Igor Abramovski
Summary of the NOTSOFAR-1 Challenge: Highlights and Learnings
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:The first Natural Office Talkers in Settings of Far-field Audio Recordings (NOTSOFAR-1) Challenge is a pivotal initiative that sets new benchmarks by offering datasets more representative of the needs of real-world business applications than those previously available. The challenge provides a unique combination of 280 recorded meetings across 30 diverse environments, capturing real-world acoustic conditions and conversational dynamics, and a 1000-hour simulated training dataset, synthesized with enhanced authenticity for real-world generalization, incorporating 15,000 real acoustic transfer functions. In this paper, we provide an overview of the systems submitted to the challenge and analyze the top-performing approaches, hypothesizing the factors behind their success. Additionally, we highlight promising directions left unexplored by participants. By presenting key findings and actionable insights, this work aims to drive further innovation and progress in DASR research and applications.
NOTSOFAR-1 Challenge: New Datasets, Baseline, and Tasks for Distant Meeting Transcription
Jan 16, 2024

Abstract:We introduce the first Natural Office Talkers in Settings of Far-field Audio Recordings (``NOTSOFAR-1'') Challenge alongside datasets and baseline system. The challenge focuses on distant speaker diarization and automatic speech recognition (DASR) in far-field meeting scenarios, with single-channel and known-geometry multi-channel tracks, and serves as a launch platform for two new datasets: First, a benchmarking dataset of 315 meetings, averaging 6 minutes each, capturing a broad spectrum of real-world acoustic conditions and conversational dynamics. It is recorded across 30 conference rooms, featuring 4-8 attendees and a total of 35 unique speakers. Second, a 1000-hour simulated training dataset, synthesized with enhanced authenticity for real-world generalization, incorporating 15,000 real acoustic transfer functions. The tasks focus on single-device DASR, where multi-channel devices always share the same known geometry. This is aligned with common setups in actual conference rooms, and avoids technical complexities associated with multi-device tasks. It also allows for the development of geometry-specific solutions. The NOTSOFAR-1 Challenge aims to advance research in the field of distant conversational speech recognition, providing key resources to unlock the potential of data-driven methods, which we believe are currently constrained by the absence of comprehensive high-quality training and benchmarking datasets.
A Real-Time Active Speaker Detection System Integrating an Audio-Visual Signal with a Spatial Querying Mechanism
Sep 15, 2023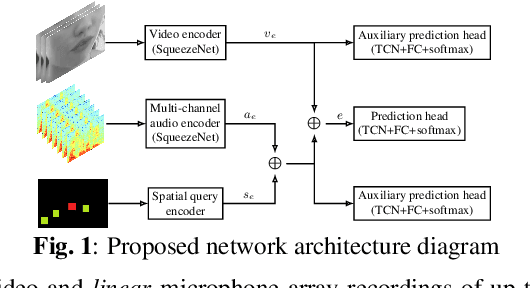


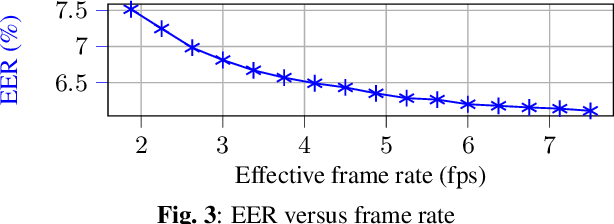
Abstract:We introduce a distinctive real-time, causal, neural network-based active speaker detection system optimized for low-power edge computing. This system drives a virtual cinematography module and is deployed on a commercial device. The system uses data originating from a microphone array and a 360-degree camera. Our network requires only 127 MFLOPs per participant, for a meeting with 14 participants. Unlike previous work, we examine the error rate of our network when the computational budget is exhausted, and find that it exhibits graceful degradation, allowing the system to operate reasonably well even in this case. Departing from conventional DOA estimation approaches, our network learns to query the available acoustic data, considering the detected head locations. We train and evaluate our algorithm on a realistic meetings dataset featuring up to 14 participants in the same meeting, overlapped speech, and other challenging scenarios.
Diarisation using location tracking with agglomerative clustering
Sep 24, 2021


Abstract:Previous works have shown that spatial location information can be complementary to speaker embeddings for a speaker diarisation task. However, the models used often assume that speakers are fairly stationary throughout a meeting. This paper proposes to relax this assumption, by explicitly modelling the movements of speakers within an Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering (AHC) diarisation framework. Kalman filters, which track the locations of speakers, are used to compute log-likelihood ratios that contribute to the cluster affinity computations for the AHC merging and stopping decisions. Experiments show that the proposed approach is able to yield improvements on a Microsoft rich meeting transcription task, compared to methods that do not use location information or that make stationarity assumptions.
Advances in Online Audio-Visual Meeting Transcription
Dec 10, 2019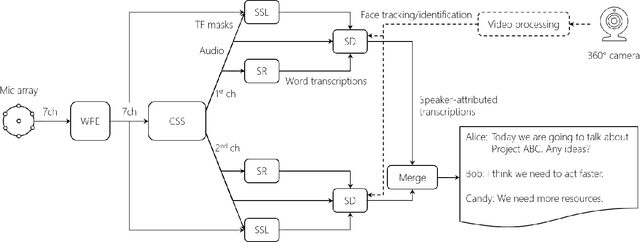
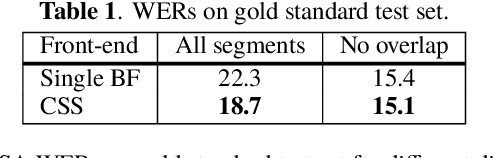
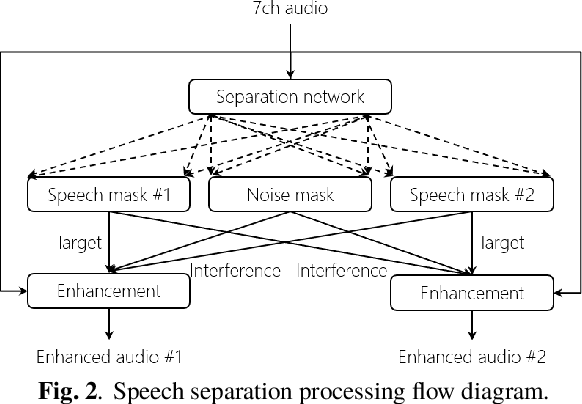
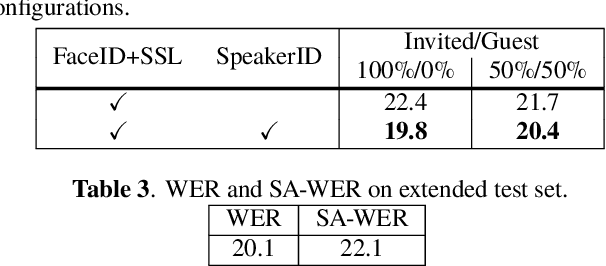
Abstract:This paper describes a system that generates speaker-annotated transcripts of meetings by using a microphone array and a 360-degree camera. The hallmark of the system is its ability to handle overlapped speech, which has been an unsolved problem in realistic settings for over a decade. We show that this problem can be addressed by using a continuous speech separation approach. In addition, we describe an online audio-visual speaker diarization method that leverages face tracking and identification, sound source localization, speaker identification, and, if available, prior speaker information for robustness to various real world challenges. All components are integrated in a meeting transcription framework called SRD, which stands for "separate, recognize, and diarize". Experimental results using recordings of natural meetings involving up to 11 attendees are reported. The continuous speech separation improves a word error rate (WER) by 16.1% compared with a highly tuned beamformer. When a complete list of meeting attendees is available, the discrepancy between WER and speaker-attributed WER is only 1.0%, indicating accurate word-to-speaker association. This increases marginally to 1.6% when 50% of the attendees are unknown to the system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge