Manuel Ladron De Guevara
MixerGAN: An MLP-Based Architecture for Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation
May 28, 2021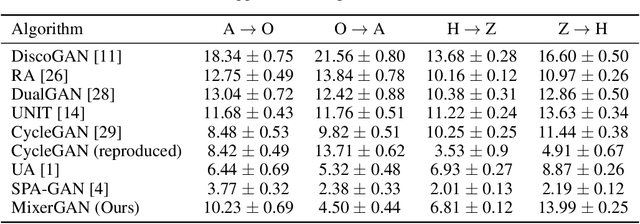
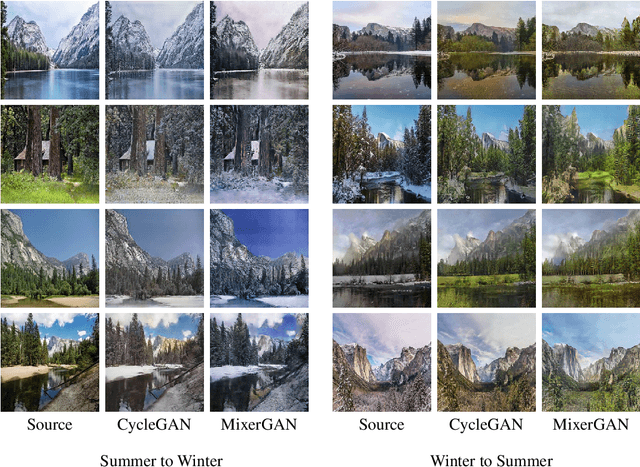
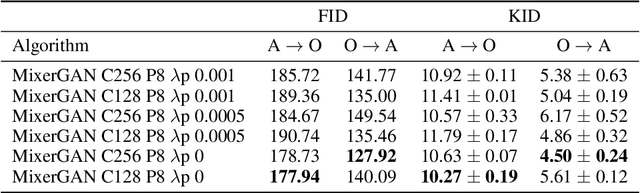
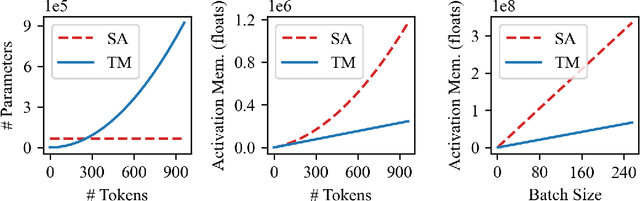
Abstract:While attention-based transformer networks achieve unparalleled success in nearly all language tasks, the large number of tokens coupled with the quadratic activation memory usage makes them prohibitive for visual tasks. As such, while language-to-language translation has been revolutionized by the transformer model, convolutional networks remain the de facto solution for image-to-image translation. The recently proposed MLP-Mixer architecture alleviates some of the speed and memory issues associated with attention-based networks while still retaining the long-range connections that make transformer models desirable. Leveraging this efficient alternative to self-attention, we propose a new unpaired image-to-image translation model called MixerGAN: a simpler MLP-based architecture that considers long-distance relationships between pixels without the need for expensive attention mechanisms. Quantitative and qualitative analysis shows that MixerGAN achieves competitive results when compared to prior convolutional-based methods.
Artistic Style in Robotic Painting; a Machine Learning Approach to Learning Brushstroke from Human Artists
Jul 07, 2020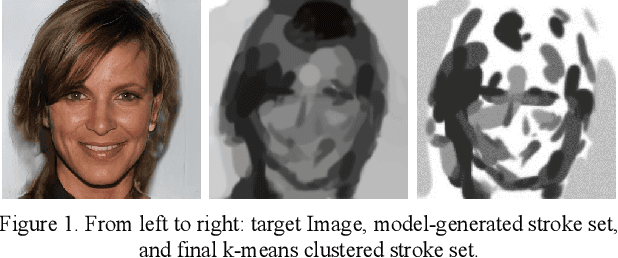
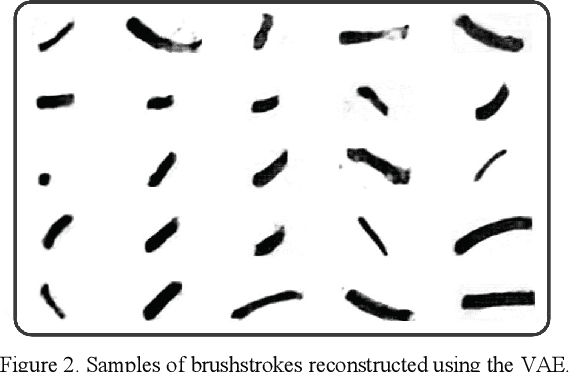
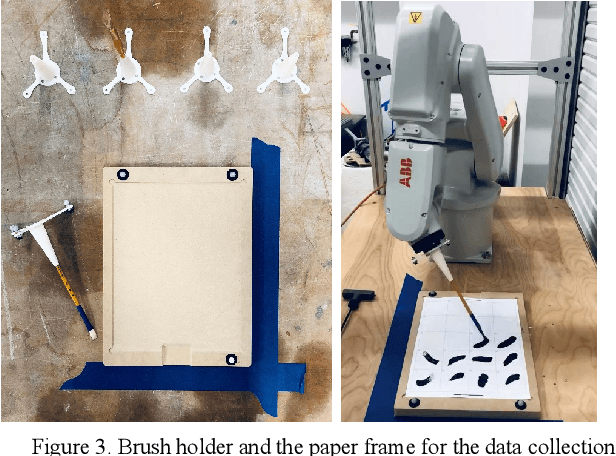

Abstract:Robotic painting has been a subject of interest among both artists and roboticists since the 1970s. Researchers and interdisciplinary artists have employed various painting techniques and human-robot collaboration models to create visual mediums on canvas. One of the challenges of robotic painting is to apply a desired artistic style to the painting. Style transfer techniques with machine learning models have helped us address this challenge with the visual style of a specific painting. However, other manual elements of style, i.e., painting techniques and brushstrokes of an artist have not been fully addressed. We propose a method to integrate an artistic style to the brushstrokes and the painting process through collaboration with a human artist. In this paper, we describe our approach to 1) collect brushstrokes and hand-brush motion samples from an artist, and 2) train a generative model to generate brushstrokes that pertains to the artist's style, and 3) integrate the learned model on a robot arm to paint on a canvas. In a preliminary study, 71% of human evaluators find our robot's paintings pertaining to the characteristics of the artist's style.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge