Elena Gribovskaya
DeepSearchQA: Bridging the Comprehensiveness Gap for Deep Research Agents
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:We introduce DeepSearchQA, a 900-prompt benchmark for evaluating agents on difficult multi-step information-seeking tasks across 17 different fields. Unlike traditional benchmarks that target single answer retrieval or broad-spectrum factuality, DeepSearchQA features a dataset of challenging, handcrafted tasks designed to evaluate an agent's ability to execute complex search plans to generate exhaustive answer lists. This shift in design explicitly tests three critical, yet under-evaluated capabilities: 1) systematic collation of fragmented information from disparate sources, 2) de-duplication and entity resolution to ensure precision, and 3) the ability to reason about stopping criteria within an open-ended search space. Each task is structured as a causal chain, where discovering information for one step is dependent on the successful completion of the previous one, stressing long-horizon planning and context retention. All tasks are grounded in the open web with objectively verifiable answer sets. Our comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art agent architectures reveals significant performance limitations: even the most advanced models struggle to balance high recall with precision. We observe distinct failure modes ranging from premature stopping (under-retrieval) to hedging behaviors, where agents cast an overly wide net of low-confidence answers to artificially boost recall. These findings highlight critical headroom in current agent designs and position DeepSearchQA as an essential diagnostic tool for driving future research toward more robust, deep-research capabilities.
The FACTS Leaderboard: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Large Language Model Factuality
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:We introduce The FACTS Leaderboard, an online leaderboard suite and associated set of benchmarks that comprehensively evaluates the ability of language models to generate factually accurate text across diverse scenarios. The suite provides a holistic measure of factuality by aggregating the performance of models on four distinct sub-leaderboards: (1) FACTS Multimodal, which measures the factuality of responses to image-based questions; (2) FACTS Parametric, which assesses models' world knowledge by answering closed-book factoid questions from internal parameters; (3) FACTS Search, which evaluates factuality in information-seeking scenarios, where the model must use a search API; and (4) FACTS Grounding (v2), which evaluates whether long-form responses are grounded in provided documents, featuring significantly improved judge models. Each sub-leaderboard employs automated judge models to score model responses, and the final suite score is an average of the four components, designed to provide a robust and balanced assessment of a model's overall factuality. The FACTS Leaderboard Suite will be actively maintained, containing both public and private splits to allow for external participation while guarding its integrity. It can be found at https://www.kaggle.com/benchmarks/google/facts .
Do Large Language Models Perform Latent Multi-Hop Reasoning without Exploiting Shortcuts?
Nov 25, 2024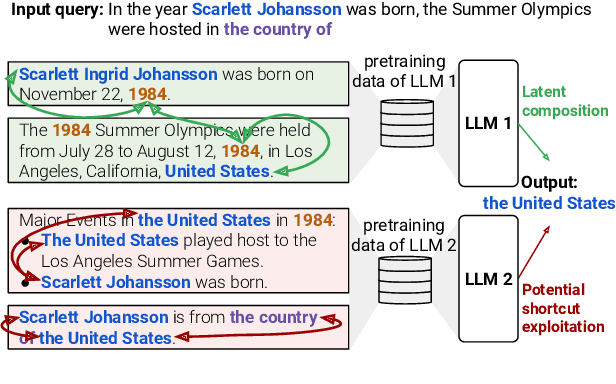
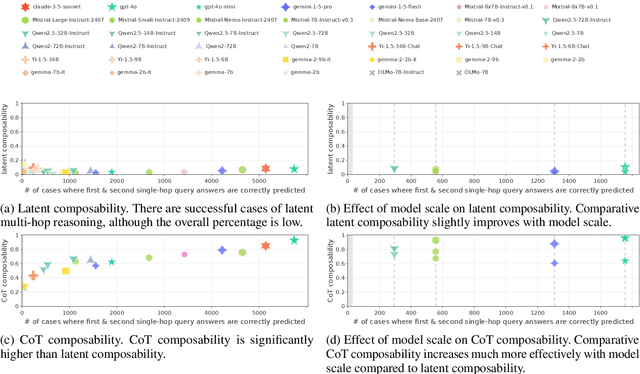

Abstract:We evaluate how well Large Language Models (LLMs) latently recall and compose facts to answer multi-hop queries like "In the year Scarlett Johansson was born, the Summer Olympics were hosted in the country of". One major challenge in evaluating this ability is that LLMs may have developed shortcuts by encounters of the head entity "Scarlett Johansson" and the answer entity "United States" in the same training sequences or merely guess the answer based on frequency-based priors. To prevent shortcuts, we exclude test queries where the head and answer entities co-appear in pretraining corpora. Through careful selection of relations and facts and systematic removal of cases where models might guess answers or exploit partial matches, we construct an evaluation dataset SOCRATES (ShOrtCut-fRee lATent rEaSoning). We observe that LLMs demonstrate promising latent multi-hop reasoning abilities without exploiting shortcuts, but only for certain types of queries. For queries requiring latent recall of countries as the intermediate answer, the best models achieve 80% latent composability, but this drops to just 5% for the recall of years. Comparisons with Chain-of-Thought composability highlight a significant gap between the ability of models to reason latently versus explicitly. Analysis reveals that latent representations of the intermediate answer are constructed more often in queries with higher latent composability, and shows the emergence of latent multi-hop reasoning during pretraining.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Do Large Language Models Latently Perform Multi-Hop Reasoning?
Feb 26, 2024



Abstract:We study whether Large Language Models (LLMs) latently perform multi-hop reasoning with complex prompts such as "The mother of the singer of 'Superstition' is". We look for evidence of a latent reasoning pathway where an LLM (1) latently identifies "the singer of 'Superstition'" as Stevie Wonder, the bridge entity, and (2) uses its knowledge of Stevie Wonder's mother to complete the prompt. We analyze these two hops individually and consider their co-occurrence as indicative of latent multi-hop reasoning. For the first hop, we test if changing the prompt to indirectly mention the bridge entity instead of any other entity increases the LLM's internal recall of the bridge entity. For the second hop, we test if increasing this recall causes the LLM to better utilize what it knows about the bridge entity. We find strong evidence of latent multi-hop reasoning for the prompts of certain relation types, with the reasoning pathway used in more than 80% of the prompts. However, the utilization is highly contextual, varying across different types of prompts. Also, on average, the evidence for the second hop and the full multi-hop traversal is rather moderate and only substantial for the first hop. Moreover, we find a clear scaling trend with increasing model size for the first hop of reasoning but not for the second hop. Our experimental findings suggest potential challenges and opportunities for future development and applications of LLMs.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Towards Robust and Efficient Continual Language Learning
Jul 11, 2023



Abstract:As the application space of language models continues to evolve, a natural question to ask is how we can quickly adapt models to new tasks. We approach this classic question from a continual learning perspective, in which we aim to continue fine-tuning models trained on past tasks on new tasks, with the goal of "transferring" relevant knowledge. However, this strategy also runs the risk of doing more harm than good, i.e., negative transfer. In this paper, we construct a new benchmark of task sequences that target different possible transfer scenarios one might face, such as a sequence of tasks with high potential of positive transfer, high potential for negative transfer, no expected effect, or a mixture of each. An ideal learner should be able to maximally exploit information from all tasks that have any potential for positive transfer, while also avoiding the negative effects of any distracting tasks that may confuse it. We then propose a simple, yet effective, learner that satisfies many of our desiderata simply by leveraging a selective strategy for initializing new models from past task checkpoints. Still, limitations remain, and we hope this benchmark can help the community to further build and analyze such learners.
StreamingQA: A Benchmark for Adaptation to New Knowledge over Time in Question Answering Models
May 23, 2022
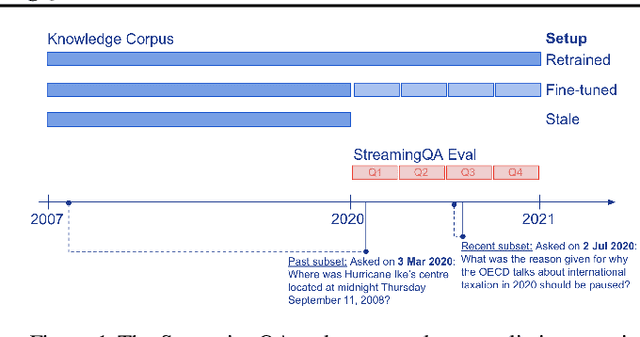

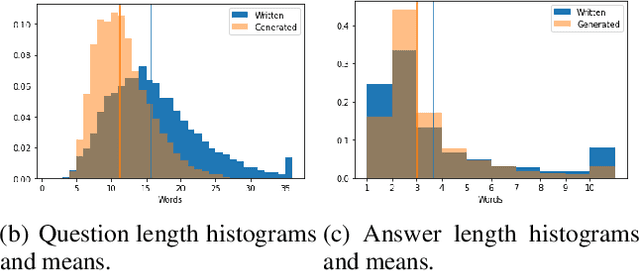
Abstract:Knowledge and language understanding of models evaluated through question answering (QA) has been usually studied on static snapshots of knowledge, like Wikipedia. However, our world is dynamic, evolves over time, and our models' knowledge becomes outdated. To study how semi-parametric QA models and their underlying parametric language models (LMs) adapt to evolving knowledge, we construct a new large-scale dataset, StreamingQA, with human written and generated questions asked on a given date, to be answered from 14 years of time-stamped news articles. We evaluate our models quarterly as they read new articles not seen in pre-training. We show that parametric models can be updated without full retraining, while avoiding catastrophic forgetting. For semi-parametric models, adding new articles into the search space allows for rapid adaptation, however, models with an outdated underlying LM under-perform those with a retrained LM. For questions about higher-frequency named entities, parametric updates are particularly beneficial. In our dynamic world, the StreamingQA dataset enables a more realistic evaluation of QA models, and our experiments highlight several promising directions for future research.
Internet-augmented language models through few-shot prompting for open-domain question answering
Mar 10, 2022
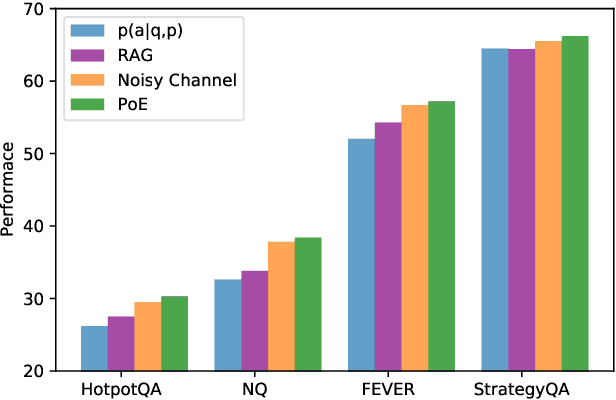
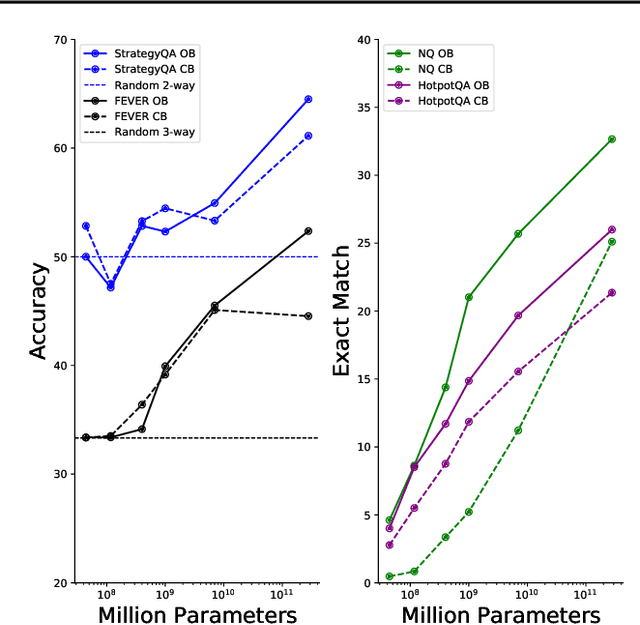
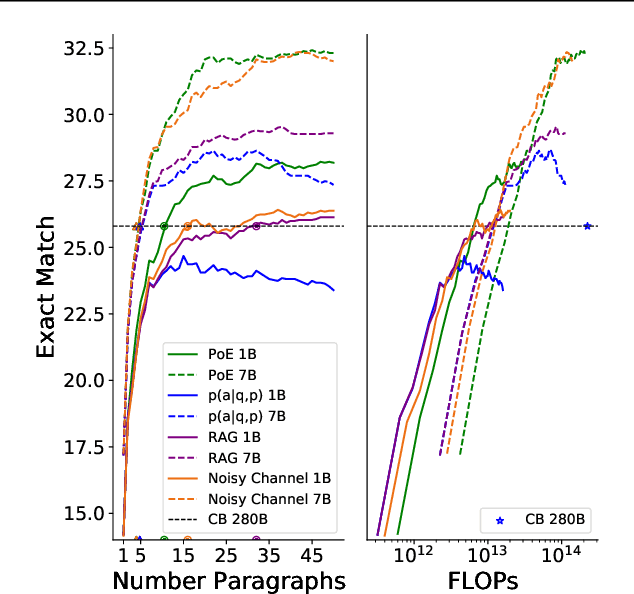
Abstract:In this work, we aim to capitalize on the unique few-shot capabilities offered by large-scale language models to overcome some of their challenges with respect to grounding to factual and up-to-date information. Motivated by semi-parametric language models, which ground their decisions in external retrieved evidence, we use few-shot prompting to learn to condition language models on information returned from the web using Google Search, a broad and constantly updated knowledge source. Our approach does not involve fine-tuning or learning additional parameters, thus making it applicable to any language model, offering like this a strong baseline. Indeed, we find that language models conditioned on the web surpass performance of closed-book models of similar, or even larger, model sizes in open-domain question answering. Finally, we find that increasing the inference-time compute of models, achieved via using multiple retrieved evidences to generate multiple answers followed by a reranking stage, alleviates generally decreased performance of smaller few-shot language models. All in all, our findings suggest that it might be beneficial to slow down the race towards the biggest model and instead shift the attention towards finding more effective ways to use models, including but not limited to better prompting or increasing inference-time compute.
Scaling Language Models: Methods, Analysis & Insights from Training Gopher
Dec 08, 2021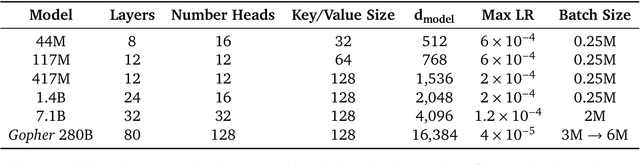
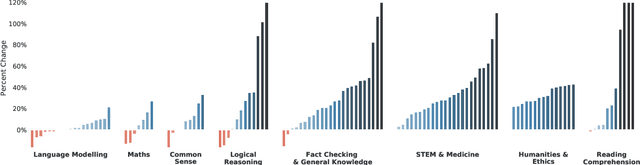
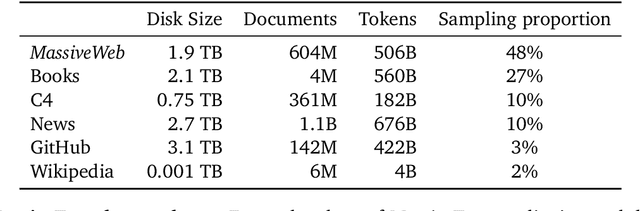
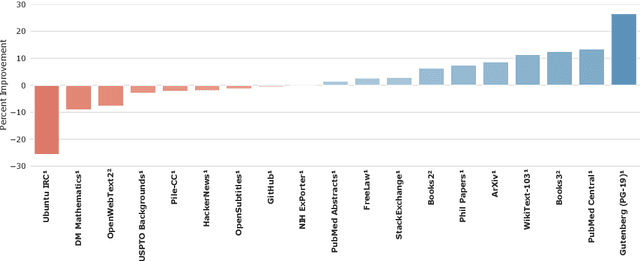
Abstract:Language modelling provides a step towards intelligent communication systems by harnessing large repositories of written human knowledge to better predict and understand the world. In this paper, we present an analysis of Transformer-based language model performance across a wide range of model scales -- from models with tens of millions of parameters up to a 280 billion parameter model called Gopher. These models are evaluated on 152 diverse tasks, achieving state-of-the-art performance across the majority. Gains from scale are largest in areas such as reading comprehension, fact-checking, and the identification of toxic language, but logical and mathematical reasoning see less benefit. We provide a holistic analysis of the training dataset and model's behaviour, covering the intersection of model scale with bias and toxicity. Finally we discuss the application of language models to AI safety and the mitigation of downstream harms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge