Eleanor Chodroff
TidyVoice 2026 Challenge Evaluation Plan
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The performance of speaker verification systems degrades significantly under language mismatch, a critical challenge exacerbated by the field's reliance on English-centric data. To address this, we propose the TidyVoice Challenge for cross-lingual speaker verification. The challenge leverages the TidyVoiceX dataset from the novel TidyVoice benchmark, a large-scale, multilingual corpus derived from Mozilla Common Voice, and specifically curated to isolate the effect of language switching across approximately 40 languages. Participants will be tasked with building systems robust to this mismatch, with performance primarily evaluated using the Equal Error Rate on cross-language trials. By providing standardized data, open-source baselines, and a rigorous evaluation protocol, this challenge aims to drive research towards fairer, more inclusive, and language-independent speaker recognition technologies, directly aligning with the Interspeech 2026 theme, "Speaking Together."
TidyVoice: A Curated Multilingual Dataset for Speaker Verification Derived from Common Voice
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:The development of robust, multilingual speaker recognition systems is hindered by a lack of large-scale, publicly available and multilingual datasets, particularly for the read-speech style crucial for applications like anti-spoofing. To address this gap, we introduce the TidyVoice dataset derived from the Mozilla Common Voice corpus after mitigating its inherent speaker heterogeneity within the provided client IDs. TidyVoice currently contains training and test data from over 212,000 monolingual speakers (Tidy-M) and around 4,500 multilingual speakers (Tidy-X) from which we derive two distinct conditions. The Tidy-M condition contains target and non-target trials from monolingual speakers across 81 languages. The Tidy-X condition contains target and non-target trials from multilingual speakers in both same- and cross-language trials. We employ two architectures of ResNet models, achieving a 0.35% EER by fine-tuning on our comprehensive Tidy-M partition. Moreover, we show that this fine-tuning enhances the model's generalization, improving performance on unseen conversational interview data from the CANDOR corpus. The complete dataset, evaluation trials, and our models are publicly released to provide a new resource for the community.
ZIPA: A family of efficient models for multilingual phone recognition
May 29, 2025Abstract:We present ZIPA, a family of efficient speech models that advances the state-of-the-art performance of crosslinguistic phone recognition. We first curated IPAPack++, a large-scale multilingual speech corpus with 17,132 hours of normalized phone transcriptions and a novel evaluation set capturing unseen languages and sociophonetic variation. With the large-scale training data, ZIPA, including transducer (ZIPA-T) and CTC-based (ZIPA-CR) variants, leverage the efficient Zipformer backbones and outperform existing phone recognition systems with much fewer parameters. Further scaling via noisy student training on 11,000 hours of pseudo-labeled multilingual data yields further improvement. While ZIPA achieves strong performance on benchmarks, error analysis reveals persistent limitations in modeling sociophonetic diversity, underscoring challenges for future research.
On the Role of Context in Reading Time Prediction
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:We present a new perspective on how readers integrate context during real-time language comprehension. Our proposals build on surprisal theory, which posits that the processing effort of a linguistic unit (e.g., a word) is an affine function of its in-context information content. We first observe that surprisal is only one out of many potential ways that a contextual predictor can be derived from a language model. Another one is the pointwise mutual information (PMI) between a unit and its context, which turns out to yield the same predictive power as surprisal when controlling for unigram frequency. Moreover, both PMI and surprisal are correlated with frequency. This means that neither PMI nor surprisal contains information about context alone. In response to this, we propose a technique where we project surprisal onto the orthogonal complement of frequency, yielding a new contextual predictor that is uncorrelated with frequency. Our experiments show that the proportion of variance in reading times explained by context is a lot smaller when context is represented by the orthogonalized predictor. From an interpretability standpoint, this indicates that previous studies may have overstated the role that context has in predicting reading times.
Tradition or Innovation: A Comparison of Modern ASR Methods for Forced Alignment
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:Forced alignment (FA) plays a key role in speech research through the automatic time alignment of speech signals with corresponding text transcriptions. Despite the move towards end-to-end architectures for speech technology, FA is still dominantly achieved through a classic GMM-HMM acoustic model. This work directly compares alignment performance from leading automatic speech recognition (ASR) methods, WhisperX and Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition (MMS), against a Kaldi-based GMM-HMM system, the Montreal Forced Aligner (MFA). Performance was assessed on the manually aligned TIMIT and Buckeye datasets, with comparisons conducted only on words correctly recognized by WhisperX and MMS. The MFA outperformed both WhisperX and MMS, revealing a shortcoming of modern ASR systems. These findings highlight the need for advancements in forced alignment and emphasize the importance of integrating traditional expertise with modern innovation to foster progress. Index Terms: forced alignment, phoneme alignment, word alignment
What Languages are Easy to Language-Model? A Perspective from Learning Probabilistic Regular Languages
Jun 07, 2024Abstract:What can large language models learn? By definition, language models (LM) are distributions over strings. Therefore, an intuitive way of addressing the above question is to formalize it as a matter of learnability of classes of distributions over strings. While prior work in this direction focused on assessing the theoretical limits, in contrast, we seek to understand the empirical learnability. Unlike prior empirical work, we evaluate neural LMs on their home turf-learning probabilistic languages-rather than as classifiers of formal languages. In particular, we investigate the learnability of regular LMs (RLMs) by RNN and Transformer LMs. We empirically test the learnability of RLMs as a function of various complexity parameters of the RLM and the hidden state size of the neural LM. We find that the RLM rank, which corresponds to the size of linear space spanned by the logits of its conditional distributions, and the expected length of sampled strings are strong and significant predictors of learnability for both RNNs and Transformers. Several other predictors also reach significance, but with differing patterns between RNNs and Transformers.
Phonetic Segmentation of the UCLA Phonetics Lab Archive
Mar 28, 2024Abstract:Research in speech technologies and comparative linguistics depends on access to diverse and accessible speech data. The UCLA Phonetics Lab Archive is one of the earliest multilingual speech corpora, with long-form audio recordings and phonetic transcriptions for 314 languages (Ladefoged et al., 2009). Recently, 95 of these languages were time-aligned with word-level phonetic transcriptions (Li et al., 2021). Here we present VoxAngeles, a corpus of audited phonetic transcriptions and phone-level alignments of the UCLA Phonetics Lab Archive, which uses the 95-language CMU re-release as our starting point. VoxAngeles also includes word- and phone-level segmentations from the original UCLA corpus, as well as phonetic measurements of word and phone durations, vowel formants, and vowel f0. This corpus enhances the usability of the original data, particularly for quantitative phonetic typology, as demonstrated through a case study of vowel intrinsic f0. We also discuss the utility of the VoxAngeles corpus for general research and pedagogy in crosslinguistic phonetics, as well as for low-resource and multilingual speech technologies. VoxAngeles is free to download and use under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license.
UniMorph 4.0: Universal Morphology
May 10, 2022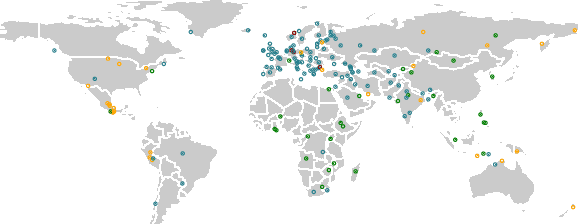
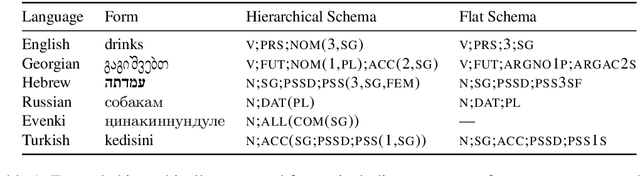
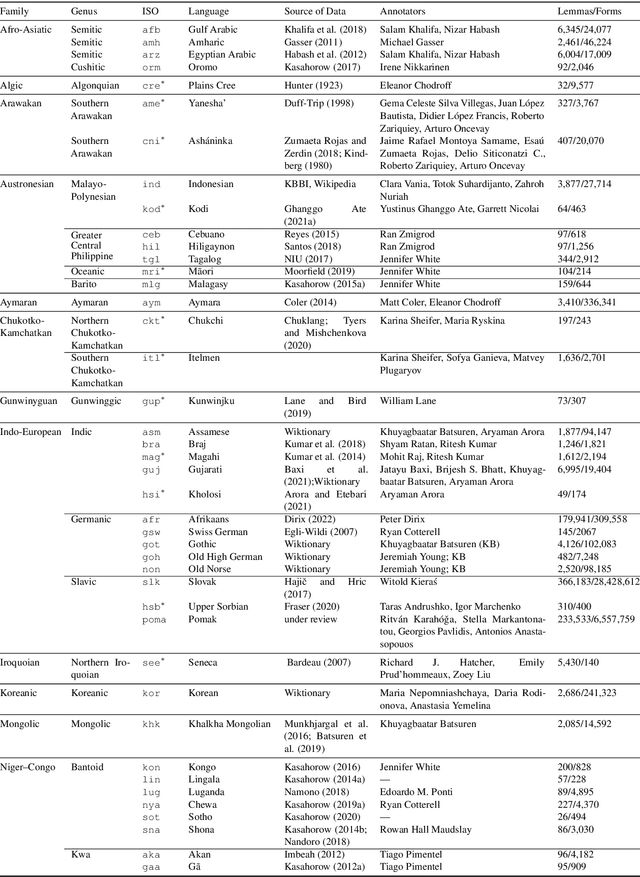
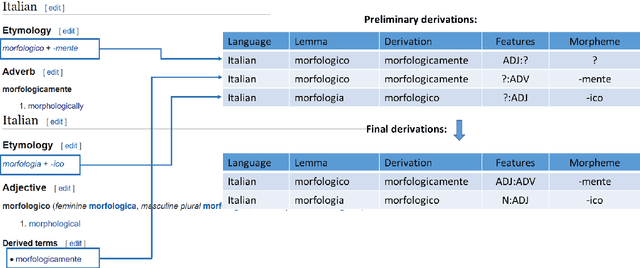
Abstract:The Universal Morphology (UniMorph) project is a collaborative effort providing broad-coverage instantiated normalized morphological inflection tables for hundreds of diverse world languages. The project comprises two major thrusts: a language-independent feature schema for rich morphological annotation and a type-level resource of annotated data in diverse languages realizing that schema. This paper presents the expansions and improvements made on several fronts over the last couple of years (since McCarthy et al. (2020)). Collaborative efforts by numerous linguists have added 67 new languages, including 30 endangered languages. We have implemented several improvements to the extraction pipeline to tackle some issues, e.g. missing gender and macron information. We have also amended the schema to use a hierarchical structure that is needed for morphological phenomena like multiple-argument agreement and case stacking, while adding some missing morphological features to make the schema more inclusive. In light of the last UniMorph release, we also augmented the database with morpheme segmentation for 16 languages. Lastly, this new release makes a push towards inclusion of derivational morphology in UniMorph by enriching the data and annotation schema with instances representing derivational processes from MorphyNet.
DeepFry: Identifying Vocal Fry Using Deep Neural Networks
Mar 31, 2022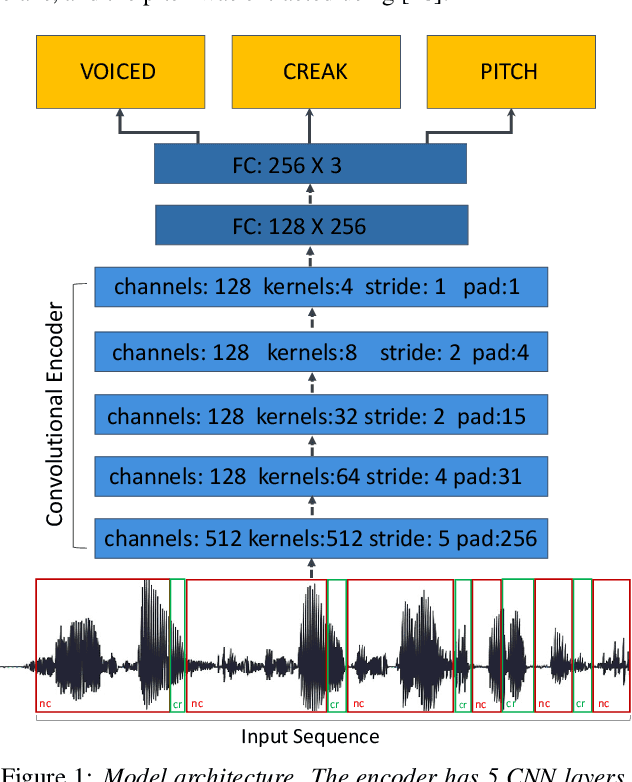
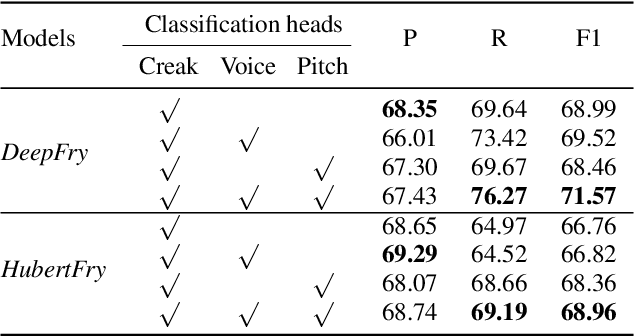
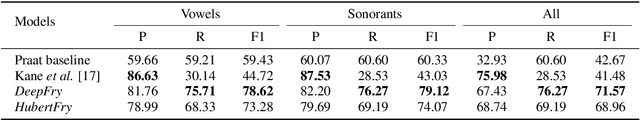
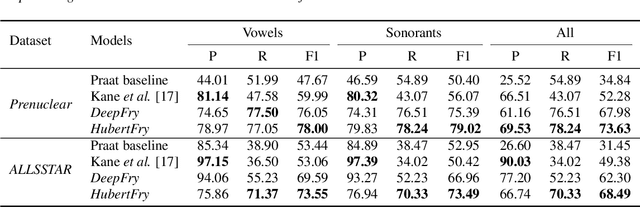
Abstract:Vocal fry or creaky voice refers to a voice quality characterized by irregular glottal opening and low pitch. It occurs in diverse languages and is prevalent in American English, where it is used not only to mark phrase finality, but also sociolinguistic factors and affect. Due to its irregular periodicity, creaky voice challenges automatic speech processing and recognition systems, particularly for languages where creak is frequently used. This paper proposes a deep learning model to detect creaky voice in fluent speech. The model is composed of an encoder and a classifier trained together. The encoder takes the raw waveform and learns a representation using a convolutional neural network. The classifier is implemented as a multi-headed fully-connected network trained to detect creaky voice, voicing, and pitch, where the last two are used to refine creak prediction. The model is trained and tested on speech of American English speakers, annotated for creak by trained phoneticians. We evaluated the performance of our system using two encoders: one is tailored for the task, and the other is based on a state-of-the-art unsupervised representation. Results suggest our best-performing system has improved recall and F1 scores compared to previous methods on unseen data.
SIGMORPHON 2020 Shared Task 0: Typologically Diverse Morphological Inflection
Jul 14, 2020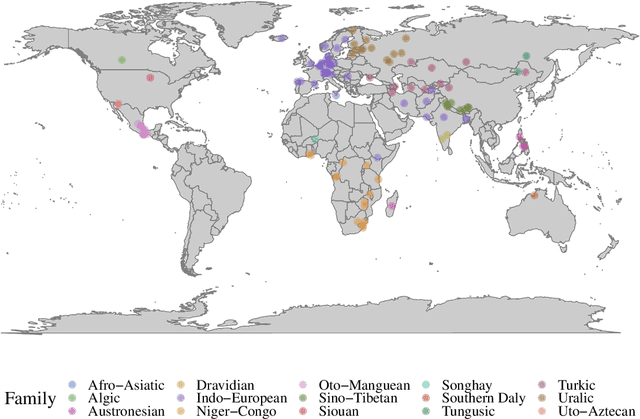
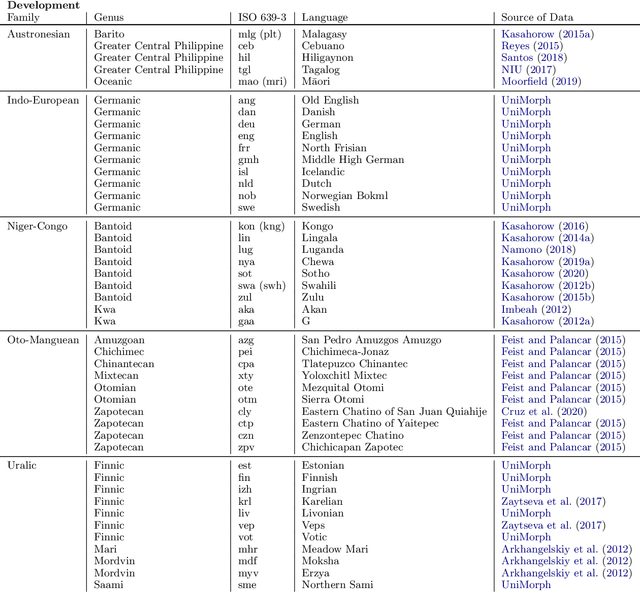
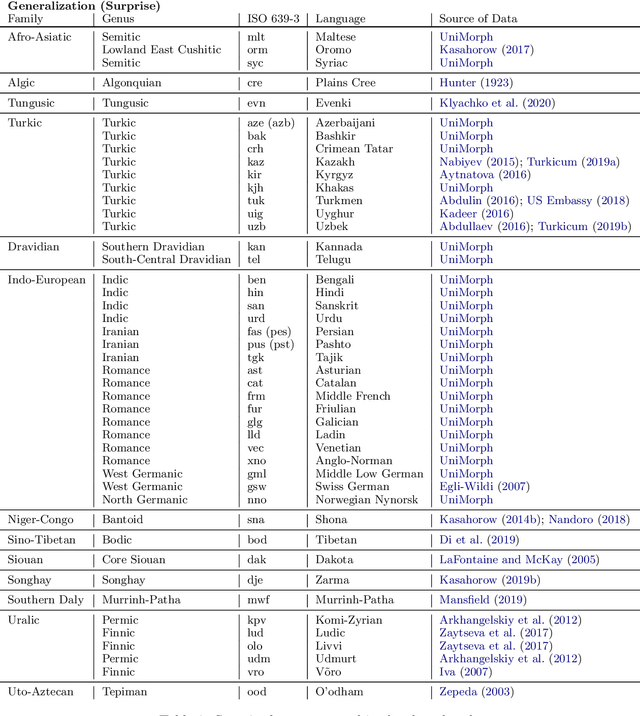
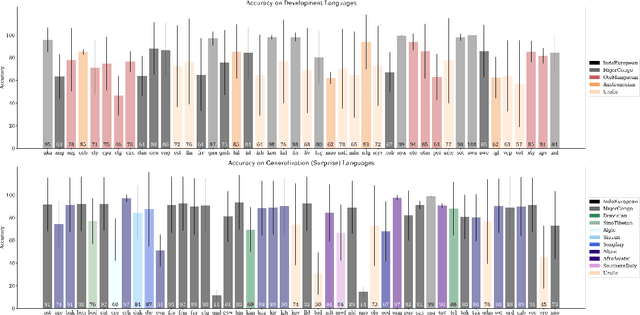
Abstract:A broad goal in natural language processing (NLP) is to develop a system that has the capacity to process any natural language. Most systems, however, are developed using data from just one language such as English. The SIGMORPHON 2020 shared task on morphological reinflection aims to investigate systems' ability to generalize across typologically distinct languages, many of which are low resource. Systems were developed using data from 45 languages and just 5 language families, fine-tuned with data from an additional 45 languages and 10 language families (13 in total), and evaluated on all 90 languages. A total of 22 systems (19 neural) from 10 teams were submitted to the task. All four winning systems were neural (two monolingual transformers and two massively multilingual RNN-based models with gated attention). Most teams demonstrate utility of data hallucination and augmentation, ensembles, and multilingual training for low-resource languages. Non-neural learners and manually designed grammars showed competitive and even superior performance on some languages (such as Ingrian, Tajik, Tagalog, Zarma, Lingala), especially with very limited data. Some language families (Afro-Asiatic, Niger-Congo, Turkic) were relatively easy for most systems and achieved over 90% mean accuracy while others were more challenging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge