DyVal: Graph-informed Dynamic Evaluation of Large Language Models
Paper and Code
Oct 05, 2023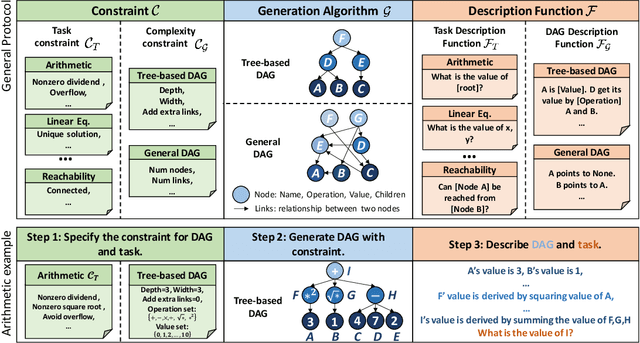
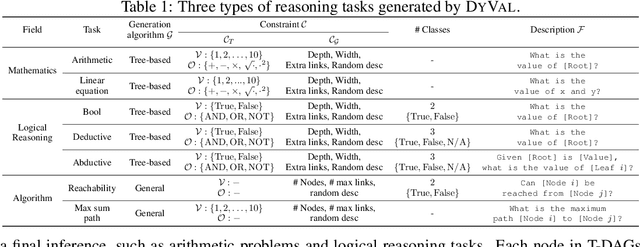
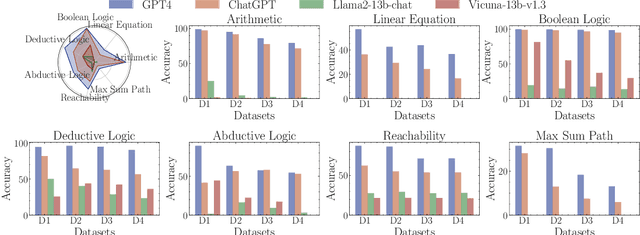
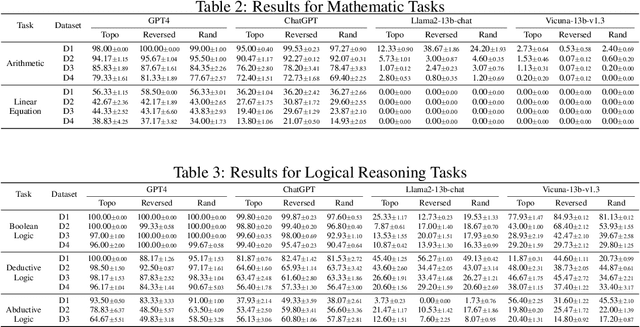
Large language models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable performance in various evaluation benchmarks. However, concerns about their performance are raised on potential data contamination in their considerable volume of training corpus. Moreover, the static nature and fixed complexity of current benchmarks may inadequately gauge the advancing capabilities of LLMs. In this paper, we introduce DyVal, a novel, general, and flexible evaluation protocol for dynamic evaluation of LLMs. Based on our proposed dynamic evaluation framework, we build graph-informed DyVal by leveraging the structural advantage of directed acyclic graphs to dynamically generate evaluation samples with controllable complexities. DyVal generates challenging evaluation sets on reasoning tasks including mathematics, logical reasoning, and algorithm problems. We evaluate various LLMs ranging from Flan-T5-large to ChatGPT and GPT4. Experiments demonstrate that LLMs perform worse in DyVal-generated evaluation samples with different complexities, emphasizing the significance of dynamic evaluation. We also analyze the failure cases and results of different prompting methods. Moreover, DyVal-generated samples are not only evaluation sets, but also helpful data for fine-tuning to improve the performance of LLMs on existing benchmarks. We hope that DyVal can shed light on the future evaluation research of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge