Brian Leonard
UniMorph 4.0: Universal Morphology
May 10, 2022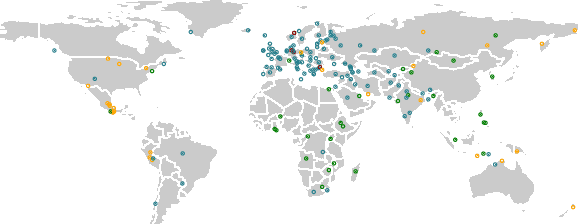
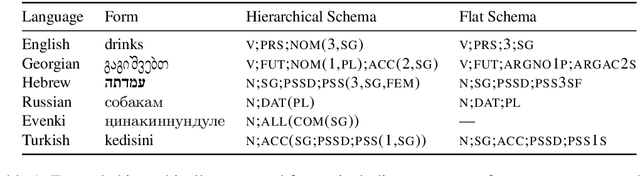
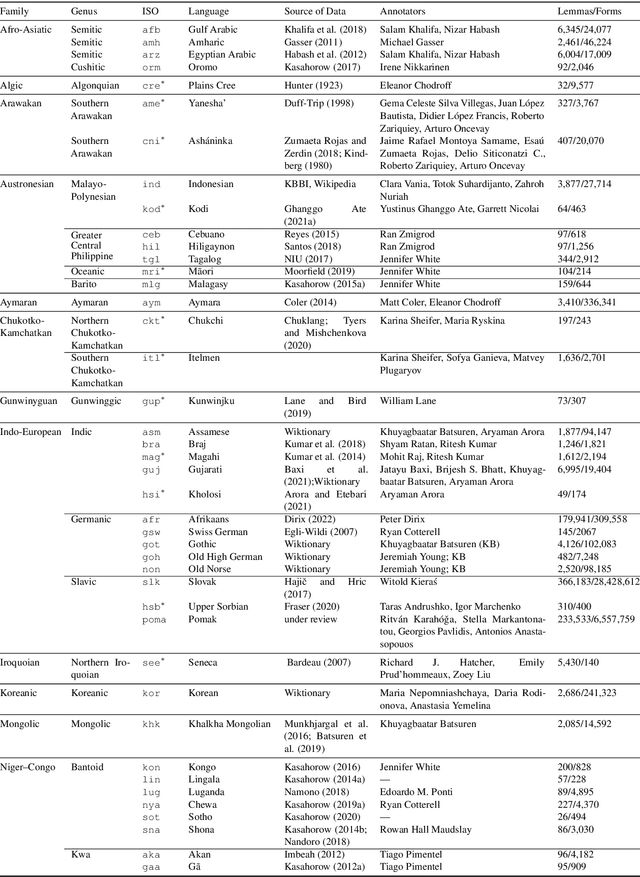
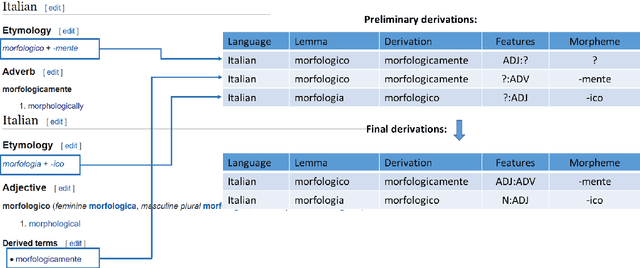
Abstract:The Universal Morphology (UniMorph) project is a collaborative effort providing broad-coverage instantiated normalized morphological inflection tables for hundreds of diverse world languages. The project comprises two major thrusts: a language-independent feature schema for rich morphological annotation and a type-level resource of annotated data in diverse languages realizing that schema. This paper presents the expansions and improvements made on several fronts over the last couple of years (since McCarthy et al. (2020)). Collaborative efforts by numerous linguists have added 67 new languages, including 30 endangered languages. We have implemented several improvements to the extraction pipeline to tackle some issues, e.g. missing gender and macron information. We have also amended the schema to use a hierarchical structure that is needed for morphological phenomena like multiple-argument agreement and case stacking, while adding some missing morphological features to make the schema more inclusive. In light of the last UniMorph release, we also augmented the database with morpheme segmentation for 16 languages. Lastly, this new release makes a push towards inclusion of derivational morphology in UniMorph by enriching the data and annotation schema with instances representing derivational processes from MorphyNet.
Distinct patterns of syntactic agreement errors in recurrent networks and humans
Jul 18, 2018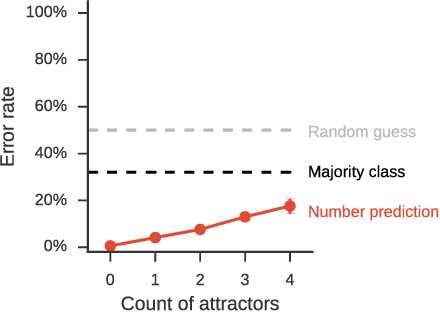
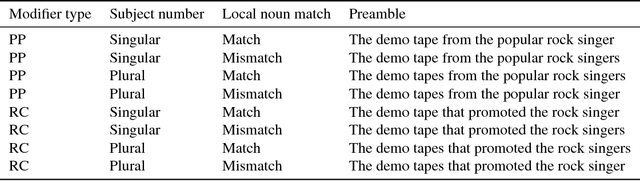
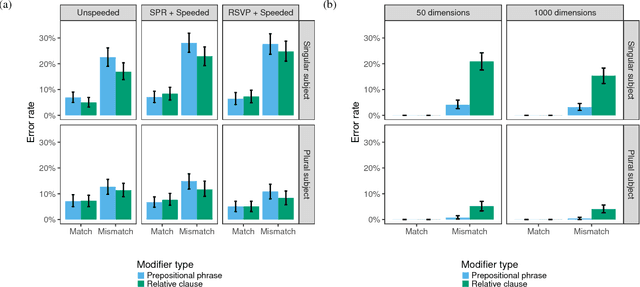
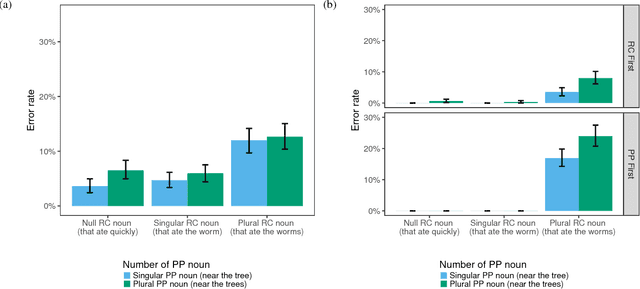
Abstract:Determining the correct form of a verb in context requires an understanding of the syntactic structure of the sentence. Recurrent neural networks have been shown to perform this task with an error rate comparable to humans, despite the fact that they are not designed with explicit syntactic representations. To examine the extent to which the syntactic representations of these networks are similar to those used by humans when processing sentences, we compare the detailed pattern of errors that RNNs and humans make on this task. Despite significant similarities (attraction errors, asymmetry between singular and plural subjects), the error patterns differed in important ways. In particular, in complex sentences with relative clauses error rates increased in RNNs but decreased in humans. Furthermore, RNNs showed a cumulative effect of attractors but humans did not. We conclude that at least in some respects the syntactic representations acquired by RNNs are fundamentally different from those used by humans.
Gender Bias in Coreference Resolution
Apr 25, 2018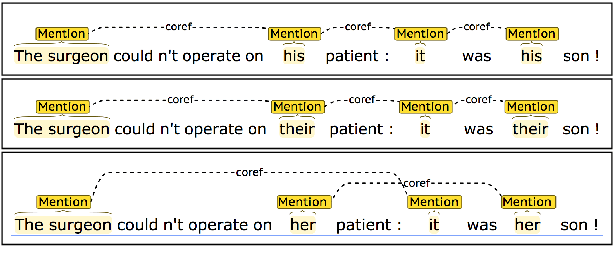
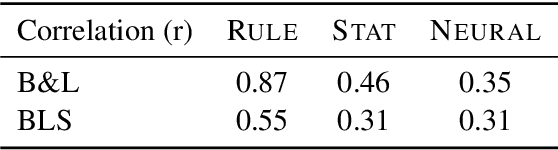
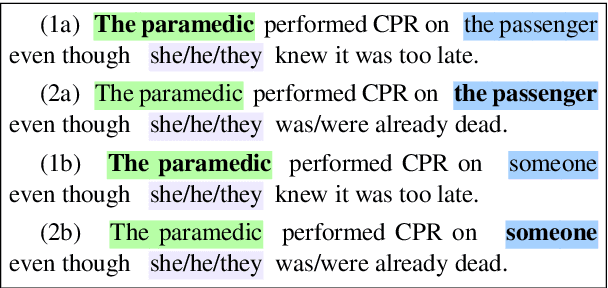
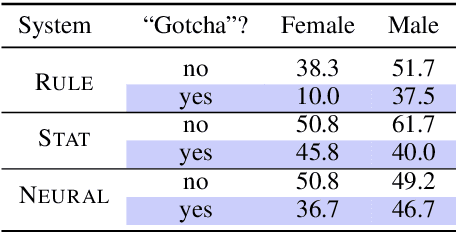
Abstract:We present an empirical study of gender bias in coreference resolution systems. We first introduce a novel, Winograd schema-style set of minimal pair sentences that differ only by pronoun gender. With these "Winogender schemas," we evaluate and confirm systematic gender bias in three publicly-available coreference resolution systems, and correlate this bias with real-world and textual gender statistics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge