Haojie Pan
GUIDE: A Guideline-Guided Dataset for Instructional Video Comprehension
Jun 26, 2024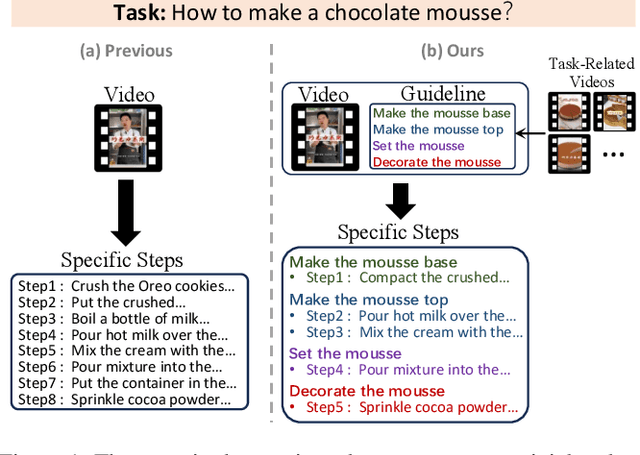
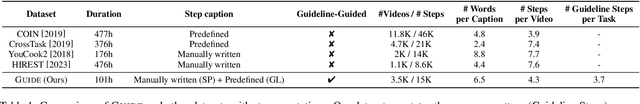
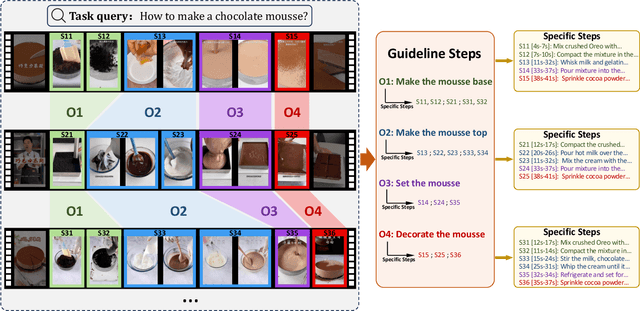

Abstract:There are substantial instructional videos on the Internet, which provide us tutorials for completing various tasks. Existing instructional video datasets only focus on specific steps at the video level, lacking experiential guidelines at the task level, which can lead to beginners struggling to learn new tasks due to the lack of relevant experience. Moreover, the specific steps without guidelines are trivial and unsystematic, making it difficult to provide a clear tutorial. To address these problems, we present the GUIDE (Guideline-Guided) dataset, which contains 3.5K videos of 560 instructional tasks in 8 domains related to our daily life. Specifically, we annotate each instructional task with a guideline, representing a common pattern shared by all task-related videos. On this basis, we annotate systematic specific steps, including their associated guideline steps, specific step descriptions and timestamps. Our proposed benchmark consists of three sub-tasks to evaluate comprehension ability of models: (1) Step Captioning: models have to generate captions for specific steps from videos. (2) Guideline Summarization: models have to mine the common pattern in task-related videos and summarize a guideline from them. (3) Guideline-Guided Captioning: models have to generate captions for specific steps under the guide of guideline. We evaluate plenty of foundation models with GUIDE and perform in-depth analysis. Given the diversity and practicality of GUIDE, we believe that it can be used as a better benchmark for instructional video comprehension.
KwaiAgents: Generalized Information-seeking Agent System with Large Language Models
Dec 08, 2023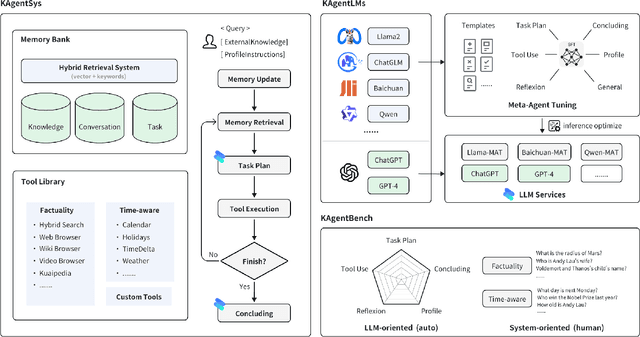
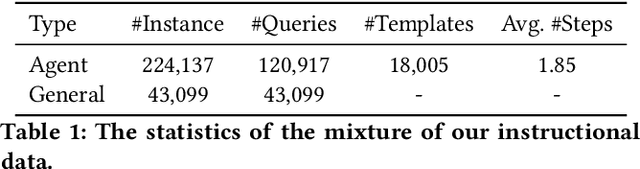
Abstract:Driven by curiosity, humans have continually sought to explore and understand the world around them, leading to the invention of various tools to satiate this inquisitiveness. Despite not having the capacity to process and memorize vast amounts of information in their brains, humans excel in critical thinking, planning, reflection, and harnessing available tools to interact with and interpret the world, enabling them to find answers efficiently. The recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) suggest that machines might also possess the aforementioned human-like capabilities, allowing them to exhibit powerful abilities even with a constrained parameter count. In this paper, we introduce KwaiAgents, a generalized information-seeking agent system based on LLMs. Within KwaiAgents, we propose an agent system that employs LLMs as its cognitive core, which is capable of understanding a user's query, behavior guidelines, and referencing external documents. The agent can also update and retrieve information from its internal memory, plan and execute actions using a time-aware search-browse toolkit, and ultimately provide a comprehensive response. We further investigate the system's performance when powered by LLMs less advanced than GPT-4, and introduce the Meta-Agent Tuning (MAT) framework, designed to ensure even an open-sourced 7B or 13B model performs well among many agent systems. We exploit both benchmark and human evaluations to systematically validate these capabilities. Extensive experiments show the superiority of our agent system compared to other autonomous agents and highlight the enhanced generalized agent-abilities of our fine-tuned LLMs.
A Unified Model for Video Understanding and Knowledge Embedding with Heterogeneous Knowledge Graph Dataset
Nov 19, 2022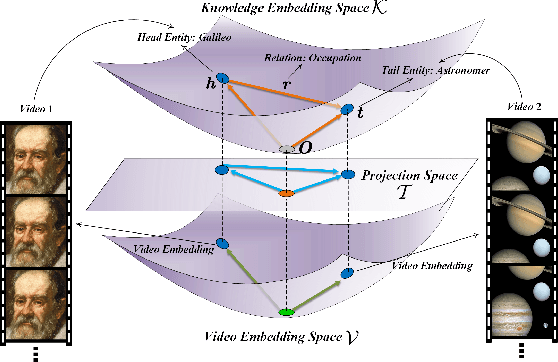
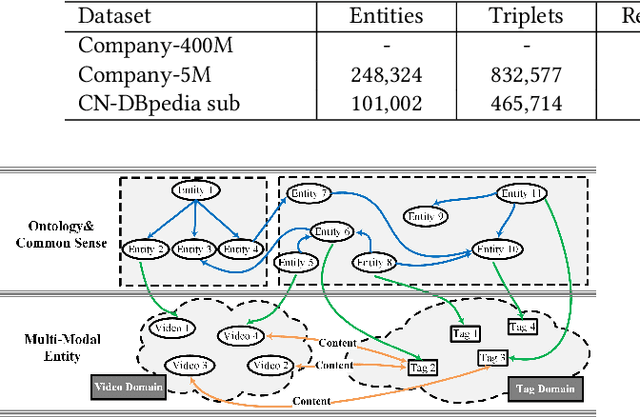
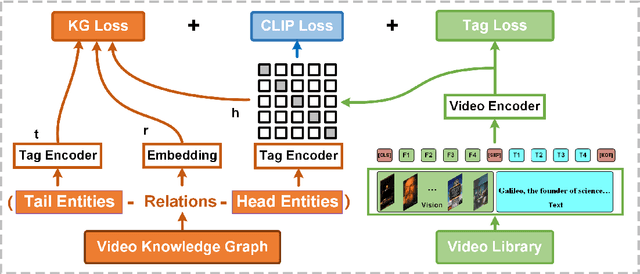
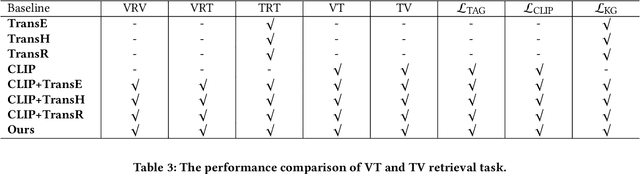
Abstract:Video understanding is an important task in short video business platforms and it has a wide application in video recommendation and classification. Most of the existing video understanding works only focus on the information that appeared within the video content, including the video frames, audio and text. However, introducing common sense knowledge from the external Knowledge Graph (KG) dataset is essential for video understanding when referring to the content which is less relevant to the video. Owing to the lack of video knowledge graph dataset, the work which integrates video understanding and KG is rare. In this paper, we propose a heterogeneous dataset that contains the multi-modal video entity and fruitful common sense relations. This dataset also provides multiple novel video inference tasks like the Video-Relation-Tag (VRT) and Video-Relation-Video (VRV) tasks. Furthermore, based on this dataset, we propose an end-to-end model that jointly optimizes the video understanding objective with knowledge graph embedding, which can not only better inject factual knowledge into video understanding but also generate effective multi-modal entity embedding for KG. Comprehensive experiments indicate that combining video understanding embedding with factual knowledge benefits the content-based video retrieval performance. Moreover, it also helps the model generate better knowledge graph embedding which outperforms traditional KGE-based methods on VRT and VRV tasks with at least 42.36% and 17.73% improvement in HITS@10.
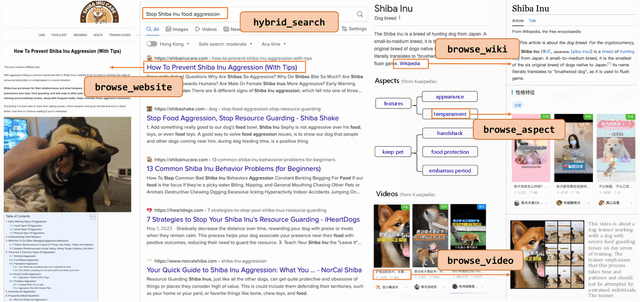
Kuaipedia: a Large-scale Multi-modal Short-video Encyclopedia
Nov 03, 2022Abstract:Online encyclopedias, such as Wikipedia, have been well-developed and researched in the last two decades. One can find any attributes or other information of a wiki item on a wiki page edited by a community of volunteers. However, the traditional text, images and tables can hardly express some aspects of an wiki item. For example, when we talk about ``Shiba Inu'', one may care more about ``How to feed it'' or ``How to train it not to protect its food''. Currently, short-video platforms have become a hallmark in the online world. Whether you're on TikTok, Instagram, Kuaishou, or YouTube Shorts, short-video apps have changed how we consume and create content today. Except for producing short videos for entertainment, we can find more and more authors sharing insightful knowledge widely across all walks of life. These short videos, which we call knowledge videos, can easily express any aspects (e.g. hair or how-to-feed) consumers want to know about an item (e.g. Shiba Inu), and they can be systematically analyzed and organized like an online encyclopedia. In this paper, we propose Kuaipedia, a large-scale multi-modal encyclopedia consisting of items, aspects, and short videos lined to them, which was extracted from billions of videos of Kuaishou (Kwai), a well-known short-video platform in China. We first collected items from multiple sources and mined user-centered aspects from millions of users' queries to build an item-aspect tree. Then we propose a new task called ``multi-modal item-aspect linking'' as an expansion of ``entity linking'' to link short videos into item-aspect pairs and build the whole short-video encyclopedia. Intrinsic evaluations show that our encyclopedia is of large scale and highly accurate. We also conduct sufficient extrinsic experiments to show how Kuaipedia can help fundamental applications such as entity typing and entity linking.
ASER: Towards Large-scale Commonsense Knowledge Acquisition via Higher-order Selectional Preference over Eventualities
Apr 05, 2021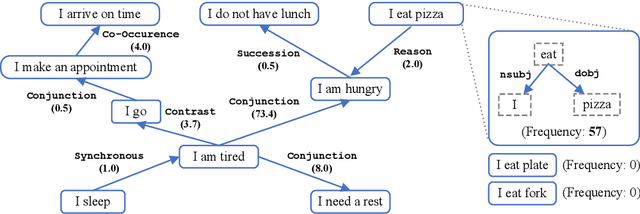
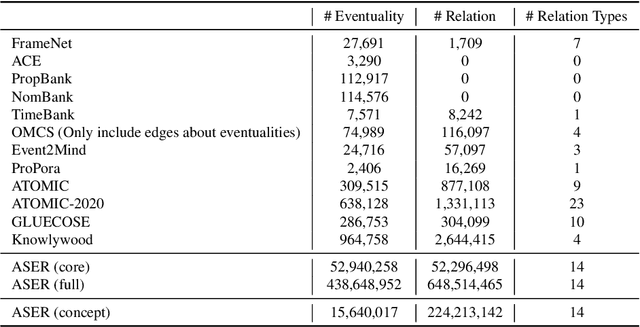
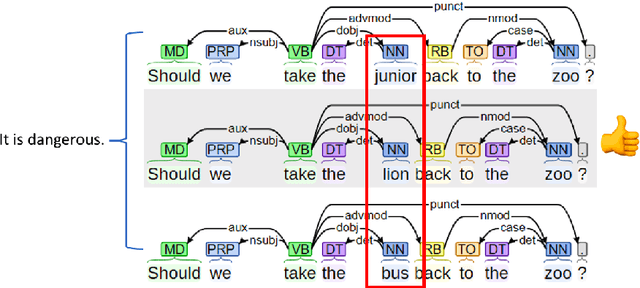
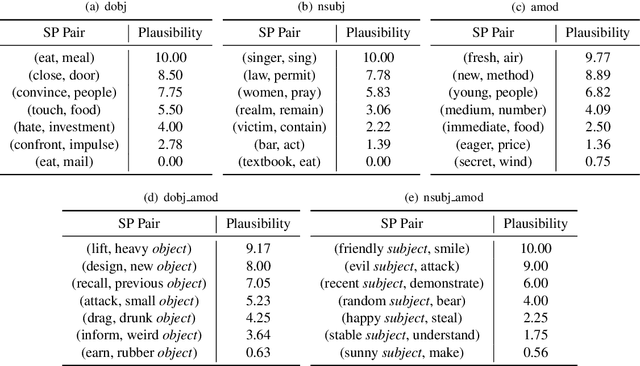
Abstract:Commonsense knowledge acquisition and reasoning have long been a core artificial intelligence problem. However, in the past, there has been a lack of scalable methods to collect commonsense knowledge. In this paper, we propose to develop principles for collecting commonsense knowledge based on selectional preference. We generalize the definition of selectional preference from one-hop linguistic syntactic relations to higher-order relations over linguistic graphs. Unlike previous commonsense knowledge definition (e.g., ConceptNet), the selectional preference (SP) knowledge only relies on statistical distribution over linguistic graphs, which can be efficiently and accurately acquired from the unlabeled corpus with modern tools. Following this principle, we develop a large-scale eventuality (a linguistic term covering activity, state, and event)-based knowledge graph ASER, where each eventuality is represented as a dependency graph, and the relation between them is a discourse relation defined in shallow discourse parsing. The higher-order selectional preference over collected linguistic graphs reflects various kinds of commonsense knowledge. Moreover, motivated by the observation that humans understand events by abstracting the observed events to a higher level and can thus transferring their knowledge to new events, we propose a conceptualization module to significantly boost the coverage of ASER. In total, ASER contains 438 million eventualities and 648 million edges between eventualities. After conceptualization with Probase, a selectional preference based concept-instance relational knowledge base, our concept graph contains 15 million conceptualized eventualities and 224 million edges between them. Detailed analysis is provided to demonstrate its quality. All the collected data, APIs, and tools are available at https://github.com/HKUST-KnowComp/ASER.
Meta-KD: A Meta Knowledge Distillation Framework for Language Model Compression across Domains
Dec 02, 2020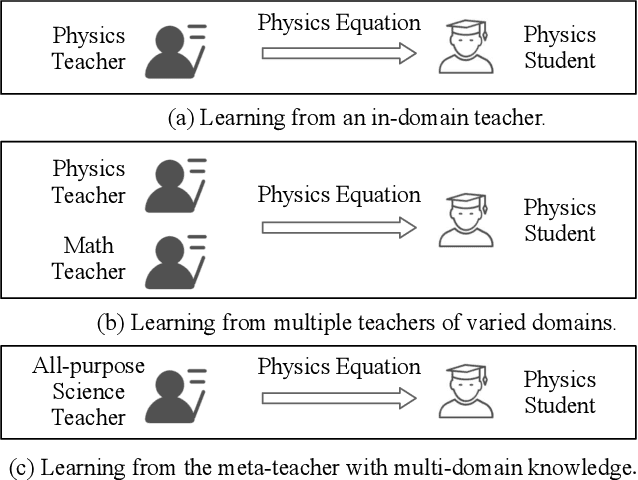
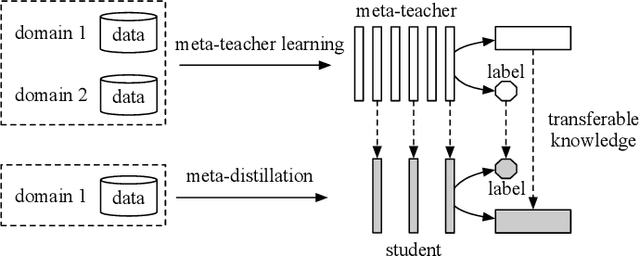
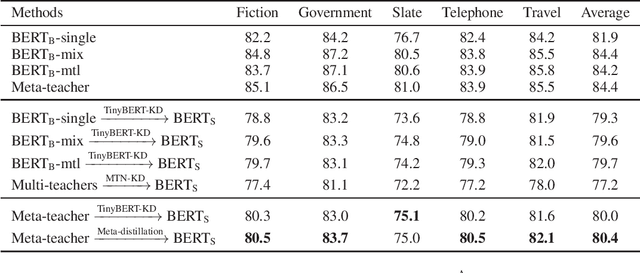
Abstract:Pre-trained language models have been applied to various NLP tasks with considerable performance gains. However, the large model sizes, together with the long inference time, limit the deployment of such models in real-time applications. Typical approaches consider knowledge distillation to distill large teacher models into small student models. However, most of these studies focus on single-domain only, which ignores the transferable knowledge from other domains. We argue that training a teacher with transferable knowledge digested across domains can achieve better generalization capability to help knowledge distillation. To this end, we propose a Meta-Knowledge Distillation (Meta-KD) framework to build a meta-teacher model that captures transferable knowledge across domains inspired by meta-learning and use it to pass knowledge to students. Specifically, we first leverage a cross-domain learning process to train the meta-teacher on multiple domains, and then propose a meta-distillation algorithm to learn single-domain student models with guidance from the meta-teacher. Experiments on two public multi-domain NLP tasks show the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed Meta-KD framework. We also demonstrate the capability of Meta-KD in both few-shot and zero-shot learning settings.
Learning to Expand: Reinforced Pseudo-relevance Feedback Selection for Information-seeking Conversations
Nov 25, 2020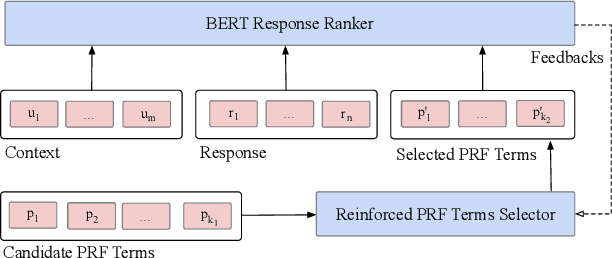
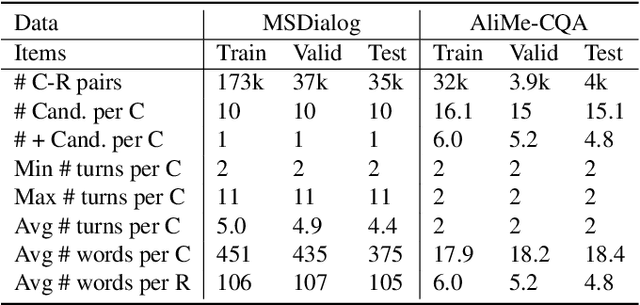
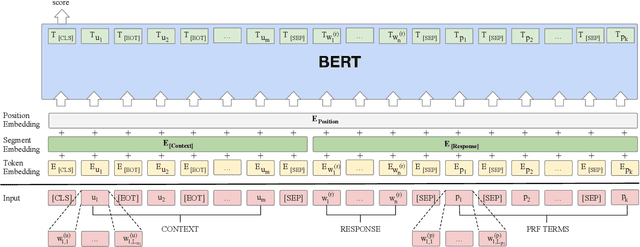
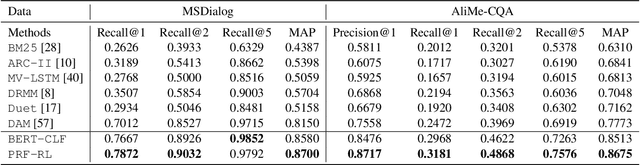
Abstract:Intelligent personal assistant systems for information-seeking conversations are increasingly popular in real-world applications, especially for e-commerce companies. With the development of research in such conversation systems, the pseudo-relevance feedback (PRF) has demonstrated its effectiveness in incorporating relevance signals from external documents. However, the existing studies are either based on heuristic rules or require heavy manual labeling. In this work, we treat the PRF selection as a learning task and proposed a reinforced learning based method that can be trained in an end-to-end manner without any human annotations. More specifically, we proposed a reinforced selector to extract useful PRF terms to enhance response candidates and a BERT based response ranker to rank the PRF-enhanced responses. The performance of the ranker serves as rewards to guide the selector to extract useful PRF terms, and thus boost the task performance. Extensive experiments on both standard benchmark and commercial datasets show the superiority of our reinforced PRF term selector compared with other potential soft or hard selection methods. Both qualitative case studies and quantitative analysis show that our model can not only select meaningful PRF terms to expand response candidates but also achieve the best results compared with all the baseline methods on a variety of evaluation metrics. We have also deployed our method on online production in an e-commerce company, which shows a significant improvement over the existing online ranking system.
Neural Subgraph Isomorphism Counting
Dec 25, 2019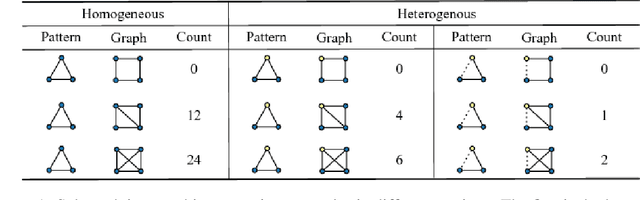

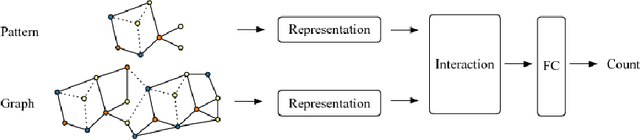
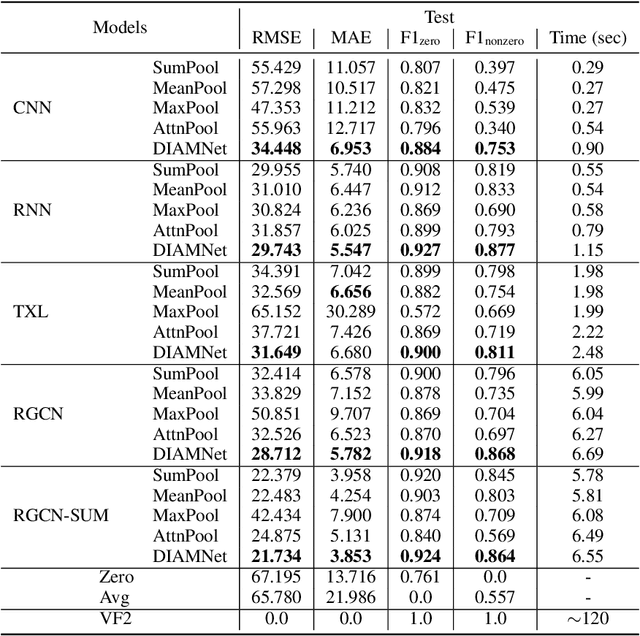
Abstract:In this paper, we study a new graph learning problem: learning to count subgraph isomorphisms. Although the learning based approach is inexact, we are able to generalize to count large patterns and data graphs in polynomial time compared to the exponential time of the original NP-complete problem. Different from other traditional graph learning problems such as node classification and link prediction, subgraph isomorphism counting requires more global inference to oversee the whole graph. To tackle this problem, we propose a dynamic intermedium attention memory network (DIAMNet) which augments different representation learning architectures and iteratively attends pattern and target data graphs to memorize different subgraph isomorphisms for the global counting. We develop both small graphs (<= 1,024 subgraph isomorphisms in each) and large graphs (<= 4,096 subgraph isomorphisms in each) sets to evaluate different models. Experimental results show that learning based subgraph isomorphism counting can help reduce the time complexity with acceptable accuracy. Our DIAMNet can further improve existing representation learning models for this more global problem.
ASER: A Large-scale Eventuality Knowledge Graph
May 01, 2019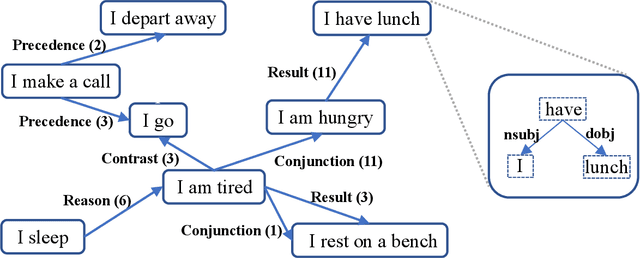
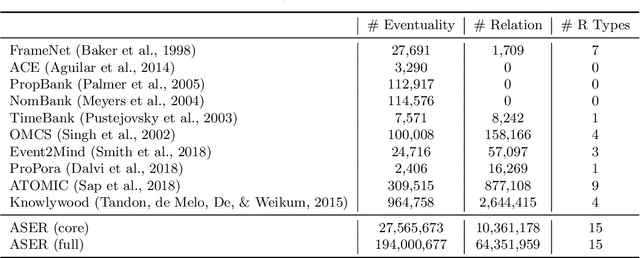
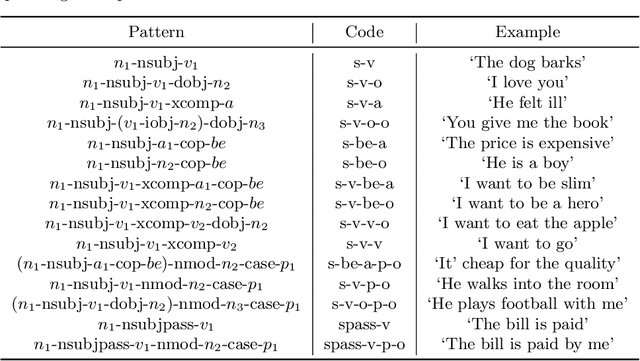
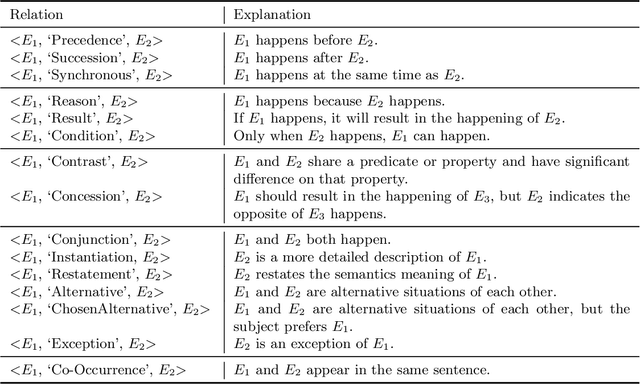
Abstract:Understanding human's language requires complex world knowledge. However, existing large-scale knowledge graphs mainly focus on knowledge about entities while ignoring knowledge about activities, states, or events, which are used to describe how entities or things act in the real world. To fill this gap, we develop ASER (activities, states, events, and their relations), a large-scale eventuality knowledge graph extracted from more than 11-billion-token unstructured textual data. ASER contains 15 relation types belonging to five categories, 194-million unique eventualities, and 64-million unique edges among them. Both human and extrinsic evaluations demonstrate the quality and effectiveness of ASER.
Dial2Desc: End-to-end Dialogue Description Generation
Nov 01, 2018


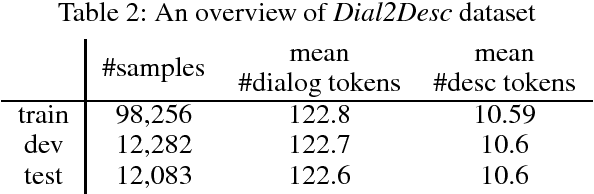
Abstract:We first propose a new task named Dialogue Description (Dial2Desc). Unlike other existing dialogue summarization tasks such as meeting summarization, we do not maintain the natural flow of a conversation but describe an object or an action of what people are talking about. The Dial2Desc system takes a dialogue text as input, then outputs a concise description of the object or the action involved in this conversation. After reading this short description, one can quickly extract the main topic of a conversation and build a clear picture in his mind, without reading or listening to the whole conversation. Based on the existing dialogue dataset, we build a new dataset, which has more than one hundred thousand dialogue-description pairs. As a step forward, we demonstrate that one can get more accurate and descriptive results using a new neural attentive model that exploits the interaction between utterances from different speakers, compared with other baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge