimental results show that the proposed method can successfully enhance the specified language, while keeping the language-agnostic ability of the many-to-one ST models.
Leveraging Timestamp Information for Serialized Joint Streaming Recognition and Translation
Oct 23, 2023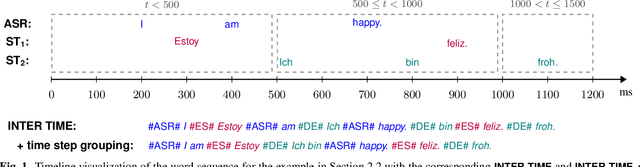
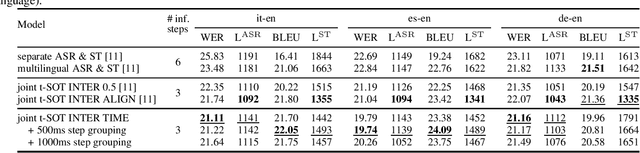
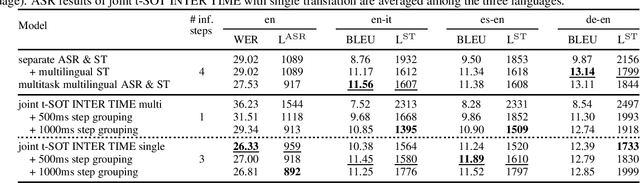
Abstract:The growing need for instant spoken language transcription and translation is driven by increased global communication and cross-lingual interactions. This has made offering translations in multiple languages essential for user applications. Traditional approaches to automatic speech recognition (ASR) and speech translation (ST) have often relied on separate systems, leading to inefficiencies in computational resources, and increased synchronization complexity in real time. In this paper, we propose a streaming Transformer-Transducer (T-T) model able to jointly produce many-to-one and one-to-many transcription and translation using a single decoder. We introduce a novel method for joint token-level serialized output training based on timestamp information to effectively produce ASR and ST outputs in the streaming setting. Experiments on {it,es,de}->en prove the effectiveness of our approach, enabling the generation of one-to-many joint outputs with a single decoder for the first time.
Improving Stability in Simultaneous Speech Translation: A Revision-Controllable Decoding Approach
Oct 06, 2023



Abstract:Simultaneous Speech-to-Text translation serves a critical role in real-time crosslingual communication. Despite the advancements in recent years, challenges remain in achieving stability in the translation process, a concern primarily manifested in the flickering of partial results. In this paper, we propose a novel revision-controllable method designed to address this issue. Our method introduces an allowed revision window within the beam search pruning process to screen out candidate translations likely to cause extensive revisions, leading to a substantial reduction in flickering and, crucially, providing the capability to completely eliminate flickering. The experiments demonstrate the proposed method can significantly improve the decoding stability without compromising substantially on the translation quality.
DiariST: Streaming Speech Translation with Speaker Diarization
Sep 14, 2023

Abstract:End-to-end speech translation (ST) for conversation recordings involves several under-explored challenges such as speaker diarization (SD) without accurate word time stamps and handling of overlapping speech in a streaming fashion. In this work, we propose DiariST, the first streaming ST and SD solution. It is built upon a neural transducer-based streaming ST system and integrates token-level serialized output training and t-vector, which were originally developed for multi-talker speech recognition. Due to the absence of evaluation benchmarks in this area, we develop a new evaluation dataset, DiariST-AliMeeting, by translating the reference Chinese transcriptions of the AliMeeting corpus into English. We also propose new metrics, called speaker-agnostic BLEU and speaker-attributed BLEU, to measure the ST quality while taking SD accuracy into account. Our system achieves a strong ST and SD capability compared to offline systems based on Whisper, while performing streaming inference for overlapping speech. To facilitate the research in this new direction, we release the evaluation data, the offline baseline systems, and the evaluation code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge