George Cazenavette
DD-Ranking: Rethinking the Evaluation of Dataset Distillation
May 19, 2025



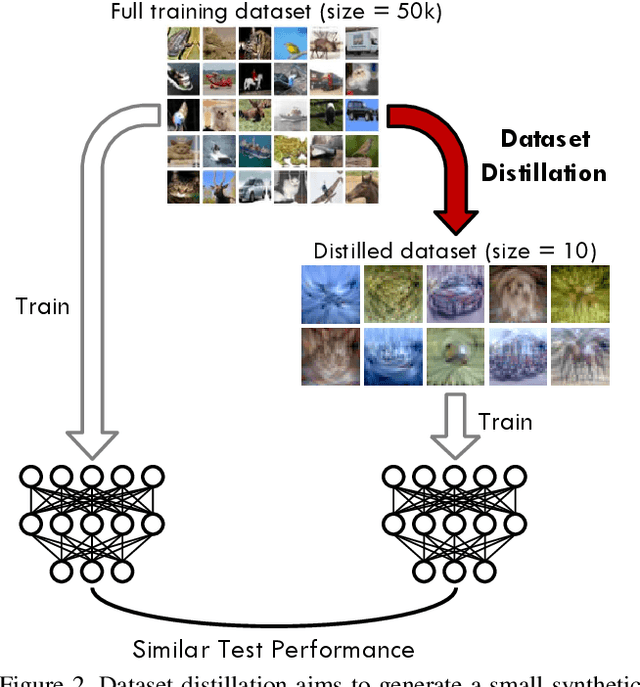
Abstract:In recent years, dataset distillation has provided a reliable solution for data compression, where models trained on the resulting smaller synthetic datasets achieve performance comparable to those trained on the original datasets. To further improve the performance of synthetic datasets, various training pipelines and optimization objectives have been proposed, greatly advancing the field of dataset distillation. Recent decoupled dataset distillation methods introduce soft labels and stronger data augmentation during the post-evaluation phase and scale dataset distillation up to larger datasets (e.g., ImageNet-1K). However, this raises a question: Is accuracy still a reliable metric to fairly evaluate dataset distillation methods? Our empirical findings suggest that the performance improvements of these methods often stem from additional techniques rather than the inherent quality of the images themselves, with even randomly sampled images achieving superior results. Such misaligned evaluation settings severely hinder the development of DD. Therefore, we propose DD-Ranking, a unified evaluation framework, along with new general evaluation metrics to uncover the true performance improvements achieved by different methods. By refocusing on the actual information enhancement of distilled datasets, DD-Ranking provides a more comprehensive and fair evaluation standard for future research advancements.
Rethinking the Role of Spatial Mixing
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:Until quite recently, the backbone of nearly every state-of-the-art computer vision model has been the 2D convolution. At its core, a 2D convolution simultaneously mixes information across both the spatial and channel dimensions of a representation. Many recent computer vision architectures consist of sequences of isotropic blocks that disentangle the spatial and channel-mixing components. This separation of the operations allows us to more closely juxtapose the effects of spatial and channel mixing in deep learning. In this paper, we take an initial step towards garnering a deeper understanding of the roles of these mixing operations. Through our experiments and analysis, we discover that on both classical (ResNet) and cutting-edge (ConvMixer) models, we can reach nearly the same level of classification performance by and leaving the spatial mixers at their random initializations. Furthermore, we show that models with random, fixed spatial mixing are naturally more robust to adversarial perturbations. Lastly, we show that this phenomenon extends past the classification regime, as such models can also decode pixel-shuffled images.
FakeInversion: Learning to Detect Images from Unseen Text-to-Image Models by Inverting Stable Diffusion
Jun 12, 2024Abstract:Due to the high potential for abuse of GenAI systems, the task of detecting synthetic images has recently become of great interest to the research community. Unfortunately, existing image-space detectors quickly become obsolete as new high-fidelity text-to-image models are developed at blinding speed. In this work, we propose a new synthetic image detector that uses features obtained by inverting an open-source pre-trained Stable Diffusion model. We show that these inversion features enable our detector to generalize well to unseen generators of high visual fidelity (e.g., DALL-E 3) even when the detector is trained only on lower fidelity fake images generated via Stable Diffusion. This detector achieves new state-of-the-art across multiple training and evaluation setups. Moreover, we introduce a new challenging evaluation protocol that uses reverse image search to mitigate stylistic and thematic biases in the detector evaluation. We show that the resulting evaluation scores align well with detectors' in-the-wild performance, and release these datasets as public benchmarks for future research.
* Project page: https://fake-inversion.github.io
Towards Lossless Dataset Distillation via Difficulty-Aligned Trajectory Matching
Oct 09, 2023



Abstract:The ultimate goal of Dataset Distillation is to synthesize a small synthetic dataset such that a model trained on this synthetic set will perform equally well as a model trained on the full, real dataset. Until now, no method of Dataset Distillation has reached this completely lossless goal, in part due to the fact that previous methods only remain effective when the total number of synthetic samples is extremely small. Since only so much information can be contained in such a small number of samples, it seems that to achieve truly loss dataset distillation, we must develop a distillation method that remains effective as the size of the synthetic dataset grows. In this work, we present such an algorithm and elucidate why existing methods fail to generate larger, high-quality synthetic sets. Current state-of-the-art methods rely on trajectory-matching, or optimizing the synthetic data to induce similar long-term training dynamics as the real data. We empirically find that the training stage of the trajectories we choose to match (i.e., early or late) greatly affects the effectiveness of the distilled dataset. Specifically, early trajectories (where the teacher network learns easy patterns) work well for a low-cardinality synthetic set since there are fewer examples wherein to distribute the necessary information. Conversely, late trajectories (where the teacher network learns hard patterns) provide better signals for larger synthetic sets since there are now enough samples to represent the necessary complex patterns. Based on our findings, we propose to align the difficulty of the generated patterns with the size of the synthetic dataset. In doing so, we successfully scale trajectory matching-based methods to larger synthetic datasets, achieving lossless dataset distillation for the very first time. Code and distilled datasets are available at https://gzyaftermath.github.io/DATM.
Diffusion with Forward Models: Solving Stochastic Inverse Problems Without Direct Supervision
Jun 20, 2023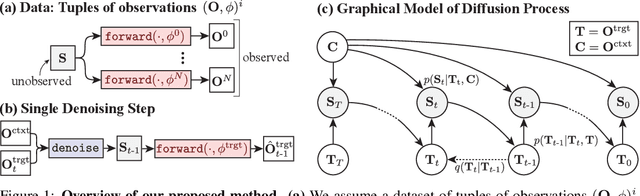
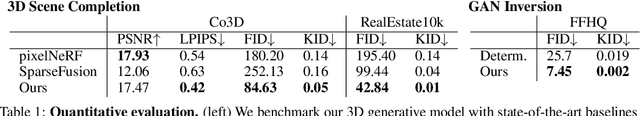

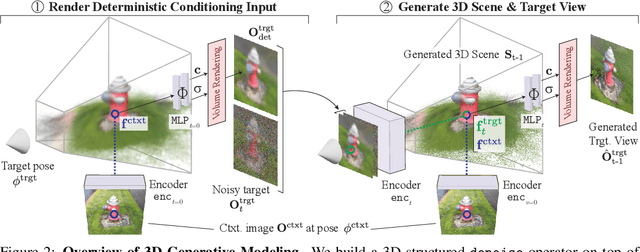
Abstract:Denoising diffusion models are a powerful type of generative models used to capture complex distributions of real-world signals. However, their applicability is limited to scenarios where training samples are readily available, which is not always the case in real-world applications. For example, in inverse graphics, the goal is to generate samples from a distribution of 3D scenes that align with a given image, but ground-truth 3D scenes are unavailable and only 2D images are accessible. To address this limitation, we propose a novel class of denoising diffusion probabilistic models that learn to sample from distributions of signals that are never directly observed. Instead, these signals are measured indirectly through a known differentiable forward model, which produces partial observations of the unknown signal. Our approach involves integrating the forward model directly into the denoising process. This integration effectively connects the generative modeling of observations with the generative modeling of the underlying signals, allowing for end-to-end training of a conditional generative model over signals. During inference, our approach enables sampling from the distribution of underlying signals that are consistent with a given partial observation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on three challenging computer vision tasks. For instance, in the context of inverse graphics, our model enables direct sampling from the distribution of 3D scenes that align with a single 2D input image.
Generalizing Dataset Distillation via Deep Generative Prior
May 03, 2023Abstract:Dataset Distillation aims to distill an entire dataset's knowledge into a few synthetic images. The idea is to synthesize a small number of synthetic data points that, when given to a learning algorithm as training data, result in a model approximating one trained on the original data. Despite recent progress in the field, existing dataset distillation methods fail to generalize to new architectures and scale to high-resolution datasets. To overcome the above issues, we propose to use the learned prior from pre-trained deep generative models to synthesize the distilled data. To achieve this, we present a new optimization algorithm that distills a large number of images into a few intermediate feature vectors in the generative model's latent space. Our method augments existing techniques, significantly improving cross-architecture generalization in all settings.
Dataset Distillation by Matching Training Trajectories
Mar 22, 2022
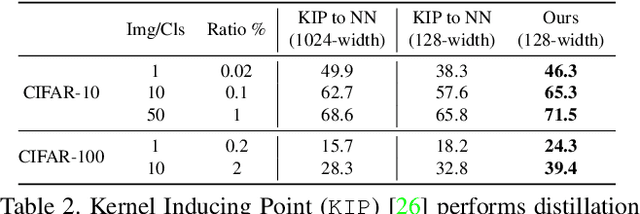
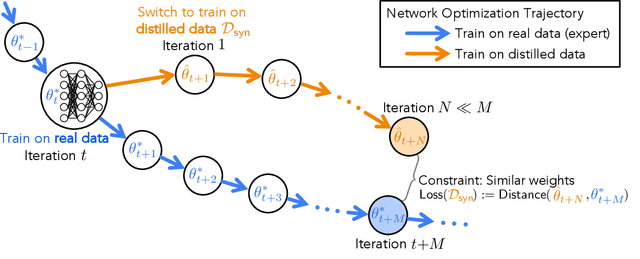
Abstract:Dataset distillation is the task of synthesizing a small dataset such that a model trained on the synthetic set will match the test accuracy of the model trained on the full dataset. In this paper, we propose a new formulation that optimizes our distilled data to guide networks to a similar state as those trained on real data across many training steps. Given a network, we train it for several iterations on our distilled data and optimize the distilled data with respect to the distance between the synthetically trained parameters and the parameters trained on real data. To efficiently obtain the initial and target network parameters for large-scale datasets, we pre-compute and store training trajectories of expert networks trained on the real dataset. Our method handily outperforms existing methods and also allows us to distill higher-resolution visual data.
MixerGAN: An MLP-Based Architecture for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation
May 28, 2021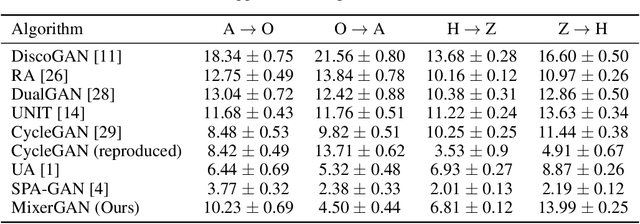
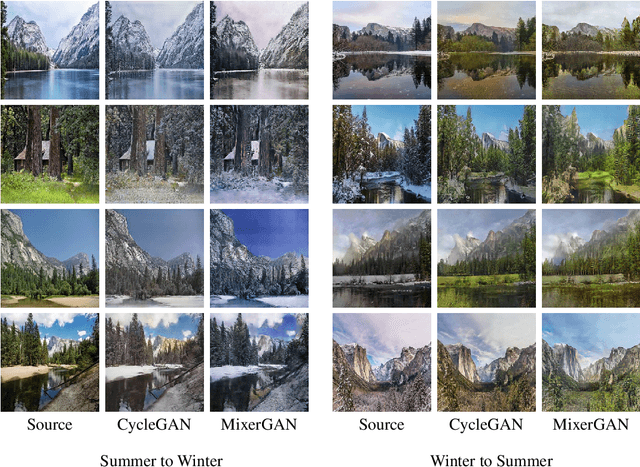
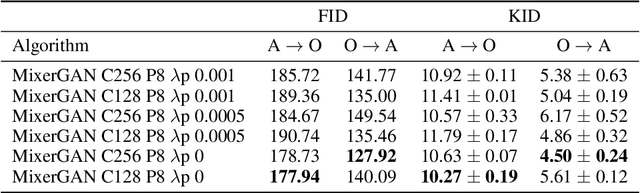
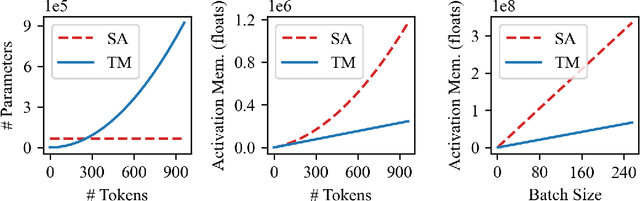
Abstract:While attention-based transformer networks achieve unparalleled success in nearly all language tasks, the large number of tokens coupled with the quadratic activation memory usage makes them prohibitive for visual tasks. As such, while language-to-language translation has been revolutionized by the transformer model, convolutional networks remain the de facto solution for image-to-image translation. The recently proposed MLP-Mixer architecture alleviates some of the speed and memory issues associated with attention-based networks while still retaining the long-range connections that make transformer models desirable. Leveraging this efficient alternative to self-attention, we propose a new unpaired image-to-image translation model called MixerGAN: a simpler MLP-based architecture that considers long-distance relationships between pixels without the need for expensive attention mechanisms. Quantitative and qualitative analysis shows that MixerGAN achieves competitive results when compared to prior convolutional-based methods.
On the Bias Against Inductive Biases
May 28, 2021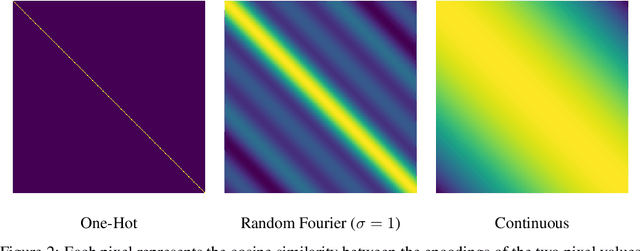
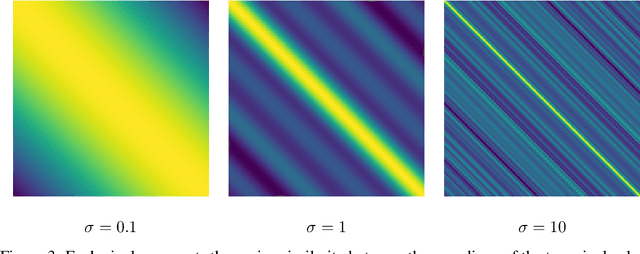
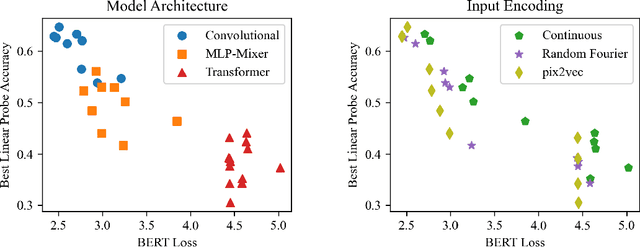
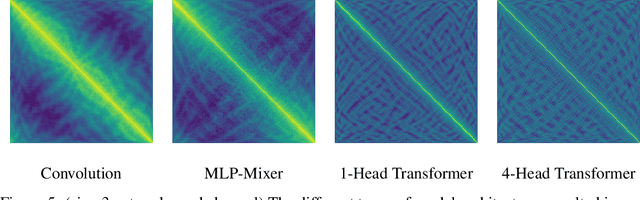
Abstract:Borrowing from the transformer models that revolutionized the field of natural language processing, self-supervised feature learning for visual tasks has also seen state-of-the-art success using these extremely deep, isotropic networks. However, the typical AI researcher does not have the resources to evaluate, let alone train, a model with several billion parameters and quadratic self-attention activations. To facilitate further research, it is necessary to understand the features of these huge transformer models that can be adequately studied by the typical researcher. One interesting characteristic of these transformer models is that they remove most of the inductive biases present in classical convolutional networks. In this work, we analyze the effect of these and more inductive biases on small to moderately-sized isotropic networks used for unsupervised visual feature learning and show that their removal is not always ideal.
Architectural Adversarial Robustness: The Case for Deep Pursuit
Nov 29, 2020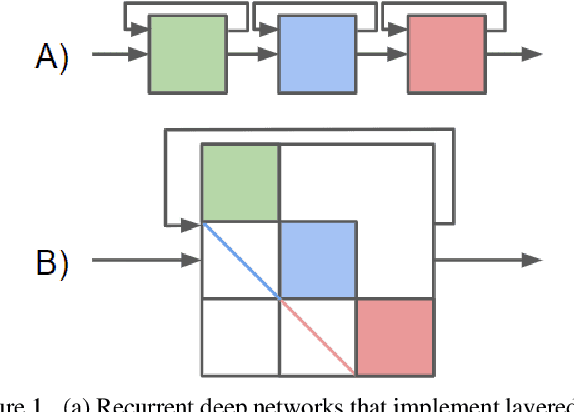
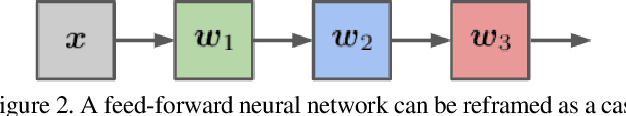
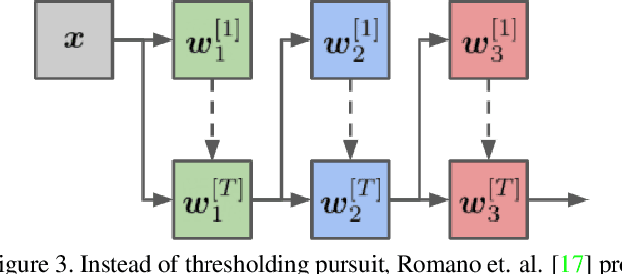
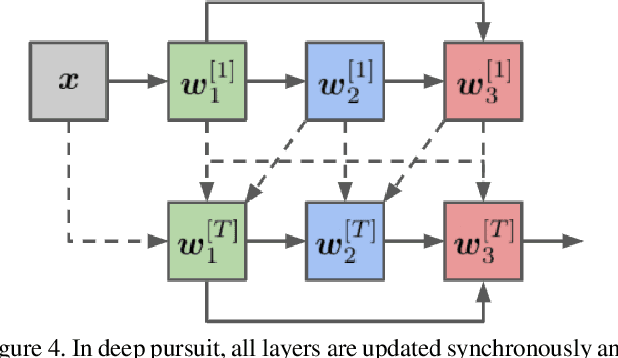
Abstract:Despite their unmatched performance, deep neural networks remain susceptible to targeted attacks by nearly imperceptible levels of adversarial noise. While the underlying cause of this sensitivity is not well understood, theoretical analyses can be simplified by reframing each layer of a feed-forward network as an approximate solution to a sparse coding problem. Iterative solutions using basis pursuit are theoretically more stable and have improved adversarial robustness. However, cascading layer-wise pursuit implementations suffer from error accumulation in deeper networks. In contrast, our new method of deep pursuit approximates the activations of all layers as a single global optimization problem, allowing us to consider deeper, real-world architectures with skip connections such as residual networks. Experimentally, our approach demonstrates improved robustness to adversarial noise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge