Jiandong Jin
RGB-Event based Pedestrian Attribute Recognition: A Benchmark Dataset and An Asymmetric RWKV Fusion Framework
Apr 14, 2025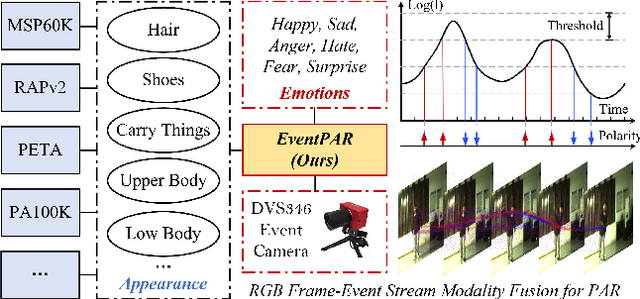
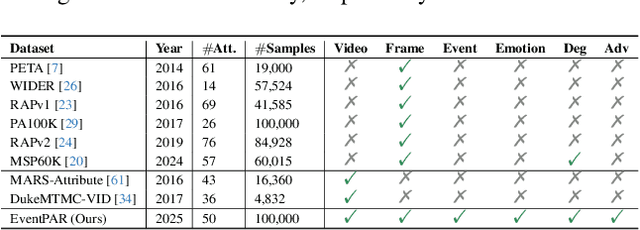

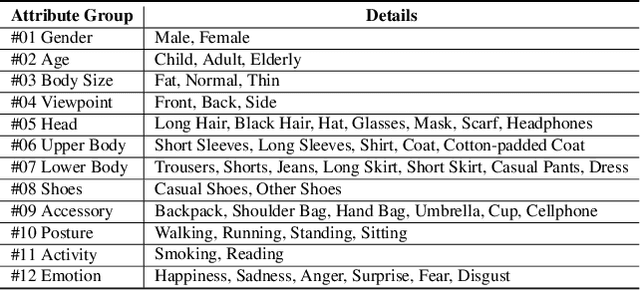
Abstract:Existing pedestrian attribute recognition methods are generally developed based on RGB frame cameras. However, these approaches are constrained by the limitations of RGB cameras, such as sensitivity to lighting conditions and motion blur, which hinder their performance. Furthermore, current attribute recognition primarily focuses on analyzing pedestrians' external appearance and clothing, lacking an exploration of emotional dimensions. In this paper, we revisit these issues and propose a novel multi-modal RGB-Event attribute recognition task by drawing inspiration from the advantages of event cameras in low-light, high-speed, and low-power consumption. Specifically, we introduce the first large-scale multi-modal pedestrian attribute recognition dataset, termed EventPAR, comprising 100K paired RGB-Event samples that cover 50 attributes related to both appearance and six human emotions, diverse scenes, and various seasons. By retraining and evaluating mainstream PAR models on this dataset, we establish a comprehensive benchmark and provide a solid foundation for future research in terms of data and algorithmic baselines. In addition, we propose a novel RWKV-based multi-modal pedestrian attribute recognition framework, featuring an RWKV visual encoder and an asymmetric RWKV fusion module. Extensive experiments are conducted on our proposed dataset as well as two simulated datasets (MARS-Attribute and DukeMTMC-VID-Attribute), achieving state-of-the-art results. The source code and dataset will be released on https://github.com/Event-AHU/OpenPAR
A Unified Modeling Framework for Automated Penetration Testing
Feb 17, 2025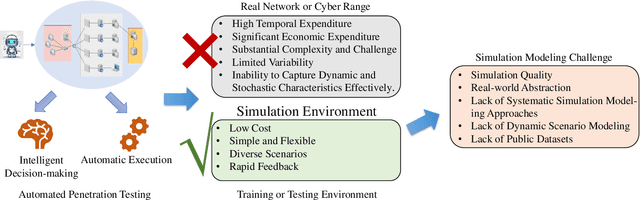
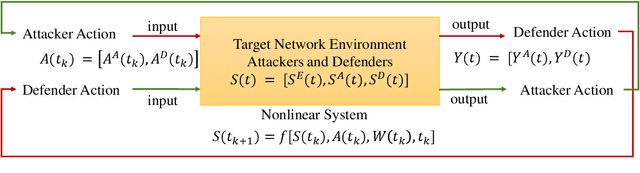
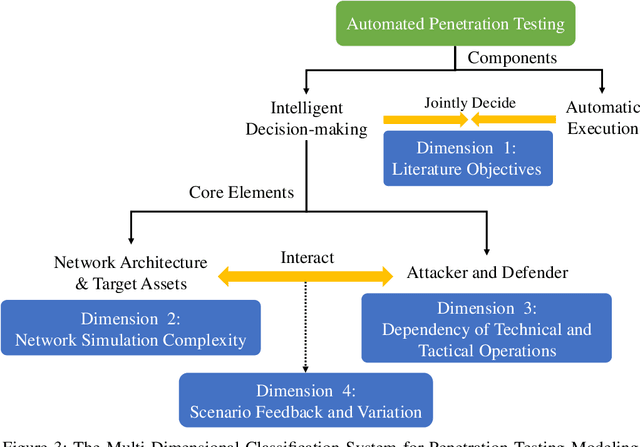
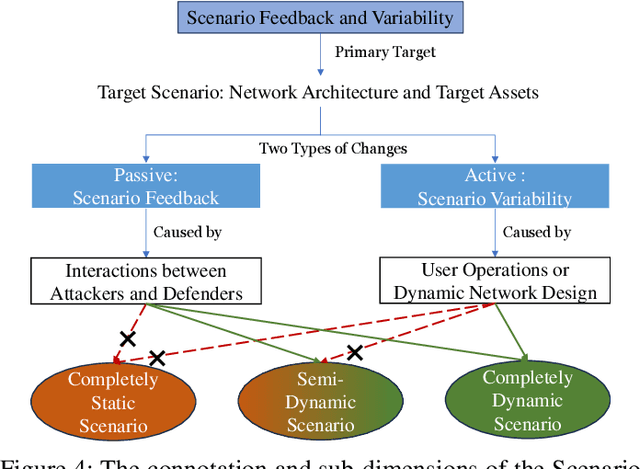
Abstract:The integration of artificial intelligence into automated penetration testing (AutoPT) has highlighted the necessity of simulation modeling for the training of intelligent agents, due to its cost-efficiency and swift feedback capabilities. Despite the proliferation of AutoPT research, there is a recognized gap in the availability of a unified framework for simulation modeling methods. This paper presents a systematic review and synthesis of existing techniques, introducing MDCPM to categorize studies based on literature objectives, network simulation complexity, dependency of technical and tactical operations, and scenario feedback and variation. To bridge the gap in unified method for multi-dimensional and multi-level simulation modeling, dynamic environment modeling, and the scarcity of public datasets, we introduce AutoPT-Sim, a novel modeling framework that based on policy automation and encompasses the combination of all sub dimensions. AutoPT-Sim offers a comprehensive approach to modeling network environments, attackers, and defenders, transcending the constraints of static modeling and accommodating networks of diverse scales. We publicly release a generated standard network environment dataset and the code of Network Generator. By integrating publicly available datasets flexibly, support is offered for various simulation modeling levels focused on policy automation in MDCPM and the network generator help researchers output customized target network data by adjusting parameters or fine-tuning the network generator.
Pedestrian Attribute Recognition: A New Benchmark Dataset and A Large Language Model Augmented Framework
Aug 19, 2024Abstract:Pedestrian Attribute Recognition (PAR) is one of the indispensable tasks in human-centered research. However, existing datasets neglect different domains (e.g., environments, times, populations, and data sources), only conducting simple random splits, and the performance of these datasets has already approached saturation. In the past five years, no large-scale dataset has been opened to the public. To address this issue, this paper proposes a new large-scale, cross-domain pedestrian attribute recognition dataset to fill the data gap, termed MSP60K. It consists of 60,122 images and 57 attribute annotations across eight scenarios. Synthetic degradation is also conducted to further narrow the gap between the dataset and real-world challenging scenarios. To establish a more rigorous benchmark, we evaluate 17 representative PAR models under both random and cross-domain split protocols on our dataset. Additionally, we propose an innovative Large Language Model (LLM) augmented PAR framework, named LLM-PAR. This framework processes pedestrian images through a Vision Transformer (ViT) backbone to extract features and introduces a multi-embedding query Transformer to learn partial-aware features for attribute classification. Significantly, we enhance this framework with LLM for ensemble learning and visual feature augmentation. Comprehensive experiments across multiple PAR benchmark datasets have thoroughly validated the efficacy of our proposed framework. The dataset and source code accompanying this paper will be made publicly available at \url{https://github.com/Event-AHU/OpenPAR}.
An Empirical Study of Mamba-based Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Current strong pedestrian attribute recognition models are developed based on Transformer networks, which are computationally heavy. Recently proposed models with linear complexity (e.g., Mamba) have garnered significant attention and have achieved a good balance between accuracy and computational cost across a variety of visual tasks. Relevant review articles also suggest that while these models can perform well on some pedestrian attribute recognition datasets, they are generally weaker than the corresponding Transformer models. To further tap into the potential of the novel Mamba architecture for PAR tasks, this paper designs and adapts Mamba into two typical PAR frameworks, i.e., the text-image fusion approach and pure vision Mamba multi-label recognition framework. It is found that interacting with attribute tags as additional input does not always lead to an improvement, specifically, Vim can be enhanced, but VMamba cannot. This paper further designs various hybrid Mamba-Transformer variants and conducts thorough experimental validations. These experimental results indicate that simply enhancing Mamba with a Transformer does not always lead to performance improvements but yields better results under certain settings. We hope this empirical study can further inspire research in Mamba for PAR, and even extend into the domain of multi-label recognition, through the design of these network structures and comprehensive experimentation. The source code of this work will be released at \url{https://github.com/Event-AHU/OpenPAR}
Pre-training on High Definition X-ray Images: An Experimental Study
Apr 27, 2024



Abstract:Existing X-ray based pre-trained vision models are usually conducted on a relatively small-scale dataset (less than 500k samples) with limited resolution (e.g., 224 $\times$ 224). However, the key to the success of self-supervised pre-training large models lies in massive training data, and maintaining high resolution in the field of X-ray images is the guarantee of effective solutions to difficult miscellaneous diseases. In this paper, we address these issues by proposing the first high-definition (1280 $\times$ 1280) X-ray based pre-trained foundation vision model on our newly collected large-scale dataset which contains more than 1 million X-ray images. Our model follows the masked auto-encoder framework which takes the tokens after mask processing (with a high rate) is used as input, and the masked image patches are reconstructed by the Transformer encoder-decoder network. More importantly, we introduce a novel context-aware masking strategy that utilizes the chest contour as a boundary for adaptive masking operations. We validate the effectiveness of our model on two downstream tasks, including X-ray report generation and disease recognition. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our pre-trained medical foundation vision model achieves comparable or even new state-of-the-art performance on downstream benchmark datasets. The source code and pre-trained models of this paper will be released on https://github.com/Event-AHU/Medical_Image_Analysis.
Spatio-Temporal Side Tuning Pre-trained Foundation Models for Video-based Pedestrian Attribute Recognition
Apr 27, 2024



Abstract:Existing pedestrian attribute recognition (PAR) algorithms are mainly developed based on a static image, however, the performance is unreliable in challenging scenarios, such as heavy occlusion, motion blur, etc. In this work, we propose to understand human attributes using video frames that can fully use temporal information by fine-tuning a pre-trained multi-modal foundation model efficiently. Specifically, we formulate the video-based PAR as a vision-language fusion problem and adopt a pre-trained foundation model CLIP to extract the visual features. More importantly, we propose a novel spatiotemporal side-tuning strategy to achieve parameter-efficient optimization of the pre-trained vision foundation model. To better utilize the semantic information, we take the full attribute list that needs to be recognized as another input and transform the attribute words/phrases into the corresponding sentence via split, expand, and prompt operations. Then, the text encoder of CLIP is utilized for embedding processed attribute descriptions. The averaged visual tokens and text tokens are concatenated and fed into a fusion Transformer for multi-modal interactive learning. The enhanced tokens will be fed into a classification head for pedestrian attribute prediction. Extensive experiments on two large-scale video-based PAR datasets fully validated the effectiveness of our proposed framework. The source code of this paper is available at https://github.com/Event-AHU/OpenPAR.
Crimson: Empowering Strategic Reasoning in Cybersecurity through Large Language Models
Mar 01, 2024



Abstract:We introduces Crimson, a system that enhances the strategic reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) within the realm of cybersecurity. By correlating CVEs with MITRE ATT&CK techniques, Crimson advances threat anticipation and strategic defense efforts. Our approach includes defining and evaluating cybersecurity strategic tasks, alongside implementing a comprehensive human-in-the-loop data-synthetic workflow to develop the CVE-to-ATT&CK Mapping (CVEM) dataset. We further enhance LLMs' reasoning abilities through a novel Retrieval-Aware Training (RAT) process and its refined iteration, RAT-R. Our findings demonstrate that an LLM fine-tuned with our techniques, possessing 7 billion parameters, approaches the performance level of GPT-4, showing markedly lower rates of hallucination and errors, and surpassing other models in strategic reasoning tasks. Moreover, domain-specific fine-tuning of embedding models significantly improves performance within cybersecurity contexts, underscoring the efficacy of our methodology. By leveraging Crimson to convert raw vulnerability data into structured and actionable insights, we bolster proactive cybersecurity defenses.
Pedestrian Attribute Recognition via CLIP based Prompt Vision-Language Fusion
Dec 17, 2023



Abstract:Existing pedestrian attribute recognition (PAR) algorithms adopt pre-trained CNN (e.g., ResNet) as their backbone network for visual feature learning, which might obtain sub-optimal results due to the insufficient employment of the relations between pedestrian images and attribute labels. In this paper, we formulate PAR as a vision-language fusion problem and fully exploit the relations between pedestrian images and attribute labels. Specifically, the attribute phrases are first expanded into sentences, and then the pre-trained vision-language model CLIP is adopted as our backbone for feature embedding of visual images and attribute descriptions. The contrastive learning objective connects the vision and language modalities well in the CLIP-based feature space, and the Transformer layers used in CLIP can capture the long-range relations between pixels. Then, a multi-modal Transformer is adopted to fuse the dual features effectively and feed-forward network is used to predict attributes. To optimize our network efficiently, we propose the region-aware prompt tuning technique to adjust very few parameters (i.e., only the prompt vectors and classification heads) and fix both the pre-trained VL model and multi-modal Transformer. Our proposed PAR algorithm only adjusts 0.75% learnable parameters compared with the fine-tuning strategy. It also achieves new state-of-the-art performance on both standard and zero-shot settings for PAR, including RAPv1, RAPv2, WIDER, PA100K, and PETA-ZS, RAP-ZS datasets. The source code and pre-trained models will be released on https://github.com/Event-AHU/OpenPAR.
SequencePAR: Understanding Pedestrian Attributes via A Sequence Generation Paradigm
Dec 04, 2023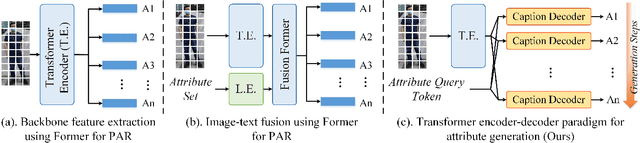
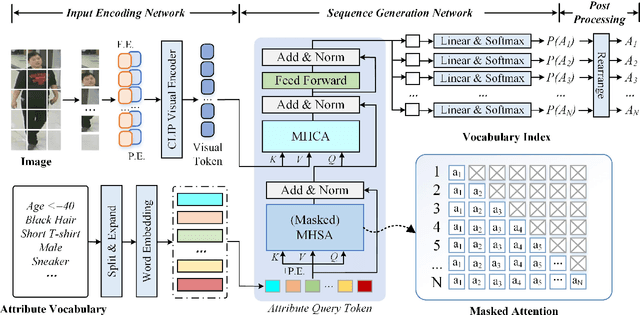
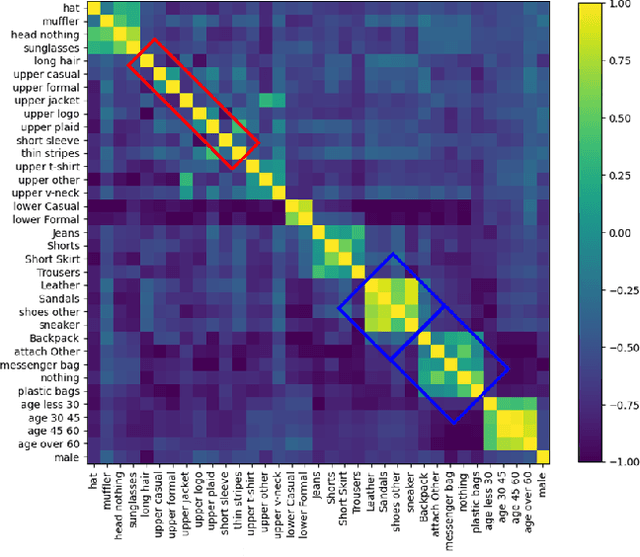
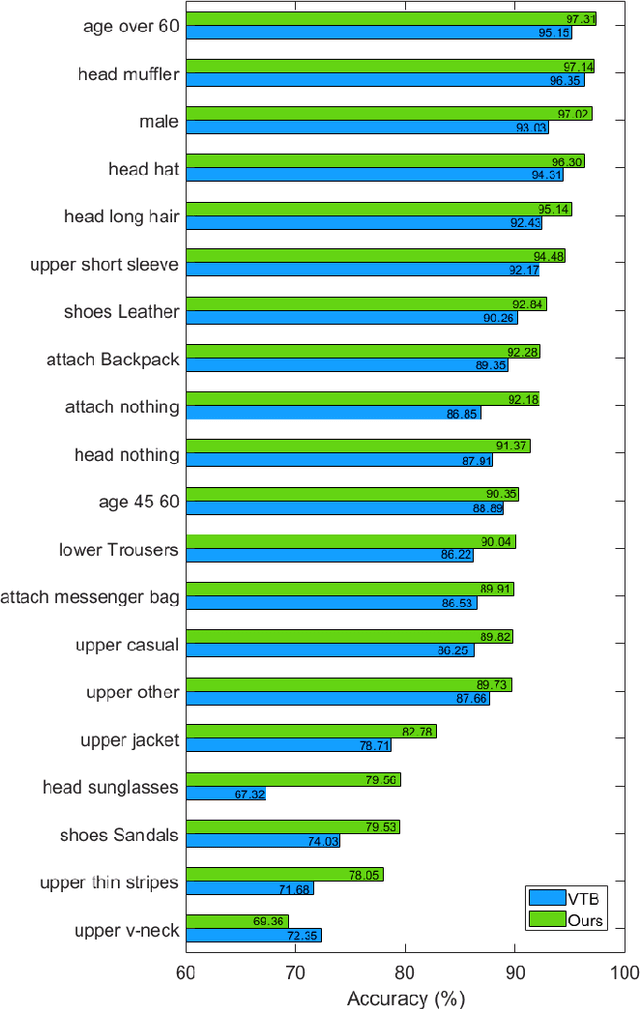
Abstract:Current pedestrian attribute recognition (PAR) algorithms are developed based on multi-label or multi-task learning frameworks, which aim to discriminate the attributes using specific classification heads. However, these discriminative models are easily influenced by imbalanced data or noisy samples. Inspired by the success of generative models, we rethink the pedestrian attribute recognition scheme and believe the generative models may perform better on modeling dependencies and complexity between human attributes. In this paper, we propose a novel sequence generation paradigm for pedestrian attribute recognition, termed SequencePAR. It extracts the pedestrian features using a pre-trained CLIP model and embeds the attribute set into query tokens under the guidance of text prompts. Then, a Transformer decoder is proposed to generate the human attributes by incorporating the visual features and attribute query tokens. The masked multi-head attention layer is introduced into the decoder module to prevent the model from remembering the next attribute while making attribute predictions during training. Extensive experiments on multiple widely used pedestrian attribute recognition datasets fully validated the effectiveness of our proposed SequencePAR. The source code and pre-trained models will be released at https://github.com/Event-AHU/OpenPAR.
Semantic-Aware Frame-Event Fusion based Pattern Recognition via Large Vision-Language Models
Nov 30, 2023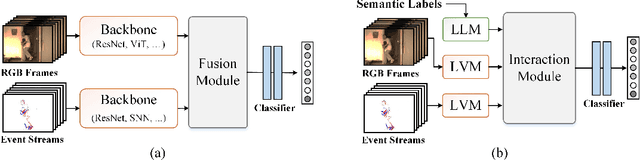

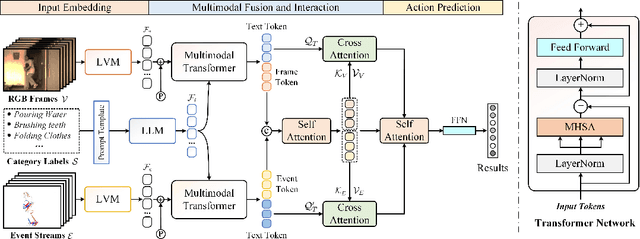
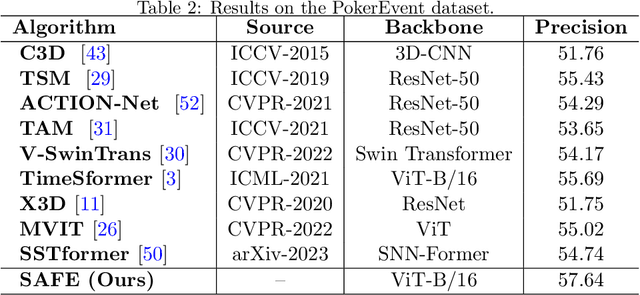
Abstract:Pattern recognition through the fusion of RGB frames and Event streams has emerged as a novel research area in recent years. Current methods typically employ backbone networks to individually extract the features of RGB frames and event streams, and subsequently fuse these features for pattern recognition. However, we posit that these methods may suffer from key issues like sematic gaps and small-scale backbone networks. In this study, we introduce a novel pattern recognition framework that consolidates the semantic labels, RGB frames, and event streams, leveraging pre-trained large-scale vision-language models. Specifically, given the input RGB frames, event streams, and all the predefined semantic labels, we employ a pre-trained large-scale vision model (CLIP vision encoder) to extract the RGB and event features. To handle the semantic labels, we initially convert them into language descriptions through prompt engineering, and then obtain the semantic features using the pre-trained large-scale language model (CLIP text encoder). Subsequently, we integrate the RGB/Event features and semantic features using multimodal Transformer networks. The resulting frame and event tokens are further amplified using self-attention layers. Concurrently, we propose to enhance the interactions between text tokens and RGB/Event tokens via cross-attention. Finally, we consolidate all three modalities using self-attention and feed-forward layers for recognition. Comprehensive experiments on the HARDVS and PokerEvent datasets fully substantiate the efficacy of our proposed SAFE model. The source code will be made available at https://github.com/Event-AHU/SAFE_LargeVLM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge