Eric Mitchell
Tony
OpenAI GPT-5 System Card
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:This is the system card published alongside the OpenAI GPT-5 launch, August 2025. GPT-5 is a unified system with a smart and fast model that answers most questions, a deeper reasoning model for harder problems, and a real-time router that quickly decides which model to use based on conversation type, complexity, tool needs, and explicit intent (for example, if you say 'think hard about this' in the prompt). The router is continuously trained on real signals, including when users switch models, preference rates for responses, and measured correctness, improving over time. Once usage limits are reached, a mini version of each model handles remaining queries. This system card focuses primarily on gpt-5-thinking and gpt-5-main, while evaluations for other models are available in the appendix. The GPT-5 system not only outperforms previous models on benchmarks and answers questions more quickly, but -- more importantly -- is more useful for real-world queries. We've made significant advances in reducing hallucinations, improving instruction following, and minimizing sycophancy, and have leveled up GPT-5's performance in three of ChatGPT's most common uses: writing, coding, and health. All of the GPT-5 models additionally feature safe-completions, our latest approach to safety training to prevent disallowed content. Similarly to ChatGPT agent, we have decided to treat gpt-5-thinking as High capability in the Biological and Chemical domain under our Preparedness Framework, activating the associated safeguards. While we do not have definitive evidence that this model could meaningfully help a novice to create severe biological harm -- our defined threshold for High capability -- we have chosen to take a precautionary approach.
FSPO: Few-Shot Preference Optimization of Synthetic Preference Data in LLMs Elicits Effective Personalization to Real Users
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Effective personalization of LLMs is critical for a broad range of user-interfacing applications such as virtual assistants and content curation. Inspired by the strong in-context learning capabilities of LLMs, we propose Few-Shot Preference Optimization (FSPO), which reframes reward modeling as a meta-learning problem. Under this framework, an LLM learns to quickly adapt to a user via a few labeled preferences from that user, constructing a personalized reward function for them. Additionally, since real-world preference data is scarce and challenging to collect at scale, we propose careful design choices to construct synthetic preference datasets for personalization, generating over 1M synthetic personalized preferences using publicly available LLMs. In particular, to successfully transfer from synthetic data to real users, we find it crucial for the data to exhibit both high diversity and coherent, self-consistent structure. We evaluate FSPO on personalized open-ended generation for up to 1,500 synthetic users across across three domains: movie reviews, pedagogical adaptation based on educational background, and general question answering, along with a controlled human study. Overall, FSPO achieves an 87% Alpaca Eval winrate on average in generating responses that are personalized to synthetic users and a 72% winrate with real human users in open-ended question answering.
OpenAI o1 System Card
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:The o1 model series is trained with large-scale reinforcement learning to reason using chain of thought. These advanced reasoning capabilities provide new avenues for improving the safety and robustness of our models. In particular, our models can reason about our safety policies in context when responding to potentially unsafe prompts, through deliberative alignment. This leads to state-of-the-art performance on certain benchmarks for risks such as generating illicit advice, choosing stereotyped responses, and succumbing to known jailbreaks. Training models to incorporate a chain of thought before answering has the potential to unlock substantial benefits, while also increasing potential risks that stem from heightened intelligence. Our results underscore the need for building robust alignment methods, extensively stress-testing their efficacy, and maintaining meticulous risk management protocols. This report outlines the safety work carried out for the OpenAI o1 and OpenAI o1-mini models, including safety evaluations, external red teaming, and Preparedness Framework evaluations.
Test-Time Alignment via Hypothesis Reweighting
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Large pretrained models often struggle with underspecified tasks -- situations where the training data does not fully define the desired behavior. For example, chatbots must handle diverse and often conflicting user preferences, requiring adaptability to various user needs. We propose a novel framework to address the general challenge of aligning models to test-time user intent, which is rarely fully specified during training. Our approach involves training an efficient ensemble, i.e., a single neural network with multiple prediction heads, each representing a different function consistent with the training data. Our main contribution is HyRe, a simple adaptation technique that dynamically reweights ensemble members at test time using a small set of labeled examples from the target distribution, which can be labeled in advance or actively queried from a larger unlabeled pool. By leveraging recent advances in scalable ensemble training, our method scales to large pretrained models, with computational costs comparable to fine-tuning a single model. We empirically validate HyRe in several underspecified scenarios, including personalization tasks and settings with distribution shifts. Additionally, with just five preference pairs from each target distribution, the same ensemble adapted via HyRe outperforms the prior state-of-the-art 2B-parameter reward model accuracy across 18 evaluation distributions.
Calibrating Language Models with Adaptive Temperature Scaling
Sep 29, 2024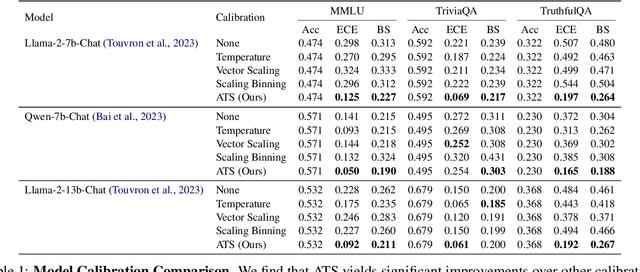

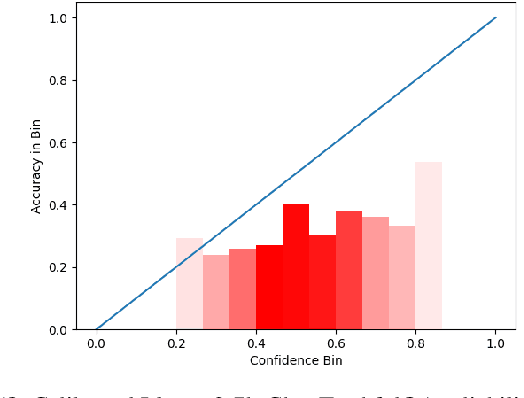
Abstract:The effectiveness of large language models (LLMs) is not only measured by their ability to generate accurate outputs but also by their calibration-how well their confidence scores reflect the probability of their outputs being correct. While unsupervised pre-training has been shown to yield LLMs with well-calibrated conditional probabilities, recent studies have shown that after fine-tuning with reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), the calibration of these models degrades significantly. In this work, we introduce Adaptive Temperature Scaling (ATS), a post-hoc calibration method that predicts a temperature scaling parameter for each token prediction. The predicted temperature values adapt based on token-level features and are fit over a standard supervised fine-tuning (SFT) dataset. The adaptive nature of ATS addresses the varying degrees of calibration shift that can occur after RLHF fine-tuning. ATS improves calibration by over 10-50% across three downstream natural language evaluation benchmarks compared to prior calibration methods and does not impede performance improvements from RLHF.
Online Adaptation of Language Models with a Memory of Amortized Contexts
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Due to the rapid generation and dissemination of information, large language models (LLMs) quickly run out of date despite enormous development costs. Due to this crucial need to keep models updated, online learning has emerged as a critical necessity when utilizing LLMs for real-world applications. However, given the ever-expanding corpus of unseen documents and the large parameter space of modern LLMs, efficient adaptation is essential. To address these challenges, we propose Memory of Amortized Contexts (MAC), an efficient and effective online adaptation framework for LLMs with strong knowledge retention. We propose an amortized feature extraction and memory-augmentation approach to compress and extract information from new documents into compact modulations stored in a memory bank. When answering questions, our model attends to and extracts relevant knowledge from this memory bank. To learn informative modulations in an efficient manner, we utilize amortization-based meta-learning, which substitutes the optimization process with a single forward pass of the encoder. Subsequently, we learn to choose from and aggregate selected documents into a single modulation by conditioning on the question, allowing us to adapt a frozen language model during test time without requiring further gradient updates. Our experiment demonstrates the superiority of MAC in multiple aspects, including online adaptation performance, time, and memory efficiency. Code is available at: https://github.com/jihoontack/MAC.
A Critical Evaluation of AI Feedback for Aligning Large Language Models
Feb 19, 2024

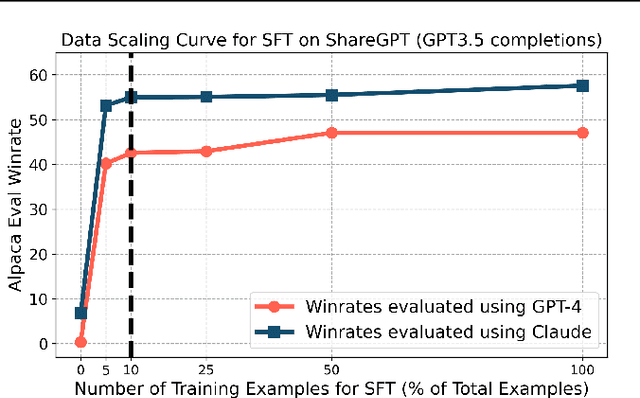
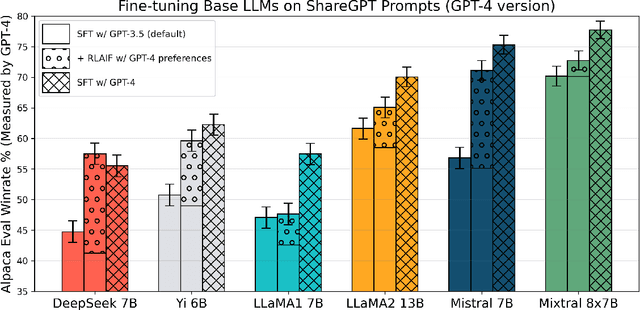
Abstract:Reinforcement learning with AI feedback (RLAIF) is a popular paradigm for improving the instruction-following abilities of powerful pre-trained language models. RLAIF first performs supervised fine-tuning (SFT) using demonstrations from a teacher model and then further fine-tunes the model with reinforcement learning (RL), using feedback from a critic model. While recent popular open-source models have demonstrated substantial improvements in performance from the RL step, in this paper we question whether the complexity of this RL step is truly warranted for AI feedback. We show that the improvements of the RL step are virtually entirely due to the widespread practice of using a weaker teacher model (e.g. GPT-3.5) for SFT data collection than the critic (e.g., GPT-4) used for AI feedback generation. Specifically, we show that simple supervised fine-tuning with GPT-4 as the teacher outperforms existing RLAIF pipelines. More generally, we find that the gains from RLAIF vary substantially across base model families, test-time evaluation protocols, and critic models. Finally, we provide a mechanistic explanation for when SFT may outperform the full two-step RLAIF pipeline as well as suggestions for making RLAIF maximally useful in practice.
RLVF: Learning from Verbal Feedback without Overgeneralization
Feb 16, 2024



Abstract:The diversity of contexts in which large language models (LLMs) are deployed requires the ability to modify or customize default model behaviors to incorporate nuanced requirements and preferences. A convenient interface to specify such model adjustments is high-level verbal feedback, such as "Don't use emojis when drafting emails to my boss." However, while writing high-level feedback is far simpler than collecting annotations for reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), we find that simply prompting a model with such feedback leads to overgeneralization of the feedback to contexts where it is not relevant. We study the problem of incorporating verbal feedback without such overgeneralization, inspiring a new method Contextualized Critiques with Constrained Preference Optimization (C3PO). C3PO uses a piece of high-level feedback to generate a small synthetic preference dataset specifying how the feedback should (and should not) be applied. It then fine-tunes the model in accordance with the synthetic preference data while minimizing the divergence from the original model for prompts where the feedback does not apply. Our experimental results indicate that our approach effectively applies verbal feedback to relevant scenarios while preserving existing behaviors for other contexts. For both human- and GPT-4-generated high-level feedback, C3PO effectively adheres to the given feedback comparably to in-context baselines while reducing overgeneralization by 30%.
Fine-tuning Language Models for Factuality
Nov 14, 2023Abstract:The fluency and creativity of large pre-trained language models (LLMs) have led to their widespread use, sometimes even as a replacement for traditional search engines. Yet language models are prone to making convincing but factually inaccurate claims, often referred to as 'hallucinations.' These errors can inadvertently spread misinformation or harmfully perpetuate misconceptions. Further, manual fact-checking of model responses is a time-consuming process, making human factuality labels expensive to acquire. In this work, we fine-tune language models to be more factual, without human labeling and targeting more open-ended generation settings than past work. We leverage two key recent innovations in NLP to do so. First, several recent works have proposed methods for judging the factuality of open-ended text by measuring consistency with an external knowledge base or simply a large model's confidence scores. Second, the direct preference optimization algorithm enables straightforward fine-tuning of language models on objectives other than supervised imitation, using a preference ranking over possible model responses. We show that learning from automatically generated factuality preference rankings, generated either through existing retrieval systems or our novel retrieval-free approach, significantly improves the factuality (percent of generated claims that are correct) of Llama-2 on held-out topics compared with RLHF or decoding strategies targeted at factuality. At 7B scale, compared to Llama-2-chat, we observe 58% and 40% reduction in factual error rate when generating biographies and answering medical questions, respectively.
An Emulator for Fine-Tuning Large Language Models using Small Language Models
Oct 19, 2023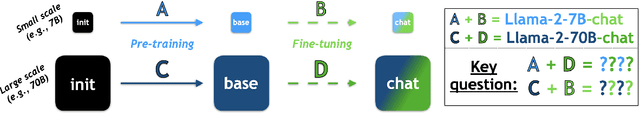
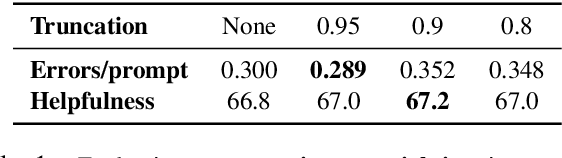
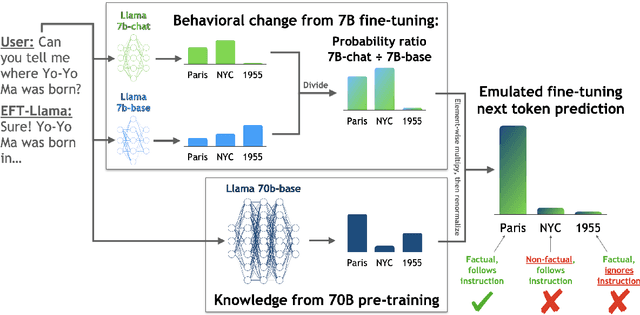
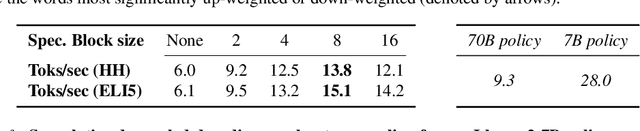
Abstract:Widely used language models (LMs) are typically built by scaling up a two-stage training pipeline: a pre-training stage that uses a very large, diverse dataset of text and a fine-tuning (sometimes, 'alignment') stage that uses targeted examples or other specifications of desired behaviors. While it has been hypothesized that knowledge and skills come from pre-training, and fine-tuning mostly filters this knowledge and skillset, this intuition has not been extensively tested. To aid in doing so, we introduce a novel technique for decoupling the knowledge and skills gained in these two stages, enabling a direct answer to the question, "What would happen if we combined the knowledge learned by a large model during pre-training with the knowledge learned by a small model during fine-tuning (or vice versa)?" Using an RL-based framework derived from recent developments in learning from human preferences, we introduce emulated fine-tuning (EFT), a principled and practical method for sampling from a distribution that approximates (or 'emulates') the result of pre-training and fine-tuning at different scales. Our experiments with EFT show that scaling up fine-tuning tends to improve helpfulness, while scaling up pre-training tends to improve factuality. Beyond decoupling scale, we show that EFT enables test-time adjustment of competing behavioral traits like helpfulness and harmlessness without additional training. Finally, a special case of emulated fine-tuning, which we call LM up-scaling, avoids resource-intensive fine-tuning of large pre-trained models by ensembling them with small fine-tuned models, essentially emulating the result of fine-tuning the large pre-trained model. Up-scaling consistently improves helpfulness and factuality of instruction-following models in the Llama, Llama-2, and Falcon families, without additional hyperparameters or training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge