Haiguang Liu
UniGenX: Unified Generation of Sequence and Structure with Autoregressive Diffusion
Mar 09, 2025Abstract:Unified generation of sequence and structure for scientific data (e.g., materials, molecules, proteins) is a critical task. Existing approaches primarily rely on either autoregressive sequence models or diffusion models, each offering distinct advantages and facing notable limitations. Autoregressive models, such as GPT, Llama, and Phi-4, have demonstrated remarkable success in natural language generation and have been extended to multimodal tasks (e.g., image, video, and audio) using advanced encoders like VQ-VAE to represent complex modalities as discrete sequences. However, their direct application to scientific domains is challenging due to the high precision requirements and the diverse nature of scientific data. On the other hand, diffusion models excel at generating high-dimensional scientific data, such as protein, molecule, and material structures, with remarkable accuracy. Yet, their inability to effectively model sequences limits their potential as general-purpose multimodal foundation models. To address these challenges, we propose UniGenX, a unified framework that combines autoregressive next-token prediction with conditional diffusion models. This integration leverages the strengths of autoregressive models to ease the training of conditional diffusion models, while diffusion-based generative heads enhance the precision of autoregressive predictions. We validate the effectiveness of UniGenX on material and small molecule generation tasks, achieving a significant leap in state-of-the-art performance for material crystal structure prediction and establishing new state-of-the-art results for small molecule structure prediction, de novo design, and conditional generation. Notably, UniGenX demonstrates significant improvements, especially in handling long sequences for complex structures, showcasing its efficacy as a versatile tool for scientific data generation.
NatureLM: Deciphering the Language of Nature for Scientific Discovery
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models have revolutionized natural language processing and artificial intelligence, significantly enhancing how machines comprehend and generate human languages. Inspired by the success of these foundation models, researchers have developed foundation models for individual scientific domains, including small molecules, materials, proteins, DNA, and RNA. However, these models are typically trained in isolation, lacking the ability to integrate across different scientific domains. Recognizing that entities within these domains can all be represented as sequences, which together form the "language of nature", we introduce Nature Language Model (briefly, NatureLM), a sequence-based science foundation model designed for scientific discovery. Pre-trained with data from multiple scientific domains, NatureLM offers a unified, versatile model that enables various applications including: (i) generating and optimizing small molecules, proteins, RNA, and materials using text instructions; (ii) cross-domain generation/design, such as protein-to-molecule and protein-to-RNA generation; and (iii) achieving state-of-the-art performance in tasks like SMILES-to-IUPAC translation and retrosynthesis on USPTO-50k. NatureLM offers a promising generalist approach for various scientific tasks, including drug discovery (hit generation/optimization, ADMET optimization, synthesis), novel material design, and the development of therapeutic proteins or nucleotides. We have developed NatureLM models in different sizes (1 billion, 8 billion, and 46.7 billion parameters) and observed a clear improvement in performance as the model size increases.
Towards Predicting Equilibrium Distributions for Molecular Systems with Deep Learning
Jun 08, 2023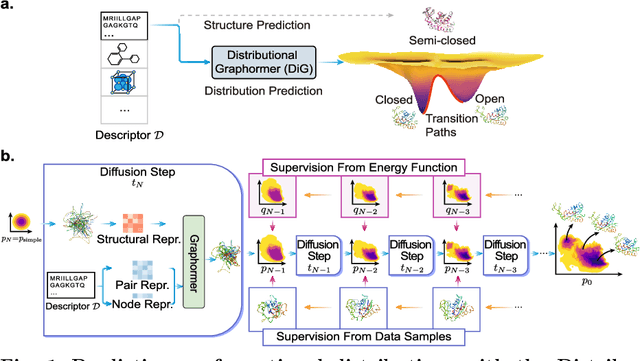
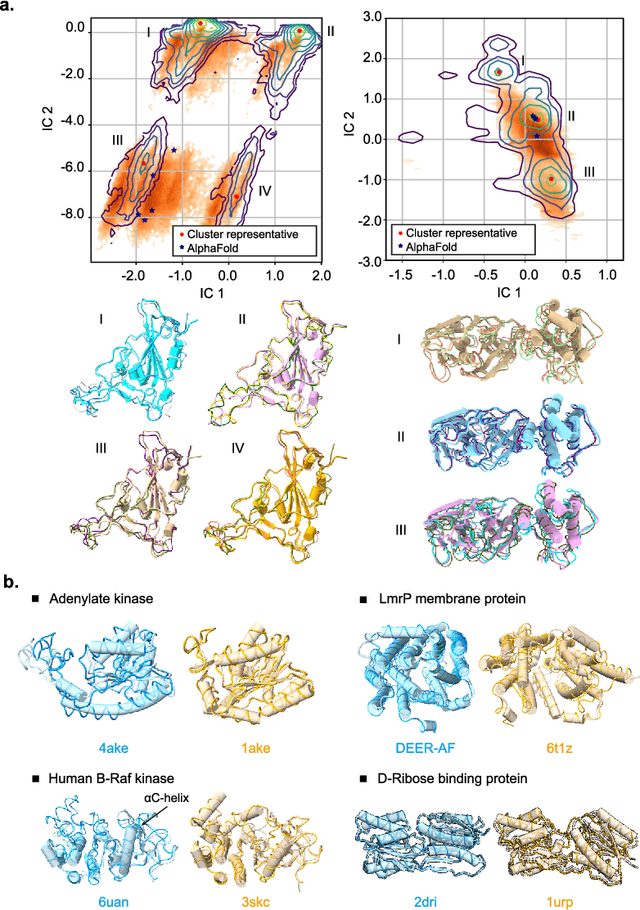
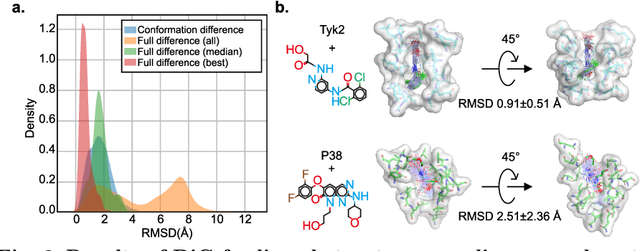
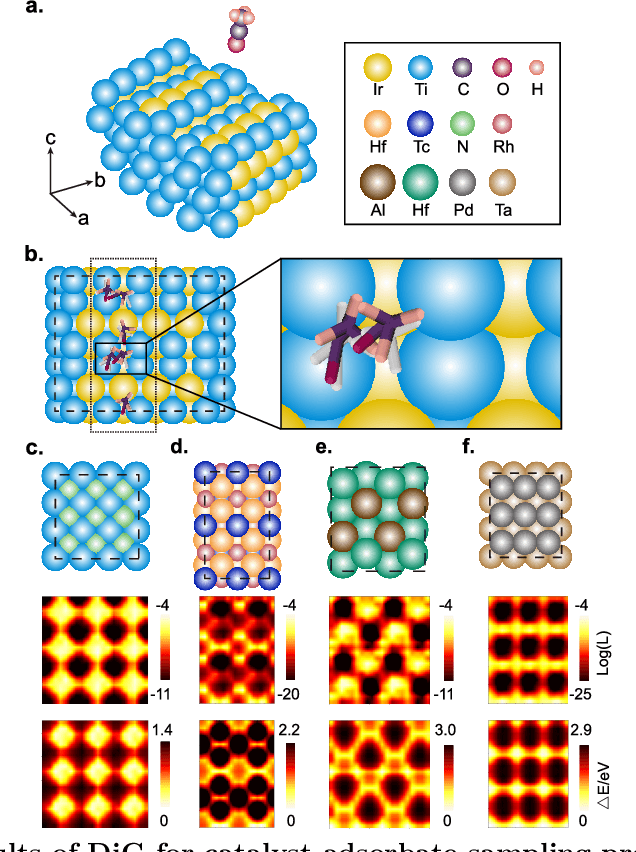
Abstract:Advances in deep learning have greatly improved structure prediction of molecules. However, many macroscopic observations that are important for real-world applications are not functions of a single molecular structure, but rather determined from the equilibrium distribution of structures. Traditional methods for obtaining these distributions, such as molecular dynamics simulation, are computationally expensive and often intractable. In this paper, we introduce a novel deep learning framework, called Distributional Graphormer (DiG), in an attempt to predict the equilibrium distribution of molecular systems. Inspired by the annealing process in thermodynamics, DiG employs deep neural networks to transform a simple distribution towards the equilibrium distribution, conditioned on a descriptor of a molecular system, such as a chemical graph or a protein sequence. This framework enables efficient generation of diverse conformations and provides estimations of state densities. We demonstrate the performance of DiG on several molecular tasks, including protein conformation sampling, ligand structure sampling, catalyst-adsorbate sampling, and property-guided structure generation. DiG presents a significant advancement in methodology for statistically understanding molecular systems, opening up new research opportunities in molecular science.
Incorporating Pre-training Paradigm for Antibody Sequence-Structure Co-design
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Antibodies are versatile proteins that can bind to pathogens and provide effective protection for human body. Recently, deep learning-based computational antibody design has attracted popular attention since it automatically mines the antibody patterns from data that could be complementary to human experiences. However, the computational methods heavily rely on high-quality antibody structure data, which is quite limited. Besides, the complementarity-determining region (CDR), which is the key component of an antibody that determines the specificity and binding affinity, is highly variable and hard to predict. Therefore, the data limitation issue further raises the difficulty of CDR generation for antibodies. Fortunately, there exists a large amount of sequence data of antibodies that can help model the CDR and alleviate the reliance on structure data. By witnessing the success of pre-training models for protein modeling, in this paper, we develop the antibody pre-training language model and incorporate it into the (antigen-specific) antibody design model in a systemic way. Specifically, we first pre-train an antibody language model based on the sequence data, then propose a one-shot way for sequence and structure generation of CDR to avoid the heavy cost and error propagation from an autoregressive manner, and finally leverage the pre-trained antibody model for the antigen-specific antibody generation model with some carefully designed modules. Through various experiments, we show that our method achieves superior performances over previous baselines on different tasks, such as sequence and structure generation and antigen-binding CDR-H3 design.
SMT-DTA: Improving Drug-Target Affinity Prediction with Semi-supervised Multi-task Training
Jun 22, 2022



Abstract:Drug-Target Affinity (DTA) prediction is an essential task for drug discovery and pharmaceutical research. Accurate predictions of DTA can greatly benefit the design of new drug. As wet experiments are costly and time consuming, the supervised data for DTA prediction is extremely limited. This seriously hinders the application of deep learning based methods, which require a large scale of supervised data. To address this challenge and improve the DTA prediction accuracy, we propose a framework with several simple yet effective strategies in this work: (1) a multi-task training strategy, which takes the DTA prediction and the masked language modeling (MLM) task on the paired drug-target dataset; (2) a semi-supervised training method to empower the drug and target representation learning by leveraging large-scale unpaired molecules and proteins in training, which differs from previous pre-training and fine-tuning methods that only utilize molecules or proteins in pre-training; and (3) a cross-attention module to enhance the interaction between drug and target representation. Extensive experiments are conducted on three real-world benchmark datasets: BindingDB, DAVIS and KIBA. The results show that our framework significantly outperforms existing methods and achieves state-of-the-art performances, e.g., $0.712$ RMSE on BindingDB IC$_{50}$ measurement with more than $5\%$ improvement than previous best work. In addition, case studies on specific drug-target binding activities, drug feature visualizations, and real-world applications demonstrate the great potential of our work. The code and data are released at https://github.com/QizhiPei/SMT-DTA
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge