Harris Chan
LMAct: A Benchmark for In-Context Imitation Learning with Long Multimodal Demonstrations
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Today's largest foundation models have increasingly general capabilities, yet when used as agents, they often struggle with simple reasoning and decision-making tasks, even though they possess good factual knowledge of the task and how to solve it. In this paper, we present a benchmark to pressure-test these models' multimodal decision-making capabilities in the very long-context regime (up to one million tokens) and investigate whether they can learn from a large number of expert demonstrations in their context. We evaluate a wide range of state-of-the-art frontier models as policies across a battery of simple interactive decision-making tasks: playing tic-tac-toe, chess, and Atari, navigating grid worlds, solving crosswords, and controlling a simulated cheetah. We measure the performance of Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Gemini 1.5 Flash, Gemini 1.5 Pro, GPT-4o, o1-mini, and o1-preview under increasing amounts of expert demonstrations in the context $\unicode{x2013}$ from no demonstrations up to 512 full episodes, pushing these models' multimodal long-context reasoning capabilities to their limits. Across our tasks, today's frontier models rarely manage to fully reach expert performance, showcasing the difficulty of our benchmark. Presenting more demonstrations often has little effect, but some models steadily improve with more demonstrations on a few tasks. We investigate the effect of encoding observations as text or images and the impact of chain-of-thought prompting. Overall, our results suggest that even today's most capable models often struggle to imitate desired behavior by generalizing purely from in-context demonstrations. To help quantify the impact of other approaches and future innovations aiming to tackle this problem, we open source our benchmark that covers the zero-, few-, and many-shot regimes in a unified evaluation.
Vision-Language Models as a Source of Rewards
Dec 14, 2023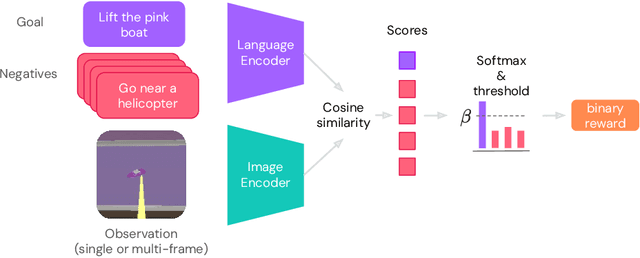
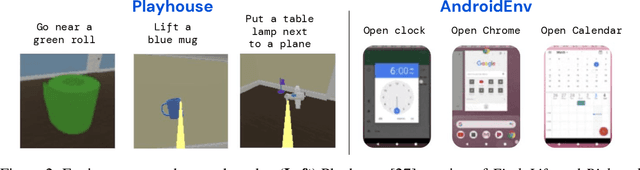
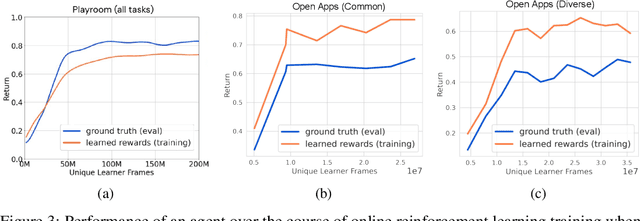
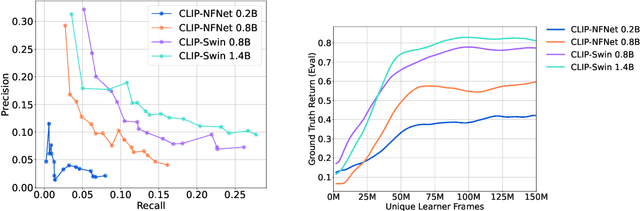
Abstract:Building generalist agents that can accomplish many goals in rich open-ended environments is one of the research frontiers for reinforcement learning. A key limiting factor for building generalist agents with RL has been the need for a large number of reward functions for achieving different goals. We investigate the feasibility of using off-the-shelf vision-language models, or VLMs, as sources of rewards for reinforcement learning agents. We show how rewards for visual achievement of a variety of language goals can be derived from the CLIP family of models, and used to train RL agents that can achieve a variety of language goals. We showcase this approach in two distinct visual domains and present a scaling trend showing how larger VLMs lead to more accurate rewards for visual goal achievement, which in turn produces more capable RL agents.
STEVE-1: A Generative Model for Text-to-Behavior in Minecraft
Jun 05, 2023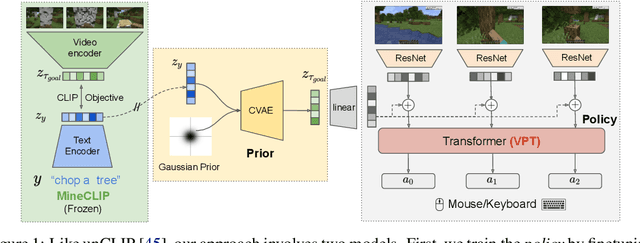

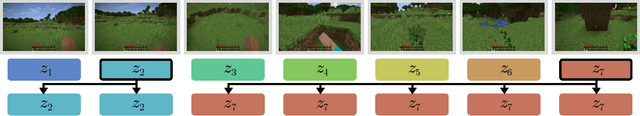

Abstract:Constructing AI models that respond to text instructions is challenging, especially for sequential decision-making tasks. This work introduces an instruction-tuned Video Pretraining (VPT) model for Minecraft called STEVE-1, demonstrating that the unCLIP approach, utilized in DALL-E 2, is also effective for creating instruction-following sequential decision-making agents. STEVE-1 is trained in two steps: adapting the pretrained VPT model to follow commands in MineCLIP's latent space, then training a prior to predict latent codes from text. This allows us to finetune VPT through self-supervised behavioral cloning and hindsight relabeling, bypassing the need for costly human text annotations. By leveraging pretrained models like VPT and MineCLIP and employing best practices from text-conditioned image generation, STEVE-1 costs just $60 to train and can follow a wide range of short-horizon open-ended text and visual instructions in Minecraft. STEVE-1 sets a new bar for open-ended instruction following in Minecraft with low-level controls (mouse and keyboard) and raw pixel inputs, far outperforming previous baselines. We provide experimental evidence highlighting key factors for downstream performance, including pretraining, classifier-free guidance, and data scaling. All resources, including our model weights, training scripts, and evaluation tools are made available for further research.
Robotic Skill Acquisition via Instruction Augmentation with Vision-Language Models
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:In recent years, much progress has been made in learning robotic manipulation policies that follow natural language instructions. Such methods typically learn from corpora of robot-language data that was either collected with specific tasks in mind or expensively re-labelled by humans with rich language descriptions in hindsight. Recently, large-scale pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) like CLIP or ViLD have been applied to robotics for learning representations and scene descriptors. Can these pretrained models serve as automatic labelers for robot data, effectively importing Internet-scale knowledge into existing datasets to make them useful even for tasks that are not reflected in their ground truth annotations? To accomplish this, we introduce Data-driven Instruction Augmentation for Language-conditioned control (DIAL): we utilize semi-supervised language labels leveraging the semantic understanding of CLIP to propagate knowledge onto large datasets of unlabelled demonstration data and then train language-conditioned policies on the augmented datasets. This method enables cheaper acquisition of useful language descriptions compared to expensive human labels, allowing for more efficient label coverage of large-scale datasets. We apply DIAL to a challenging real-world robotic manipulation domain where 96.5% of the 80,000 demonstrations do not contain crowd-sourced language annotations. DIAL enables imitation learning policies to acquire new capabilities and generalize to 60 novel instructions unseen in the original dataset.
Large Language Models Are Human-Level Prompt Engineers
Nov 03, 2022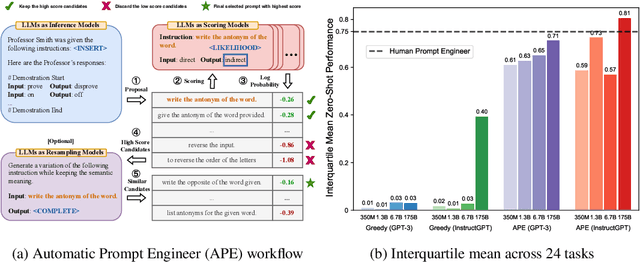
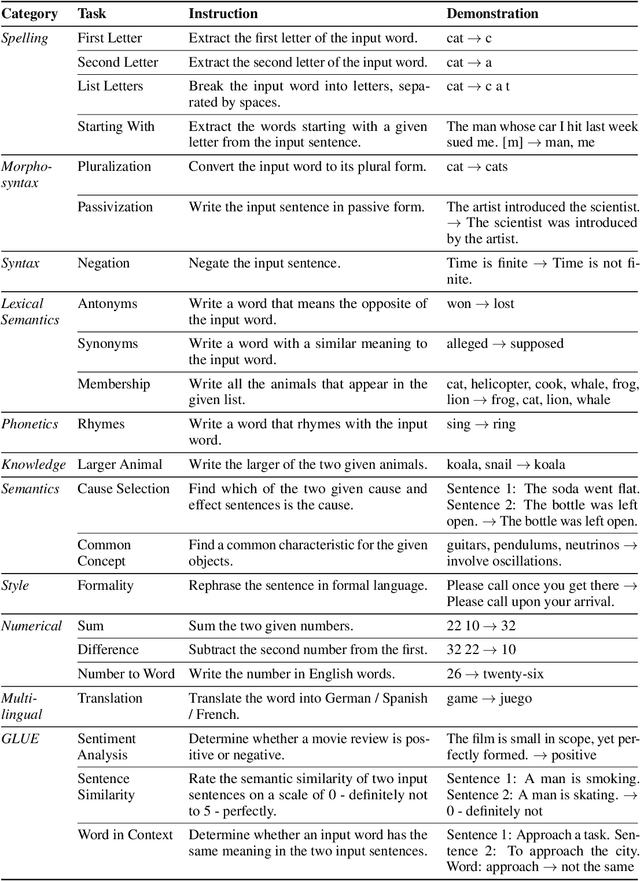
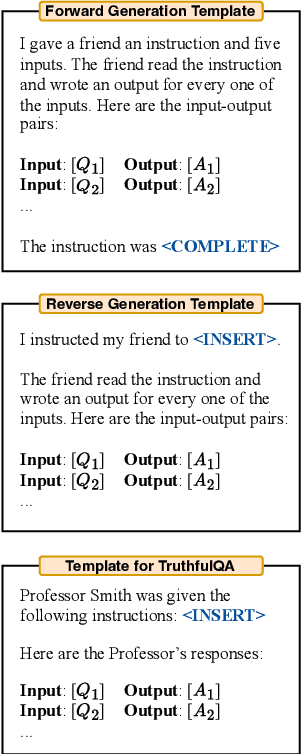
Abstract:By conditioning on natural language instructions, large language models (LLMs) have displayed impressive capabilities as general-purpose computers. However, task performance depends significantly on the quality of the prompt used to steer the model, and most effective prompts have been handcrafted by humans. Inspired by classical program synthesis and the human approach to prompt engineering, we propose Automatic Prompt Engineer (APE) for automatic instruction generation and selection. In our method, we treat the instruction as the "program," optimized by searching over a pool of instruction candidates proposed by an LLM in order to maximize a chosen score function. To evaluate the quality of the selected instruction, we evaluate the zero-shot performance of another LLM following the selected instruction. Experiments on 24 NLP tasks show that our automatically generated instructions outperform the prior LLM baseline by a large margin and achieve better or comparable performance to the instructions generated by human annotators on 19/24 tasks. We conduct extensive qualitative and quantitative analyses to explore the performance of APE. We show that APE-engineered prompts can be applied to steer models toward truthfulness and/or informativeness, as well as to improve few-shot learning performance by simply prepending them to standard in-context learning prompts. Please check out our webpage at https://sites.google.com/view/automatic-prompt-engineer.
Inner Monologue: Embodied Reasoning through Planning with Language Models
Jul 12, 2022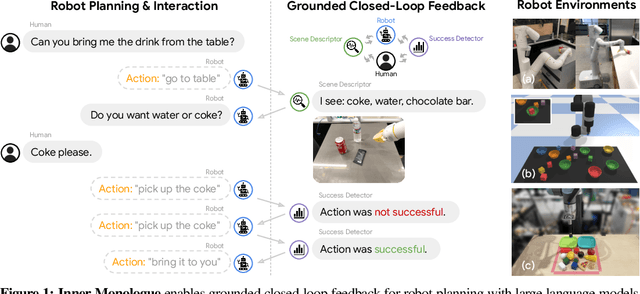
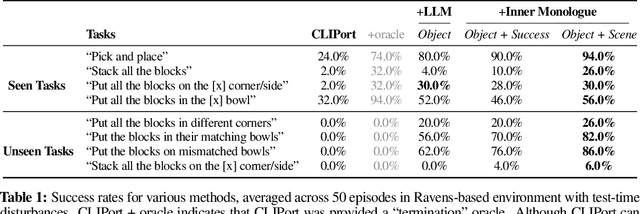
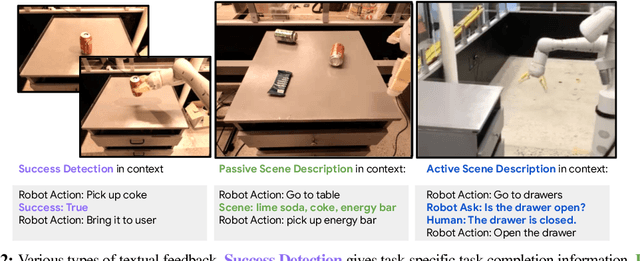
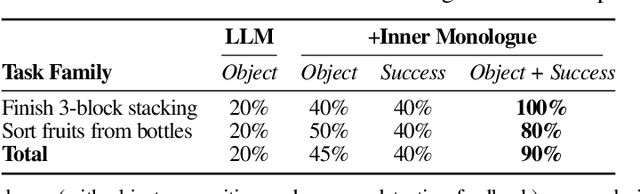
Abstract:Recent works have shown how the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) can be applied to domains beyond natural language processing, such as planning and interaction for robots. These embodied problems require an agent to understand many semantic aspects of the world: the repertoire of skills available, how these skills influence the world, and how changes to the world map back to the language. LLMs planning in embodied environments need to consider not just what skills to do, but also how and when to do them - answers that change over time in response to the agent's own choices. In this work, we investigate to what extent LLMs used in such embodied contexts can reason over sources of feedback provided through natural language, without any additional training. We propose that by leveraging environment feedback, LLMs are able to form an inner monologue that allows them to more richly process and plan in robotic control scenarios. We investigate a variety of sources of feedback, such as success detection, scene description, and human interaction. We find that closed-loop language feedback significantly improves high-level instruction completion on three domains, including simulated and real table top rearrangement tasks and long-horizon mobile manipulation tasks in a kitchen environment in the real world.
Learning Domain Invariant Representations in Goal-conditioned Block MDPs
Oct 28, 2021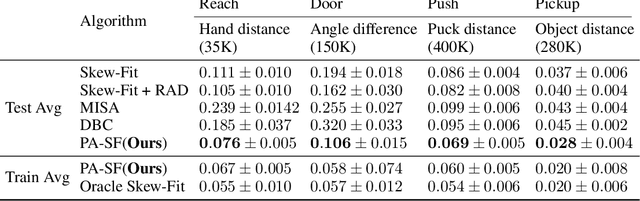
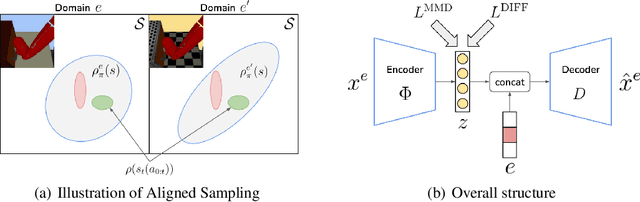

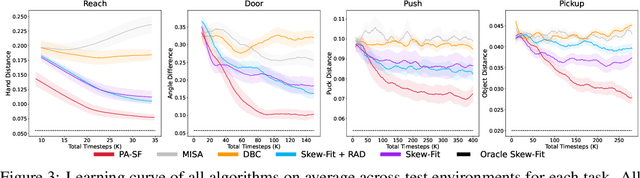
Abstract:Deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) is successful in solving many complex Markov Decision Processes (MDPs) problems. However, agents often face unanticipated environmental changes after deployment in the real world. These changes are often spurious and unrelated to the underlying problem, such as background shifts for visual input agents. Unfortunately, deep RL policies are usually sensitive to these changes and fail to act robustly against them. This resembles the problem of domain generalization in supervised learning. In this work, we study this problem for goal-conditioned RL agents. We propose a theoretical framework in the Block MDP setting that characterizes the generalizability of goal-conditioned policies to new environments. Under this framework, we develop a practical method PA-SkewFit that enhances domain generalization. The empirical evaluation shows that our goal-conditioned RL agent can perform well in various unseen test environments, improving by 50% over baselines.
* 33 pages
Multichannel Generative Language Model: Learning All Possible Factorizations Within and Across Channels
Oct 09, 2020
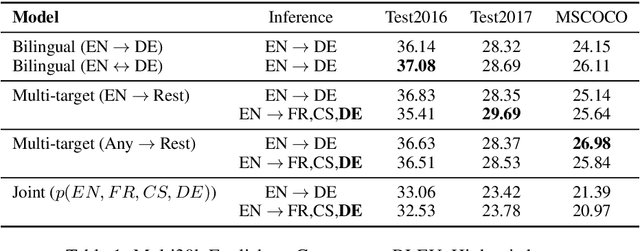
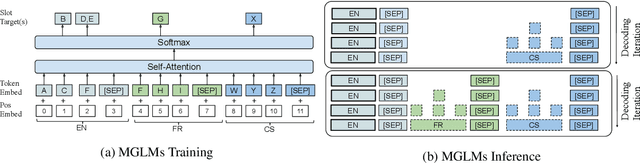
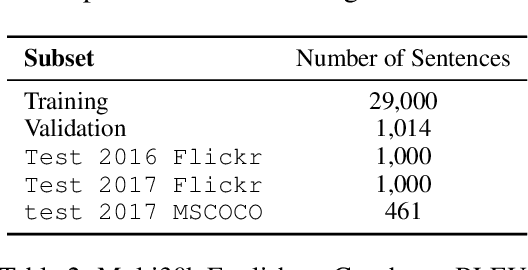
Abstract:A channel corresponds to a viewpoint or transformation of an underlying meaning. A pair of parallel sentences in English and French express the same underlying meaning, but through two separate channels corresponding to their languages. In this work, we present the Multichannel Generative Language Model (MGLM). MGLM is a generative joint distribution model over channels. MGLM marginalizes over all possible factorizations within and across all channels. MGLM endows flexible inference, including unconditional generation, conditional generation (where 1 channel is observed and other channels are generated), and partially observed generation (where incomplete observations are spread across all the channels). We experiment with the Multi30K dataset containing English, French, Czech, and German. We demonstrate experiments with unconditional, conditional, and partially conditional generation. We provide qualitative samples sampled unconditionally from the generative joint distribution. We also quantitatively analyze the quality-diversity trade-offs and find MGLM outperforms traditional bilingual discriminative models.
Maximum Entropy Gain Exploration for Long Horizon Multi-goal Reinforcement Learning
Jul 06, 2020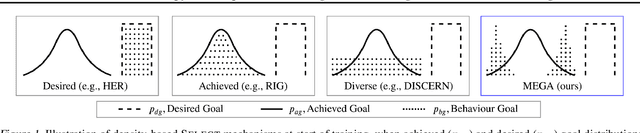
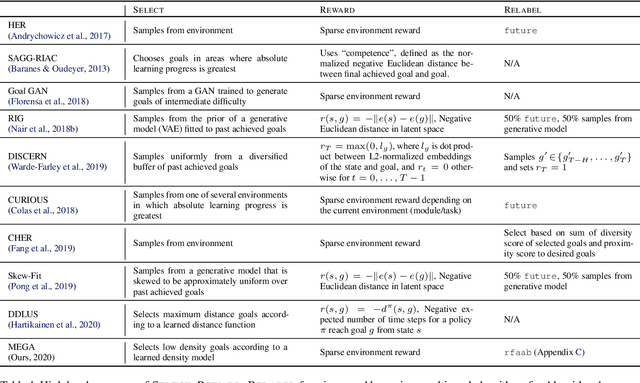
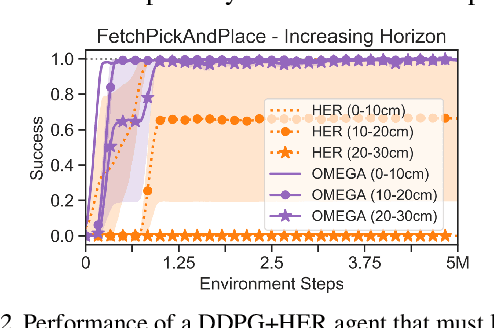
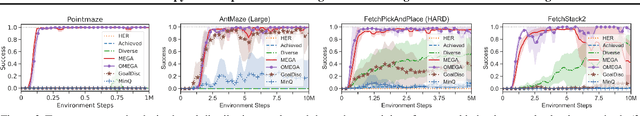
Abstract:What goals should a multi-goal reinforcement learning agent pursue during training in long-horizon tasks? When the desired (test time) goal distribution is too distant to offer a useful learning signal, we argue that the agent should not pursue unobtainable goals. Instead, it should set its own intrinsic goals that maximize the entropy of the historical achieved goal distribution. We propose to optimize this objective by having the agent pursue past achieved goals in sparsely explored areas of the goal space, which focuses exploration on the frontier of the achievable goal set. We show that our strategy achieves an order of magnitude better sample efficiency than the prior state of the art on long-horizon multi-goal tasks including maze navigation and block stacking.
An Inductive Bias for Distances: Neural Nets that Respect the Triangle Inequality
Feb 14, 2020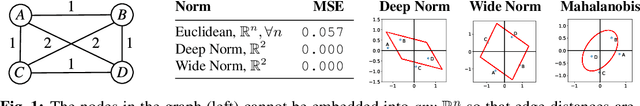
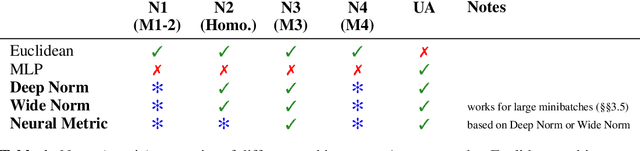
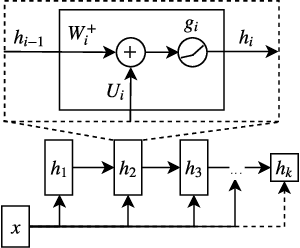
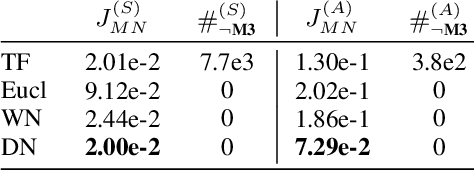
Abstract:Distances are pervasive in machine learning. They serve as similarity measures, loss functions, and learning targets; it is said that a good distance measure solves a task. When defining distances, the triangle inequality has proven to be a useful constraint, both theoretically--to prove convergence and optimality guarantees--and empirically--as an inductive bias. Deep metric learning architectures that respect the triangle inequality rely, almost exclusively, on Euclidean distance in the latent space. Though effective, this fails to model two broad classes of subadditive distances, common in graphs and reinforcement learning: asymmetric metrics, and metrics that cannot be embedded into Euclidean space. To address these problems, we introduce novel architectures that are guaranteed to satisfy the triangle inequality. We prove our architectures universally approximate norm-induced metrics on $\mathbb{R}^n$, and present a similar result for modified Input Convex Neural Networks. We show that our architectures outperform existing metric approaches when modeling graph distances and have a better inductive bias than non-metric approaches when training data is limited in the multi-goal reinforcement learning setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge