Sunit Sivasankaran
Streaming Speaker Change Detection and Gender Classification for Transducer-Based Multi-Talker Speech Translation
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:Streaming multi-talker speech translation is a task that involves not only generating accurate and fluent translations with low latency but also recognizing when a speaker change occurs and what the speaker's gender is. Speaker change information can be used to create audio prompts for a zero-shot text-to-speech system, and gender can help to select speaker profiles in a conventional text-to-speech model. We propose to tackle streaming speaker change detection and gender classification by incorporating speaker embeddings into a transducer-based streaming end-to-end speech translation model. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed methods can achieve high accuracy for both speaker change detection and gender classification.
Target word activity detector: An approach to obtain ASR word boundaries without lexicon
Sep 20, 2024Abstract:Obtaining word timestamp information from end-to-end (E2E) ASR models remains challenging due to the lack of explicit time alignment during training. This issue is further complicated in multilingual models. Existing methods, either rely on lexicons or introduce additional tokens, leading to scalability issues and increased computational costs. In this work, we propose a new approach to estimate word boundaries without relying on lexicons. Our method leverages word embeddings from sub-word token units and a pretrained ASR model, requiring only word alignment information during training. Our proposed method can scale-up to any number of languages without incurring any additional cost. We validate our approach using a multilingual ASR model trained on five languages and demonstrate its effectiveness against a strong baseline.
WavLLM: Towards Robust and Adaptive Speech Large Language Model
Mar 31, 2024Abstract:The recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized the field of natural language processing, progressively broadening their scope to multimodal perception and generation. However, effectively integrating listening capabilities into LLMs poses significant challenges, particularly with respect to generalizing across varied contexts and executing complex auditory tasks. In this work, we introduce WavLLM, a robust and adaptive speech large language model with dual encoders, and a prompt-aware LoRA weight adapter, optimized by a two-stage curriculum learning approach. Leveraging dual encoders, we decouple different types of speech information, utilizing a Whisper encoder to process the semantic content of speech, and a WavLM encoder to capture the unique characteristics of the speaker's identity. Within the curriculum learning framework, WavLLM first builds its foundational capabilities by optimizing on mixed elementary single tasks, followed by advanced multi-task training on more complex tasks such as combinations of the elementary tasks. To enhance the flexibility and adherence to different tasks and instructions, a prompt-aware LoRA weight adapter is introduced in the second advanced multi-task training stage. We validate the proposed model on universal speech benchmarks including tasks such as ASR, ST, SV, ER, and also apply it to specialized datasets like Gaokao English listening comprehension set for SQA, and speech Chain-of-Thought (CoT) evaluation set. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance across a range of speech tasks on the same model size, exhibiting robust generalization capabilities in executing complex tasks using CoT approach. Furthermore, our model successfully completes Gaokao tasks without specialized training. The codes, models, audio, and Gaokao evaluation set can be accessed at \url{aka.ms/wavllm}.
NOTSOFAR-1 Challenge: New Datasets, Baseline, and Tasks for Distant Meeting Transcription
Jan 16, 2024

Abstract:We introduce the first Natural Office Talkers in Settings of Far-field Audio Recordings (``NOTSOFAR-1'') Challenge alongside datasets and baseline system. The challenge focuses on distant speaker diarization and automatic speech recognition (DASR) in far-field meeting scenarios, with single-channel and known-geometry multi-channel tracks, and serves as a launch platform for two new datasets: First, a benchmarking dataset of 315 meetings, averaging 6 minutes each, capturing a broad spectrum of real-world acoustic conditions and conversational dynamics. It is recorded across 30 conference rooms, featuring 4-8 attendees and a total of 35 unique speakers. Second, a 1000-hour simulated training dataset, synthesized with enhanced authenticity for real-world generalization, incorporating 15,000 real acoustic transfer functions. The tasks focus on single-device DASR, where multi-channel devices always share the same known geometry. This is aligned with common setups in actual conference rooms, and avoids technical complexities associated with multi-device tasks. It also allows for the development of geometry-specific solutions. The NOTSOFAR-1 Challenge aims to advance research in the field of distant conversational speech recognition, providing key resources to unlock the potential of data-driven methods, which we believe are currently constrained by the absence of comprehensive high-quality training and benchmarking datasets.
COSMIC: Data Efficient Instruction-tuning For Speech In-Context Learning
Nov 03, 2023



Abstract:We present a data and cost efficient way of incorporating the speech modality into a large language model (LLM). The resulting multi-modal LLM is a COntextual Speech Model with Instruction-following/in-context-learning Capabilities - COSMIC. Speech comprehension test question-answer (SQA) pairs are generated using GPT-3.5 based on the speech transcriptions as a part of the supervision for the instruction tuning. With fewer than 20M trainable parameters and as little as 450 hours of English speech data for SQA generation, COSMIC exhibits emergent instruction-following and in-context learning capabilities in speech-to-text tasks. The model is able to follow the given text instructions to generate text response even on the unseen EN$\to$X speech-to-text translation (S2TT) task with zero-shot setting. We evaluate the model's in-context learning via various tasks such as EN$\to$X S2TT and few-shot domain adaptation. And instruction-following capabilities are evaluated through a contextual biasing benchmark. Our results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed low cost recipe for building a speech LLM and that with the new instruction-tuning data.
Simulating realistic speech overlaps improves multi-talker ASR
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Multi-talker automatic speech recognition (ASR) has been studied to generate transcriptions of natural conversation including overlapping speech of multiple speakers. Due to the difficulty in acquiring real conversation data with high-quality human transcriptions, a na\"ive simulation of multi-talker speech by randomly mixing multiple utterances was conventionally used for model training. In this work, we propose an improved technique to simulate multi-talker overlapping speech with realistic speech overlaps, where an arbitrary pattern of speech overlaps is represented by a sequence of discrete tokens. With this representation, speech overlapping patterns can be learned from real conversations based on a statistical language model, such as N-gram, which can be then used to generate multi-talker speech for training. In our experiments, multi-talker ASR models trained with the proposed method show consistent improvement on the word error rates across multiple datasets.
Speech separation with large-scale self-supervised learning
Nov 09, 2022Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) methods such as WavLM have shown promising speech separation (SS) results in small-scale simulation-based experiments. In this work, we extend the exploration of the SSL-based SS by massively scaling up both the pre-training data (more than 300K hours) and fine-tuning data (10K hours). We also investigate various techniques to efficiently integrate the pre-trained model with the SS network under a limited computation budget, including a low frame rate SSL model training setup and a fine-tuning scheme using only the part of the pre-trained model. Compared with a supervised baseline and the WavLM-based SS model using feature embeddings obtained with the previously released 94K hours trained WavLM, our proposed model obtains 15.9% and 11.2% of relative word error rate (WER) reductions, respectively, for a simulated far-field speech mixture test set. For conversation transcription on real meeting recordings using continuous speech separation, the proposed model achieves 6.8% and 10.6% of relative WER reductions over the purely supervised baseline on AMI and ICSI evaluation sets, respectively, while reducing the computational cost by 38%.
The Speed Submission to DIHARD II: Contributions & Lessons Learned
Nov 06, 2019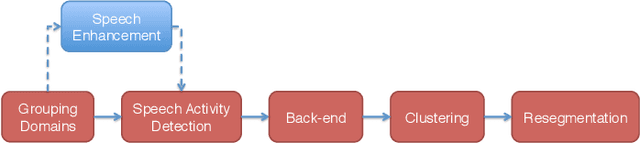
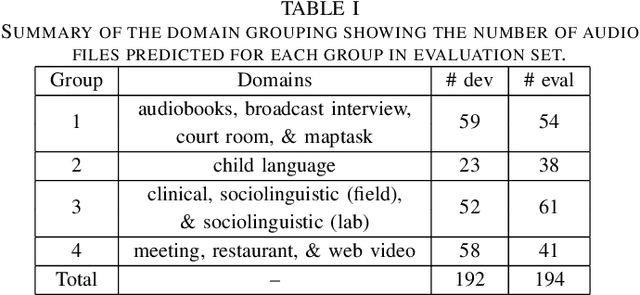

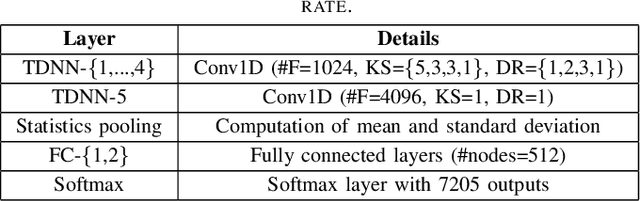
Abstract:This paper describes the speaker diarization systems developed for the Second DIHARD Speech Diarization Challenge (DIHARD II) by the Speed team. Besides describing the system, which considerably outperformed the challenge baselines, we also focus on the lessons learned from numerous approaches that we tried for single and multi-channel systems. We present several components of our diarization system, including categorization of domains, speech enhancement, speech activity detection, speaker embeddings, clustering methods, resegmentation, and system fusion. We analyze and discuss the effect of each such component on the overall diarization performance within the realistic settings of the challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge