Tianwei Yin
From Slow Bidirectional to Fast Causal Video Generators
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Current video diffusion models achieve impressive generation quality but struggle in interactive applications due to bidirectional attention dependencies. The generation of a single frame requires the model to process the entire sequence, including the future. We address this limitation by adapting a pretrained bidirectional diffusion transformer to a causal transformer that generates frames on-the-fly. To further reduce latency, we extend distribution matching distillation (DMD) to videos, distilling 50-step diffusion model into a 4-step generator. To enable stable and high-quality distillation, we introduce a student initialization scheme based on teacher's ODE trajectories, as well as an asymmetric distillation strategy that supervises a causal student model with a bidirectional teacher. This approach effectively mitigates error accumulation in autoregressive generation, allowing long-duration video synthesis despite training on short clips. Our model supports fast streaming generation of high quality videos at 9.4 FPS on a single GPU thanks to KV caching. Our approach also enables streaming video-to-video translation, image-to-video, and dynamic prompting in a zero-shot manner. We will release the code based on an open-source model in the future.
Turbo3D: Ultra-fast Text-to-3D Generation
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:We present Turbo3D, an ultra-fast text-to-3D system capable of generating high-quality Gaussian splatting assets in under one second. Turbo3D employs a rapid 4-step, 4-view diffusion generator and an efficient feed-forward Gaussian reconstructor, both operating in latent space. The 4-step, 4-view generator is a student model distilled through a novel Dual-Teacher approach, which encourages the student to learn view consistency from a multi-view teacher and photo-realism from a single-view teacher. By shifting the Gaussian reconstructor's inputs from pixel space to latent space, we eliminate the extra image decoding time and halve the transformer sequence length for maximum efficiency. Our method demonstrates superior 3D generation results compared to previous baselines, while operating in a fraction of their runtime.
Improved Distribution Matching Distillation for Fast Image Synthesis
May 23, 2024
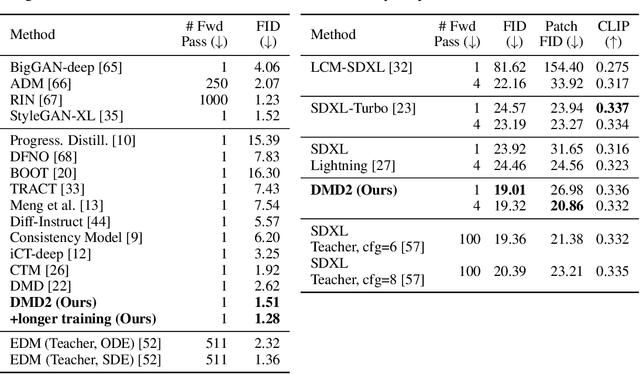

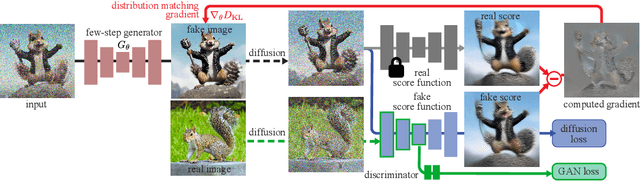
Abstract:Recent approaches have shown promises distilling diffusion models into efficient one-step generators. Among them, Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD) produces one-step generators that match their teacher in distribution, without enforcing a one-to-one correspondence with the sampling trajectories of their teachers. However, to ensure stable training, DMD requires an additional regression loss computed using a large set of noise-image pairs generated by the teacher with many steps of a deterministic sampler. This is costly for large-scale text-to-image synthesis and limits the student's quality, tying it too closely to the teacher's original sampling paths. We introduce DMD2, a set of techniques that lift this limitation and improve DMD training. First, we eliminate the regression loss and the need for expensive dataset construction. We show that the resulting instability is due to the fake critic not estimating the distribution of generated samples accurately and propose a two time-scale update rule as a remedy. Second, we integrate a GAN loss into the distillation procedure, discriminating between generated samples and real images. This lets us train the student model on real data, mitigating the imperfect real score estimation from the teacher model, and enhancing quality. Lastly, we modify the training procedure to enable multi-step sampling. We identify and address the training-inference input mismatch problem in this setting, by simulating inference-time generator samples during training time. Taken together, our improvements set new benchmarks in one-step image generation, with FID scores of 1.28 on ImageNet-64x64 and 8.35 on zero-shot COCO 2014, surpassing the original teacher despite a 500X reduction in inference cost. Further, we show our approach can generate megapixel images by distilling SDXL, demonstrating exceptional visual quality among few-step methods.
One-step Diffusion with Distribution Matching Distillation
Dec 05, 2023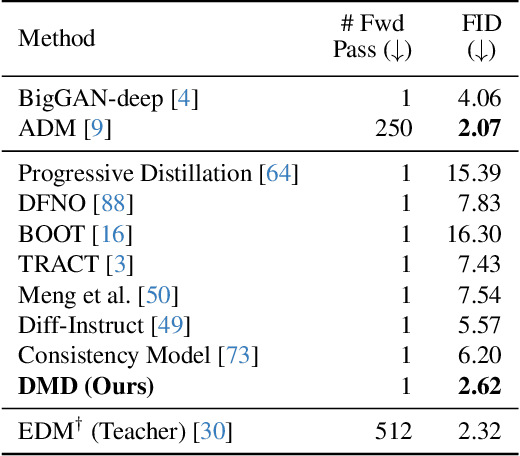
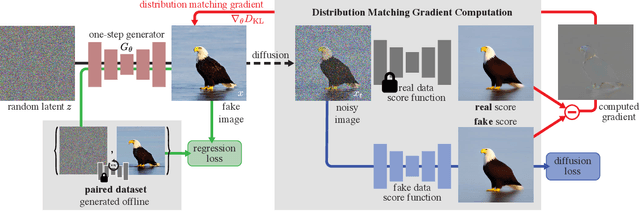
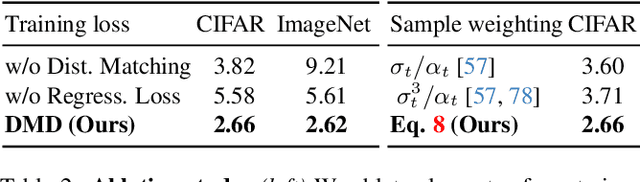
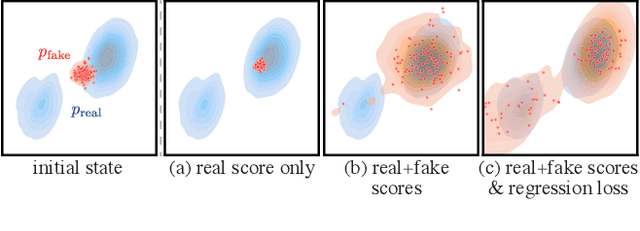
Abstract:Diffusion models generate high-quality images but require dozens of forward passes. We introduce Distribution Matching Distillation (DMD), a procedure to transform a diffusion model into a one-step image generator with minimal impact on image quality. We enforce the one-step image generator match the diffusion model at distribution level, by minimizing an approximate KL divergence whose gradient can be expressed as the difference between 2 score functions, one of the target distribution and the other of the synthetic distribution being produced by our one-step generator. The score functions are parameterized as two diffusion models trained separately on each distribution. Combined with a simple regression loss matching the large-scale structure of the multi-step diffusion outputs, our method outperforms all published few-step diffusion approaches, reaching 2.62 FID on ImageNet 64x64 and 11.49 FID on zero-shot COCO-30k, comparable to Stable Diffusion but orders of magnitude faster. Utilizing FP16 inference, our model generates images at 20 FPS on modern hardware.
Diffusion with Forward Models: Solving Stochastic Inverse Problems Without Direct Supervision
Jun 20, 2023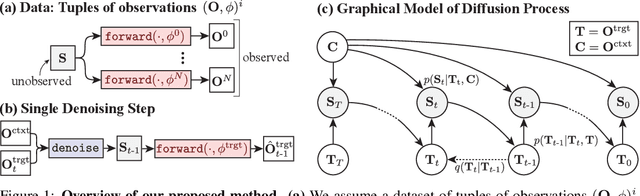
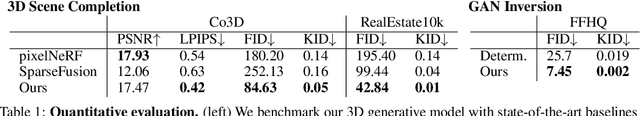

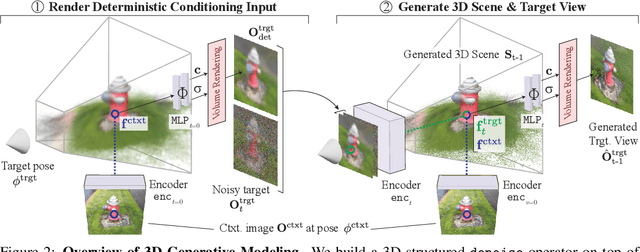
Abstract:Denoising diffusion models are a powerful type of generative models used to capture complex distributions of real-world signals. However, their applicability is limited to scenarios where training samples are readily available, which is not always the case in real-world applications. For example, in inverse graphics, the goal is to generate samples from a distribution of 3D scenes that align with a given image, but ground-truth 3D scenes are unavailable and only 2D images are accessible. To address this limitation, we propose a novel class of denoising diffusion probabilistic models that learn to sample from distributions of signals that are never directly observed. Instead, these signals are measured indirectly through a known differentiable forward model, which produces partial observations of the unknown signal. Our approach involves integrating the forward model directly into the denoising process. This integration effectively connects the generative modeling of observations with the generative modeling of the underlying signals, allowing for end-to-end training of a conditional generative model over signals. During inference, our approach enables sampling from the distribution of underlying signals that are consistent with a given partial observation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on three challenging computer vision tasks. For instance, in the context of inverse graphics, our model enables direct sampling from the distribution of 3D scenes that align with a single 2D input image.
FastComposer: Tuning-Free Multi-Subject Image Generation with Localized Attention
May 21, 2023
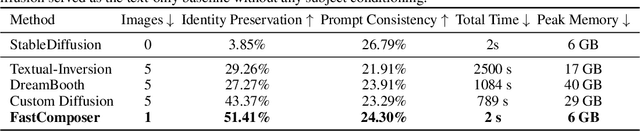


Abstract:Diffusion models excel at text-to-image generation, especially in subject-driven generation for personalized images. However, existing methods are inefficient due to the subject-specific fine-tuning, which is computationally intensive and hampers efficient deployment. Moreover, existing methods struggle with multi-subject generation as they often blend features among subjects. We present FastComposer which enables efficient, personalized, multi-subject text-to-image generation without fine-tuning. FastComposer uses subject embeddings extracted by an image encoder to augment the generic text conditioning in diffusion models, enabling personalized image generation based on subject images and textual instructions with only forward passes. To address the identity blending problem in the multi-subject generation, FastComposer proposes cross-attention localization supervision during training, enforcing the attention of reference subjects localized to the correct regions in the target images. Naively conditioning on subject embeddings results in subject overfitting. FastComposer proposes delayed subject conditioning in the denoising step to maintain both identity and editability in subject-driven image generation. FastComposer generates images of multiple unseen individuals with different styles, actions, and contexts. It achieves 300$\times$-2500$\times$ speedup compared to fine-tuning-based methods and requires zero extra storage for new subjects. FastComposer paves the way for efficient, personalized, and high-quality multi-subject image creation. Code, model, and dataset are available at https://github.com/mit-han-lab/fastcomposer.
Learning Task-Specific Strategies for Accelerated MRI
Apr 25, 2023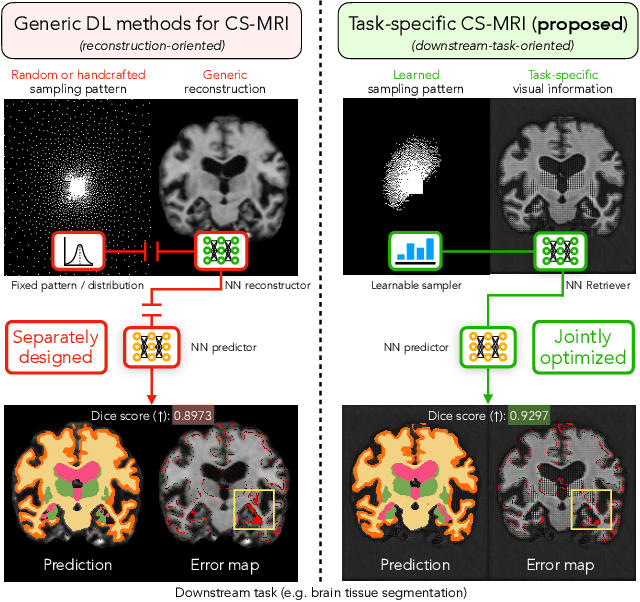
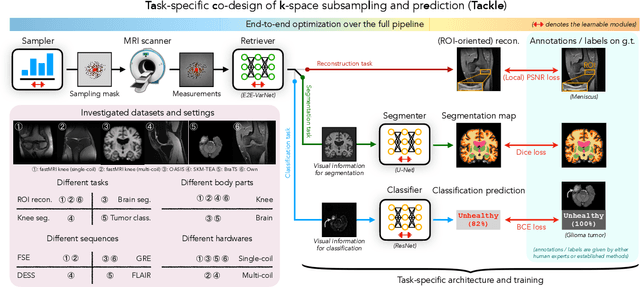

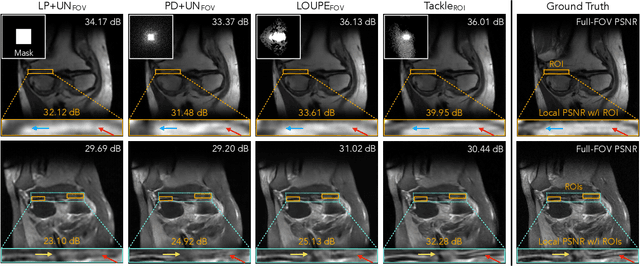
Abstract:Compressed sensing magnetic resonance imaging (CS-MRI) seeks to recover visual information from subsampled measurements for diagnostic tasks. Traditional CS-MRI methods often separately address measurement subsampling, image reconstruction, and task prediction, resulting in suboptimal end-to-end performance. In this work, we propose TACKLE as a unified framework for designing CS-MRI systems tailored to specific tasks. Leveraging recent co-design techniques, TACKLE jointly optimizes subsampling, reconstruction, and prediction strategies to enhance the performance on the downstream task. Our results on multiple public MRI datasets show that the proposed framework achieves improved performance on various tasks over traditional CS-MRI methods. We also evaluate the generalization ability of TACKLE by experimentally collecting a new dataset using different acquisition setups from the training data. Without additional fine-tuning, TACKLE functions robustly and leads to both numerical and visual improvements.
Global Tracking Transformers
Mar 24, 2022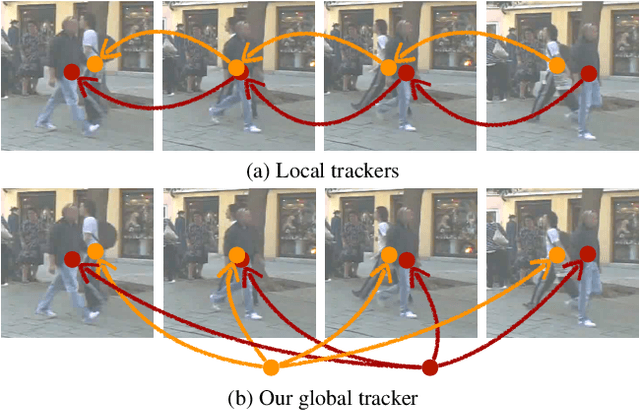
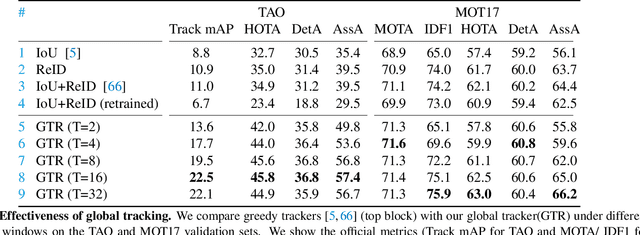
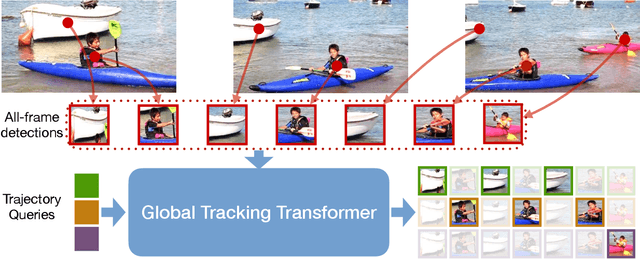
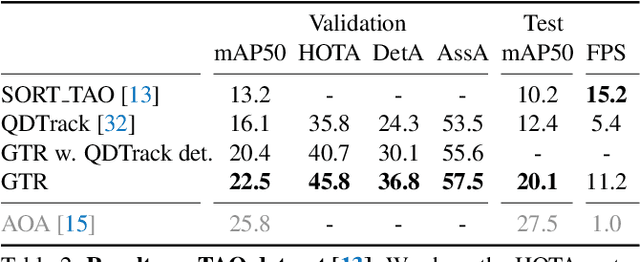
Abstract:We present a novel transformer-based architecture for global multi-object tracking. Our network takes a short sequence of frames as input and produces global trajectories for all objects. The core component is a global tracking transformer that operates on objects from all frames in the sequence. The transformer encodes object features from all frames, and uses trajectory queries to group them into trajectories. The trajectory queries are object features from a single frame and naturally produce unique trajectories. Our global tracking transformer does not require intermediate pairwise grouping or combinatorial association, and can be jointly trained with an object detector. It achieves competitive performance on the popular MOT17 benchmark, with 75.3 MOTA and 59.1 HOTA. More importantly, our framework seamlessly integrates into state-of-the-art large-vocabulary detectors to track any objects. Experiments on the challenging TAO dataset show that our framework consistently improves upon baselines that are based on pairwise association, outperforming published works by a significant 7.7 tracking mAP. Code is available at https://github.com/xingyizhou/GTR.
Multimodal Virtual Point 3D Detection
Nov 12, 2021



Abstract:Lidar-based sensing drives current autonomous vehicles. Despite rapid progress, current Lidar sensors still lag two decades behind traditional color cameras in terms of resolution and cost. For autonomous driving, this means that large objects close to the sensors are easily visible, but far-away or small objects comprise only one measurement or two. This is an issue, especially when these objects turn out to be driving hazards. On the other hand, these same objects are clearly visible in onboard RGB sensors. In this work, we present an approach to seamlessly fuse RGB sensors into Lidar-based 3D recognition. Our approach takes a set of 2D detections to generate dense 3D virtual points to augment an otherwise sparse 3D point cloud. These virtual points naturally integrate into any standard Lidar-based 3D detectors along with regular Lidar measurements. The resulting multi-modal detector is simple and effective. Experimental results on the large-scale nuScenes dataset show that our framework improves a strong CenterPoint baseline by a significant 6.6 mAP, and outperforms competing fusion approaches. Code and more visualizations are available at https://tianweiy.github.io/mvp/
End-to-End Sequential Sampling and Reconstruction for MR Imaging
May 13, 2021



Abstract:Accelerated MRI shortens acquisition time by subsampling in the measurement k-space. Recovering a high-fidelity anatomical image from subsampled measurements requires close cooperation between two components: (1) a sampler that chooses the subsampling pattern and (2) a reconstructor that recovers images from incomplete measurements. In this paper, we leverage the sequential nature of MRI measurements, and propose a fully differentiable framework that jointly learns a sequential sampling policy simultaneously with a reconstruction strategy. This co-designed framework is able to adapt during acquisition in order to capture the most informative measurements for a particular target (Figure 1). Experimental results on the fastMRI knee dataset demonstrate that the proposed approach successfully utilizes intermediate information during the sampling process to boost reconstruction performance. In particular, our proposed method outperforms the current state-of-the-art learned k-space sampling baseline on up to 96.96% of test samples. We also investigate the individual and collective benefits of the sequential sampling and co-design strategies. Code and more visualizations are available at http://imaging.cms.caltech.edu/seq-mri
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge