Junhao Gong
PaperX: A Unified Framework for Multimodal Academic Presentation Generation with Scholar DAG
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Transforming scientific papers into multimodal presentation content is essential for research dissemination but remains labor intensive. Existing automated solutions typically treat each format as an isolated downstream task, leading to redundant processing and semantic inconsistency. We introduce PaperX, a unified framework that models academic presentation generation as a structural transformation and rendering process. Central to our approach is the Scholar DAG, an intermediate representation that decouples the paper's logical structure from its final presentation syntax. By applying adaptive graph traversal strategies, PaperX generates diverse, high quality outputs from a single source. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that our framework achieves the state of the art performance in content fidelity and aesthetic quality while significantly improving cost efficiency compared to specialized single task agents.
ShotFinder: Imagination-Driven Open-Domain Video Shot Retrieval via Web Search
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:In recent years, large language models (LLMs) have made rapid progress in information retrieval, yet existing research has mainly focused on text or static multimodal settings. Open-domain video shot retrieval, which involves richer temporal structure and more complex semantics, still lacks systematic benchmarks and analysis. To fill this gap, we introduce ShotFinder, a benchmark that formalizes editing requirements as keyframe-oriented shot descriptions and introduces five types of controllable single-factor constraints: Temporal order, Color, Visual style, Audio, and Resolution. We curate 1,210 high-quality samples from YouTube across 20 thematic categories, using large models for generation with human verification. Based on the benchmark, we propose ShotFinder, a text-driven three-stage retrieval and localization pipeline: (1) query expansion via video imagination, (2) candidate video retrieval with a search engine, and (3) description-guided temporal localization. Experiments on multiple closed-source and open-source models reveal a significant gap to human performance, with clear imbalance across constraints: temporal localization is relatively tractable, while color and visual style remain major challenges. These results reveal that open-domain video shot retrieval is still a critical capability that multimodal large models have yet to overcome.
Multimodal Multi-Agent Empowered Legal Judgment Prediction
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Legal Judgment Prediction (LJP) aims to predict the outcomes of legal cases based on factual descriptions, serving as a fundamental task to advance the development of legal systems. Traditional methods often rely on statistical analyses or role-based simulations but face challenges with multiple allegations, diverse evidence, and lack adaptability. In this paper, we introduce JurisMMA, a novel framework for LJP that effectively decomposes trial tasks, standardizes processes, and organizes them into distinct stages. Furthermore, we build JurisMM, a large dataset with over 100,000 recent Chinese judicial records, including both text and multimodal video-text data, enabling comprehensive evaluation. Experiments on JurisMM and the benchmark LawBench validate our framework's effectiveness. These results indicate that our framework is effective not only for LJP but also for a broader range of legal applications, offering new perspectives for the development of future legal methods and datasets.
SandWorm: Event-based Visuotactile Perception with Active Vibration for Screw-Actuated Robot in Granular Media
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Perception in granular media remains challenging due to unpredictable particle dynamics. To address this challenge, we present SandWorm, a biomimetic screw-actuated robot augmented by peristaltic motion to enhance locomotion, and SWTac, a novel event-based visuotactile sensor with an actively vibrated elastomer. The event camera is mechanically decoupled from vibrations by a spring isolation mechanism, enabling high-quality tactile imaging of both dynamic and stationary objects. For algorithm design, we propose an IMU-guided temporal filter to enhance imaging consistency, improving MSNR by 24%. Moreover, we systematically optimize SWTac with vibration parameters, event camera settings and elastomer properties. Motivated by asymmetric edge features, we also implement contact surface estimation by U-Net. Experimental validation demonstrates SWTac's 0.2 mm texture resolution, 98% stone classification accuracy, and 0.15 N force estimation error, while SandWorm demonstrates versatile locomotion (up to 12.5 mm/s) in challenging terrains, successfully executes pipeline dredging and subsurface exploration in complex granular media (observed 90% success rate). Field experiments further confirm the system's practical performance.
CEI: A Unified Interface for Cross-Embodiment Visuomotor Policy Learning in 3D Space
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Robotic foundation models trained on large-scale manipulation datasets have shown promise in learning generalist policies, but they often overfit to specific viewpoints, robot arms, and especially parallel-jaw grippers due to dataset biases. To address this limitation, we propose Cross-Embodiment Interface (\CEI), a framework for cross-embodiment learning that enables the transfer of demonstrations across different robot arm and end-effector morphologies. \CEI introduces the concept of \textit{functional similarity}, which is quantified using Directional Chamfer Distance. Then it aligns robot trajectories through gradient-based optimization, followed by synthesizing observations and actions for unseen robot arms and end-effectors. In experiments, \CEI transfers data and policies from a Franka Panda robot to \textbf{16} different embodiments across \textbf{3} tasks in simulation, and supports bidirectional transfer between a UR5+AG95 gripper robot and a UR5+Xhand robot across \textbf{6} real-world tasks, achieving an average transfer ratio of 82.4\%. Finally, we demonstrate that \CEI can also be extended with spatial generalization and multimodal motion generation capabilities using our proposed techniques. Project website: https://cross-embodiment-interface.github.io/
QuantEval: A Benchmark for Financial Quantitative Tasks in Large Language Models
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown strong capabilities across many domains, yet their evaluation in financial quantitative tasks remains fragmented and mostly limited to knowledge-centric question answering. We introduce QuantEval, a benchmark that evaluates LLMs across three essential dimensions of quantitative finance: knowledge-based QA, quantitative mathematical reasoning, and quantitative strategy coding. Unlike prior financial benchmarks, QuantEval integrates a CTA-style backtesting framework that executes model-generated strategies and evaluates them using financial performance metrics, enabling a more realistic assessment of quantitative coding ability. We evaluate some state-of-the-art open-source and proprietary LLMs and observe substantial gaps to human experts, particularly in reasoning and strategy coding. Finally, we conduct large-scale supervised fine-tuning and reinforcement learning experiments on domain-aligned data, demonstrating consistent improvements. We hope QuantEval will facilitate research on LLMs' quantitative finance capabilities and accelerate their practical adoption in real-world trading workflows. We additionally release the full deterministic backtesting configuration (asset universe, cost model, and metric definitions) to ensure strict reproducibility.
FlexiCup: Wireless Multimodal Suction Cup with Dual-Zone Vision-Tactile Sensing
Nov 18, 2025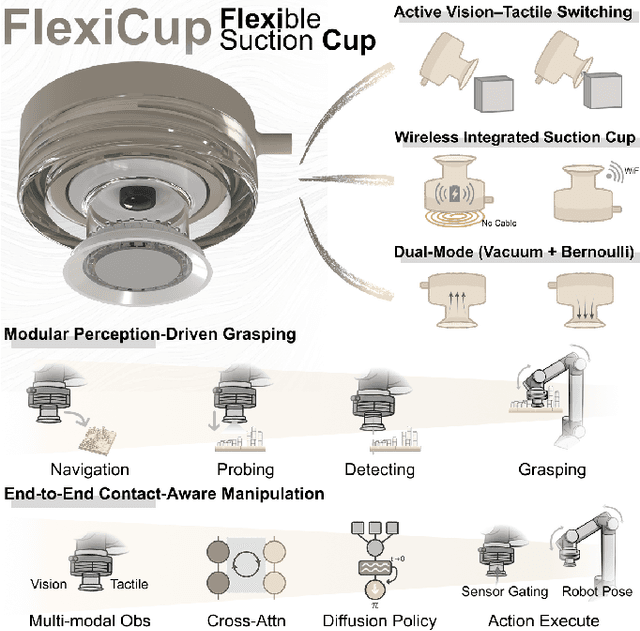
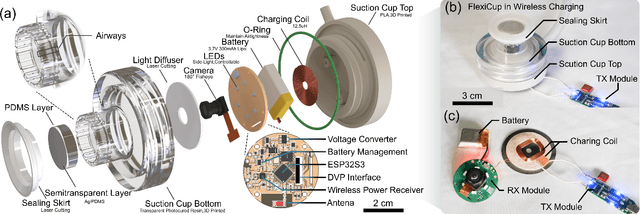
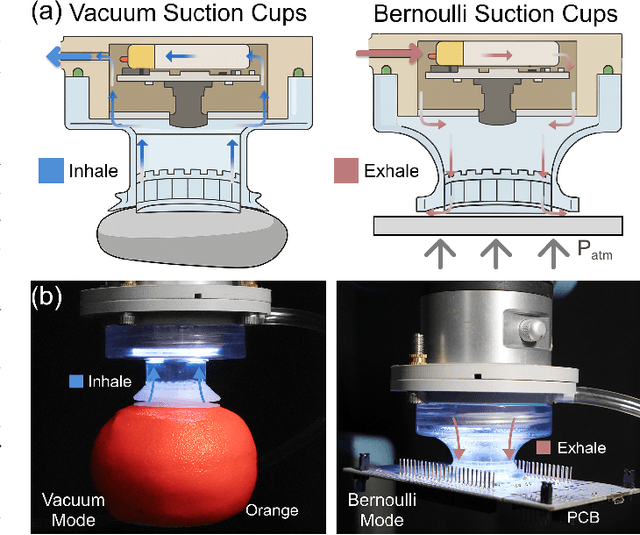
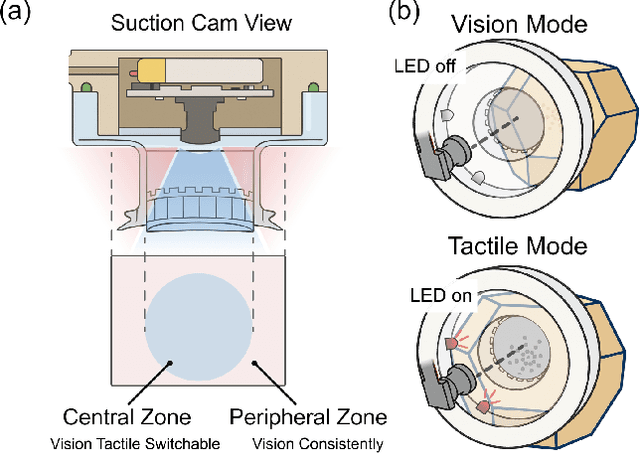
Abstract:Conventional suction cups lack sensing capabilities for contact-aware manipulation in unstructured environments. This paper presents FlexiCup, a fully wireless multimodal suction cup that integrates dual-zone vision-tactile sensing. The central zone dynamically switches between vision and tactile modalities via illumination control for contact detection, while the peripheral zone provides continuous spatial awareness for approach planning. FlexiCup supports both vacuum and Bernoulli suction modes through modular mechanical configurations, achieving complete wireless autonomy with onboard computation and power. We validate hardware versatility through dual control paradigms. Modular perception-driven grasping across structured surfaces with varying obstacle densities demonstrates comparable performance between vacuum (90.0% mean success) and Bernoulli (86.7% mean success) modes. Diffusion-based end-to-end learning achieves 73.3% success on inclined transport and 66.7% on orange extraction tasks. Ablation studies confirm that multi-head attention coordinating dual-zone observations provides 13% improvements for contact-aware manipulation. Hardware designs and firmware are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/api/repo/FlexiCup-DA7D/file/index.html?v=8f531b44.
MoiréTac: A Dual-Mode Visuotactile Sensor for Multidimensional Perception Using Moiré Pattern Amplification
Sep 16, 2025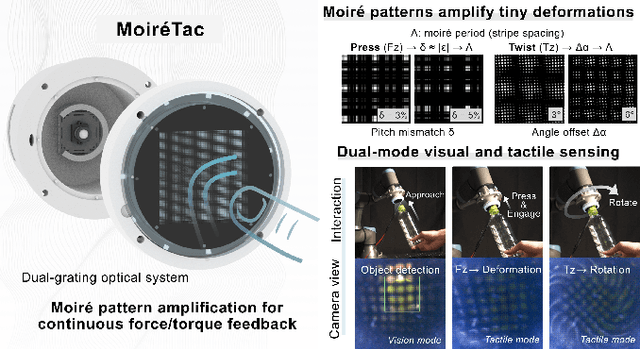

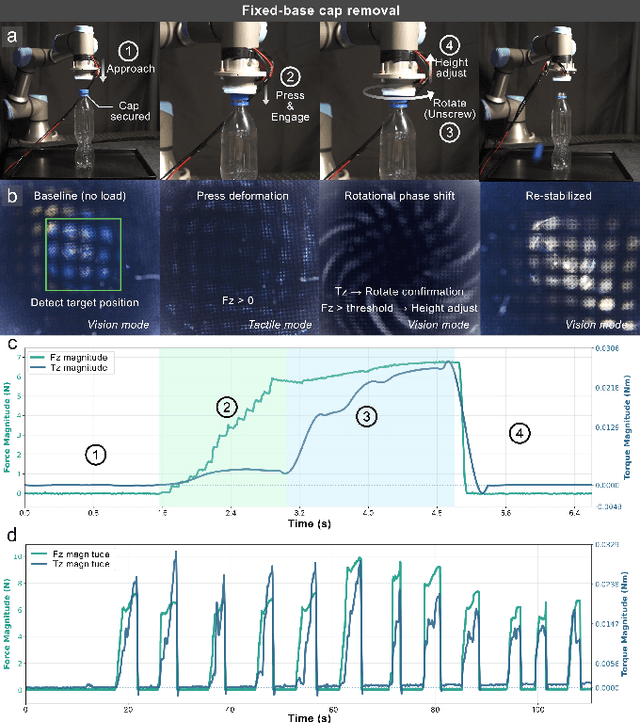
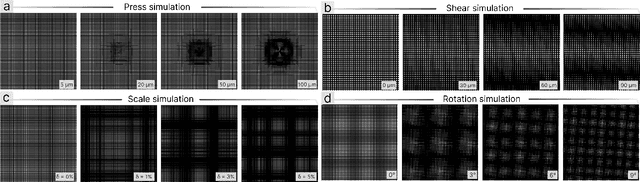
Abstract:Visuotactile sensors typically employ sparse marker arrays that limit spatial resolution and lack clear analytical force-to-image relationships. To solve this problem, we present \textbf{Moir\'eTac}, a dual-mode sensor that generates dense interference patterns via overlapping micro-gratings within a transparent architecture. When two gratings overlap with misalignment, they create moir\'e patterns that amplify microscopic deformations. The design preserves optical clarity for vision tasks while producing continuous moir\'e fields for tactile sensing, enabling simultaneous 6-axis force/torque measurement, contact localization, and visual perception. We combine physics-based features (brightness, phase gradient, orientation, and period) from moir\'e patterns with deep spatial features. These are mapped to 6-axis force/torque measurements, enabling interpretable regression through end-to-end learning. Experimental results demonstrate three capabilities: force/torque measurement with R^2 > 0.98 across tested axes; sensitivity tuning through geometric parameters (threefold gain adjustment); and vision functionality for object classification despite moir\'e overlay. Finally, we integrate the sensor into a robotic arm for cap removal with coordinated force and torque control, validating its potential for dexterous manipulation.
UltraTac: Integrated Ultrasound-Augmented Visuotactile Sensor for Enhanced Robotic Perception
Aug 29, 2025



Abstract:Visuotactile sensors provide high-resolution tactile information but are incapable of perceiving the material features of objects. We present UltraTac, an integrated sensor that combines visuotactile imaging with ultrasound sensing through a coaxial optoacoustic architecture. The design shares structural components and achieves consistent sensing regions for both modalities. Additionally, we incorporate acoustic matching into the traditional visuotactile sensor structure, enabling integration of the ultrasound sensing modality without compromising visuotactile performance. Through tactile feedback, we dynamically adjust the operating state of the ultrasound module to achieve flexible functional coordination. Systematic experiments demonstrate three key capabilities: proximity sensing in the 3-8 cm range ($R^2=0.90$), material classification (average accuracy: 99.20%), and texture-material dual-mode object recognition achieving 92.11% accuracy on a 15-class task. Finally, we integrate the sensor into a robotic manipulation system to concurrently detect container surface patterns and internal content, which verifies its potential for advanced human-machine interaction and precise robotic manipulation.
HSSBench: Benchmarking Humanities and Social Sciences Ability for Multimodal Large Language Models
Jun 04, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant potential to advance a broad range of domains. However, current benchmarks for evaluating MLLMs primarily emphasize general knowledge and vertical step-by-step reasoning typical of STEM disciplines, while overlooking the distinct needs and potential of the Humanities and Social Sciences (HSS). Tasks in the HSS domain require more horizontal, interdisciplinary thinking and a deep integration of knowledge across related fields, which presents unique challenges for MLLMs, particularly in linking abstract concepts with corresponding visual representations. Addressing this gap, we present HSSBench, a dedicated benchmark designed to assess the capabilities of MLLMs on HSS tasks in multiple languages, including the six official languages of the United Nations. We also introduce a novel data generation pipeline tailored for HSS scenarios, in which multiple domain experts and automated agents collaborate to generate and iteratively refine each sample. HSSBench contains over 13,000 meticulously designed samples, covering six key categories. We benchmark more than 20 mainstream MLLMs on HSSBench and demonstrate that it poses significant challenges even for state-of-the-art models. We hope that this benchmark will inspire further research into enhancing the cross-disciplinary reasoning abilities of MLLMs, especially their capacity to internalize and connect knowledge across fields.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge