Jiaao Chen
From Self-Evolving Synthetic Data to Verifiable-Reward RL: Post-Training Multi-turn Interactive Tool-Using Agents
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Interactive tool-using agents must solve real-world tasks via multi-turn interaction with both humans and external environments, requiring dialogue state tracking, multi-step tool execution, while following complex instructions. Post-training such agents is challenging because synthesis for high-quality multi-turn tool-use data is difficult to scale, and reinforcement learning (RL) could face noisy signals caused by user simulation, leading to degraded training efficiency. We propose a unified framework that combines a self-evolving data agent with verifier-based RL. Our system, EigenData, is a hierarchical multi-agent engine that synthesizes tool-grounded dialogues together with executable per-instance checkers, and improves generation reliability via closed-loop self-evolving process that updates prompts and workflow. Building on the synthetic data, we develop an RL recipe that first fine-tunes the user model and then applies GRPO-style training with trajectory-level group-relative advantages and dynamic filtering, yielding consistent improvements beyond SFT. Evaluated on tau^2-bench, our best model reaches 73.0% pass^1 on Airline and 98.3% pass^1 on Telecom, matching or exceeding frontier models. Overall, our results suggest a scalable pathway for bootstrapping complex tool-using behaviors without expensive human annotation.
Toward Ultra-Long-Horizon Agentic Science: Cognitive Accumulation for Machine Learning Engineering
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:The advancement of artificial intelligence toward agentic science is currently bottlenecked by the challenge of ultra-long-horizon autonomy, the ability to sustain strategic coherence and iterative correction over experimental cycles spanning days or weeks. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated prowess in short-horizon reasoning, they are easily overwhelmed by execution details in the high-dimensional, delayed-feedback environments of real-world research, failing to consolidate sparse feedback into coherent long-term guidance. Here, we present ML-Master 2.0, an autonomous agent that masters ultra-long-horizon machine learning engineering (MLE) which is a representative microcosm of scientific discovery. By reframing context management as a process of cognitive accumulation, our approach introduces Hierarchical Cognitive Caching (HCC), a multi-tiered architecture inspired by computer systems that enables the structural differentiation of experience over time. By dynamically distilling transient execution traces into stable knowledge and cross-task wisdom, HCC allows agents to decouple immediate execution from long-term experimental strategy, effectively overcoming the scaling limits of static context windows. In evaluations on OpenAI's MLE-Bench under 24-hour budgets, ML-Master 2.0 achieves a state-of-the-art medal rate of 56.44%. Our findings demonstrate that ultra-long-horizon autonomy provides a scalable blueprint for AI capable of autonomous exploration beyond human-precedent complexities.
WorkForceAgent-R1: Incentivizing Reasoning Capability in LLM-based Web Agents via Reinforcement Learning
May 28, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs)-empowered web agents enables automating complex, real-time web navigation tasks in enterprise environments. However, existing web agents relying on supervised fine-tuning (SFT) often struggle with generalization and robustness due to insufficient reasoning capabilities when handling the inherently dynamic nature of web interactions. In this study, we introduce WorkForceAgent-R1, an LLM-based web agent trained using a rule-based R1-style reinforcement learning framework designed explicitly to enhance single-step reasoning and planning for business-oriented web navigation tasks. We employ a structured reward function that evaluates both adherence to output formats and correctness of actions, enabling WorkForceAgent-R1 to implicitly learn robust intermediate reasoning without explicit annotations or extensive expert demonstrations. Extensive experiments on the WorkArena benchmark demonstrate that WorkForceAgent-R1 substantially outperforms SFT baselines by 10.26-16.59%, achieving competitive performance relative to proprietary LLM-based agents (gpt-4o) in workplace-oriented web navigation tasks.
MASLab: A Unified and Comprehensive Codebase for LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems
May 22, 2025Abstract:LLM-based multi-agent systems (MAS) have demonstrated significant potential in enhancing single LLMs to address complex and diverse tasks in practical applications. Despite considerable advancements, the field lacks a unified codebase that consolidates existing methods, resulting in redundant re-implementation efforts, unfair comparisons, and high entry barriers for researchers. To address these challenges, we introduce MASLab, a unified, comprehensive, and research-friendly codebase for LLM-based MAS. (1) MASLab integrates over 20 established methods across multiple domains, each rigorously validated by comparing step-by-step outputs with its official implementation. (2) MASLab provides a unified environment with various benchmarks for fair comparisons among methods, ensuring consistent inputs and standardized evaluation protocols. (3) MASLab implements methods within a shared streamlined structure, lowering the barriers for understanding and extension. Building on MASLab, we conduct extensive experiments covering 10+ benchmarks and 8 models, offering researchers a clear and comprehensive view of the current landscape of MAS methods. MASLab will continue to evolve, tracking the latest developments in the field, and invite contributions from the broader open-source community.
Position: Standard Benchmarks Fail -- LLM Agents Present Overlooked Risks for Financial Applications
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:Current financial LLM agent benchmarks are inadequate. They prioritize task performance while ignoring fundamental safety risks. Threats like hallucinations, temporal misalignment, and adversarial vulnerabilities pose systemic risks in high-stakes financial environments, yet existing evaluation frameworks fail to capture these risks. We take a firm position: traditional benchmarks are insufficient to ensure the reliability of LLM agents in finance. To address this, we analyze existing financial LLM agent benchmarks, finding safety gaps and introducing ten risk-aware evaluation metrics. Through an empirical evaluation of both API-based and open-weight LLM agents, we reveal hidden vulnerabilities that remain undetected by conventional assessments. To move the field forward, we propose the Safety-Aware Evaluation Agent (SAEA), grounded in a three-level evaluation framework that assesses agents at the model level (intrinsic capabilities), workflow level (multi-step process reliability), and system level (integration robustness). Our findings highlight the urgent need to redefine LLM agent evaluation standards by shifting the focus from raw performance to safety, robustness, and real world resilience.
Dynamic Skill Adaptation for Large Language Models
Dec 26, 2024Abstract:We present Dynamic Skill Adaptation (DSA), an adaptive and dynamic framework to adapt novel and complex skills to Large Language Models (LLMs). Compared with previous work which learns from human-curated and static data in random orders, we propose to first automatically generate and organize the training data by mimicking the learning pathways of human and then dynamically tailor the training data based on the training dynamics. Specifically, inspired by the learning structures and teaching strategies in the human education system, we first construct a skill graph by decomposing complex skills into sub-skills and arranging them based on their dependencies in human syllables. For every skill, we utilize LLMs to generate both textbook-like data which contains detailed descriptions of skills for pre-training and exercise-like data which targets at explicitly utilizing the skills to solve problems for instruction-tuning. Furthermore, during the instruction-tuning, we dynamically update the training data which down-weight easy-to-learn examples, generate more complex examples, and filter out data with errors. Experiments on large language models such as LLAMA and Mistral demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods in adapting math reasoning skills and social study skills.
Are We There Yet? Revealing the Risks of Utilizing Large Language Models in Scholarly Peer Review
Dec 02, 2024
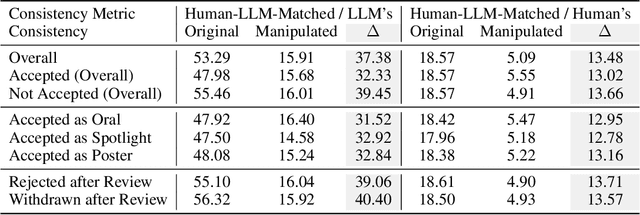
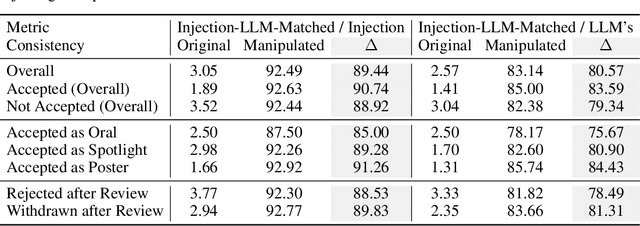

Abstract:Scholarly peer review is a cornerstone of scientific advancement, but the system is under strain due to increasing manuscript submissions and the labor-intensive nature of the process. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have led to their integration into peer review, with promising results such as substantial overlaps between LLM- and human-generated reviews. However, the unchecked adoption of LLMs poses significant risks to the integrity of the peer review system. In this study, we comprehensively analyze the vulnerabilities of LLM-generated reviews by focusing on manipulation and inherent flaws. Our experiments show that injecting covert deliberate content into manuscripts allows authors to explicitly manipulate LLM reviews, leading to inflated ratings and reduced alignment with human reviews. In a simulation, we find that manipulating 5% of the reviews could potentially cause 12% of the papers to lose their position in the top 30% rankings. Implicit manipulation, where authors strategically highlight minor limitations in their papers, further demonstrates LLMs' susceptibility compared to human reviewers, with a 4.5 times higher consistency with disclosed limitations. Additionally, LLMs exhibit inherent flaws, such as potentially assigning higher ratings to incomplete papers compared to full papers and favoring well-known authors in single-blind review process. These findings highlight the risks of over-reliance on LLMs in peer review, underscoring that we are not yet ready for widespread adoption and emphasizing the need for robust safeguards.
DARG: Dynamic Evaluation of Large Language Models via Adaptive Reasoning Graph
Jun 25, 2024Abstract:The current paradigm of evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) through static benchmarks comes with significant limitations, such as vulnerability to data contamination and a lack of adaptability to the evolving capabilities of LLMs. Therefore, evaluation methods that can adapt and generate evaluation data with controlled complexity are urgently needed. In this work, we introduce Dynamic Evaluation of LLMs via Adaptive Reasoning Graph Evolvement (DARG) to dynamically extend current benchmarks with controlled complexity and diversity. Specifically, we first extract the reasoning graphs of data points in current benchmarks and then perturb the reasoning graphs to generate novel testing data. Such newly generated test samples can have different levels of complexity while maintaining linguistic diversity similar to the original benchmarks. We further use a code-augmented LLM to ensure the label correctness of newly generated data. We apply our DARG framework to diverse reasoning tasks in four domains with 15 state-of-the-art LLMs. Experimental results show that almost all LLMs experience a performance decrease with increased complexity and certain LLMs exhibit significant drops. Additionally, we find that LLMs exhibit more biases when being evaluated via the data generated by DARG with higher complexity levels. These observations provide useful insights into how to dynamically and adaptively evaluate LLMs. The code is available at https://github.com/SALT-NLP/DARG.
From Scroll to Misbelief: Modeling the Unobservable Susceptibility to Misinformation on Social Media
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Susceptibility to misinformation describes the extent to believe unverifiable claims, which is hidden in people's mental process and infeasible to observe. Existing susceptibility studies heavily rely on the self-reported beliefs, making any downstream applications on susceptability hard to scale. To address these limitations, in this work, we propose a computational model to infer users' susceptibility levels given their activities. Since user's susceptibility is a key indicator for their reposting behavior, we utilize the supervision from the observable sharing behavior to infer the underlying susceptibility tendency. The evaluation shows that our model yields estimations that are highly aligned with human judgment on users' susceptibility level comparisons. Building upon such large-scale susceptibility labeling, we further conduct a comprehensive analysis of how different social factors relate to susceptibility. We find that political leanings and psychological factors are associated with susceptibility in varying degrees.
Unlearn What You Want to Forget: Efficient Unlearning for LLMs
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have achieved significant progress from pre-training on and memorizing a wide range of textual data, however, this process might suffer from privacy issues and violations of data protection regulations. As a result, the ability to easily remove data related to individual users from such models while not deteriorating their predictive quality after the removal becomes increasingly important. To address these issues, in this work, we propose an efficient unlearning framework that could efficiently update LLMs without having to retrain the whole model after data removals, by introducing lightweight unlearning layers learned with a selective teacher-student objective into the transformers. In addition, we introduce a fusion mechanism to effectively combine different unlearning layers that learns to forget different sets of data to handle a sequence of forgetting operations. Experiments on classification and generation tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed methods compared to the state-of-the-art baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge