Bonnie Li
LMAct: A Benchmark for In-Context Imitation Learning with Long Multimodal Demonstrations
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Today's largest foundation models have increasingly general capabilities, yet when used as agents, they often struggle with simple reasoning and decision-making tasks, even though they possess good factual knowledge of the task and how to solve it. In this paper, we present a benchmark to pressure-test these models' multimodal decision-making capabilities in the very long-context regime (up to one million tokens) and investigate whether they can learn from a large number of expert demonstrations in their context. We evaluate a wide range of state-of-the-art frontier models as policies across a battery of simple interactive decision-making tasks: playing tic-tac-toe, chess, and Atari, navigating grid worlds, solving crosswords, and controlling a simulated cheetah. We measure the performance of Claude 3.5 Sonnet, Gemini 1.5 Flash, Gemini 1.5 Pro, GPT-4o, o1-mini, and o1-preview under increasing amounts of expert demonstrations in the context $\unicode{x2013}$ from no demonstrations up to 512 full episodes, pushing these models' multimodal long-context reasoning capabilities to their limits. Across our tasks, today's frontier models rarely manage to fully reach expert performance, showcasing the difficulty of our benchmark. Presenting more demonstrations often has little effect, but some models steadily improve with more demonstrations on a few tasks. We investigate the effect of encoding observations as text or images and the impact of chain-of-thought prompting. Overall, our results suggest that even today's most capable models often struggle to imitate desired behavior by generalizing purely from in-context demonstrations. To help quantify the impact of other approaches and future innovations aiming to tackle this problem, we open source our benchmark that covers the zero-, few-, and many-shot regimes in a unified evaluation.
Domain Adversarial Reinforcement Learning
Feb 14, 2021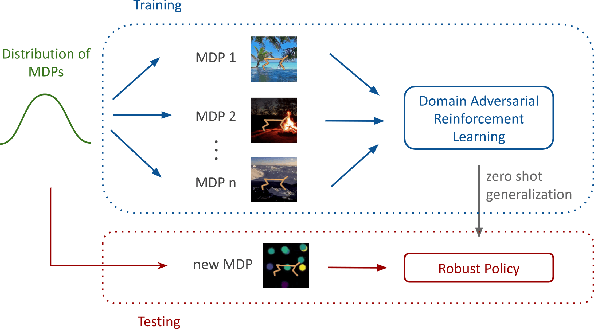

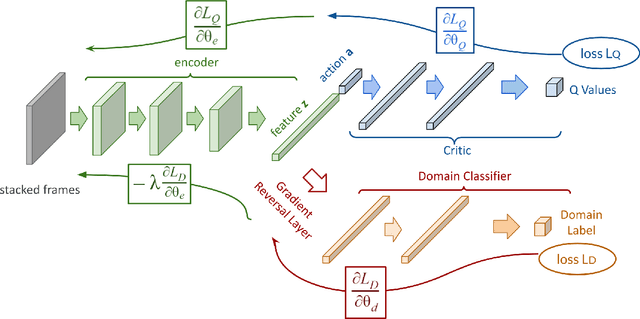
Abstract:We consider the problem of generalization in reinforcement learning where visual aspects of the observations might differ, e.g. when there are different backgrounds or change in contrast, brightness, etc. We assume that our agent has access to only a few of the MDPs from the MDP distribution during training. The performance of the agent is then reported on new unknown test domains drawn from the distribution (e.g. unseen backgrounds). For this "zero-shot RL" task, we enforce invariance of the learned representations to visual domains via a domain adversarial optimization process. We empirically show that this approach allows achieving a significant generalization improvement to new unseen domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge